
Match the orbital overlap figures shown in List-I with the description gives in List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I List-II P.
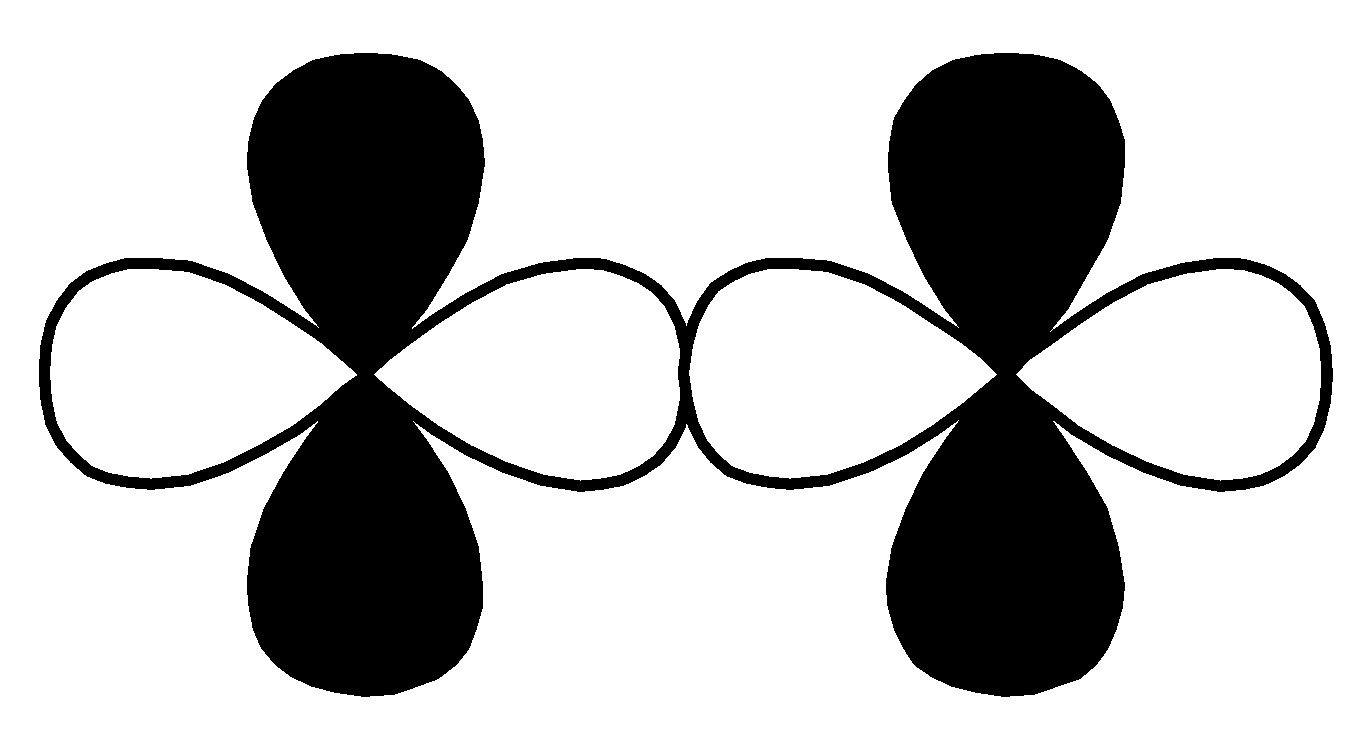
$p - d$ $\pi \;antibonding$ Q.
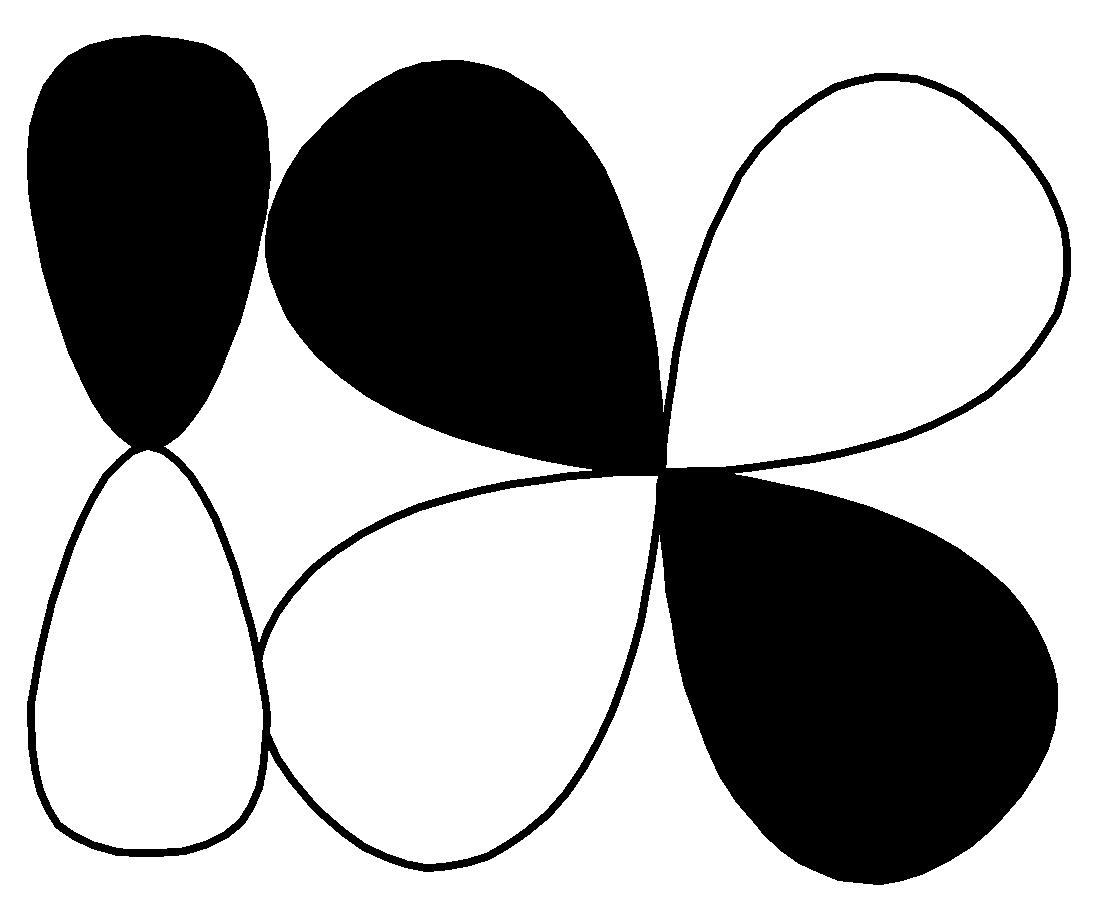
$d - d$ $\sigma\; bonding$ R.
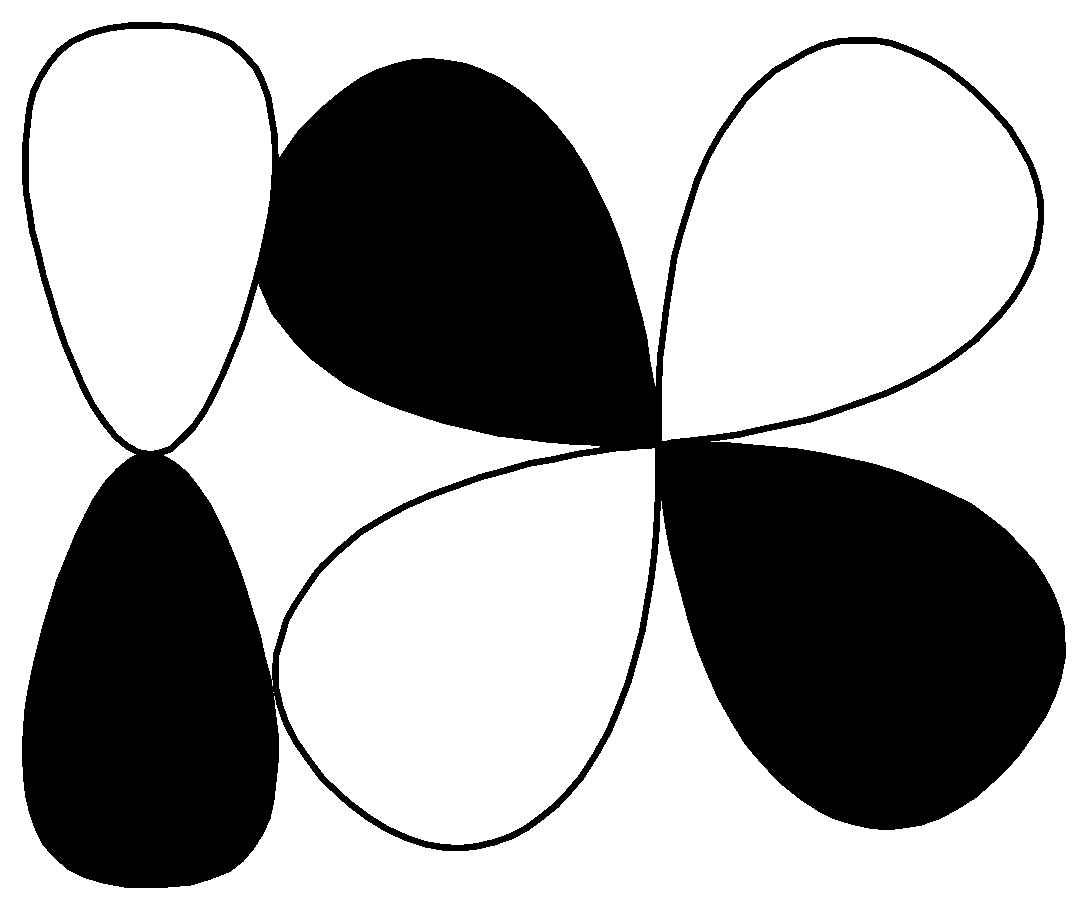
$p - d$ $\pi\; bonding$ S.
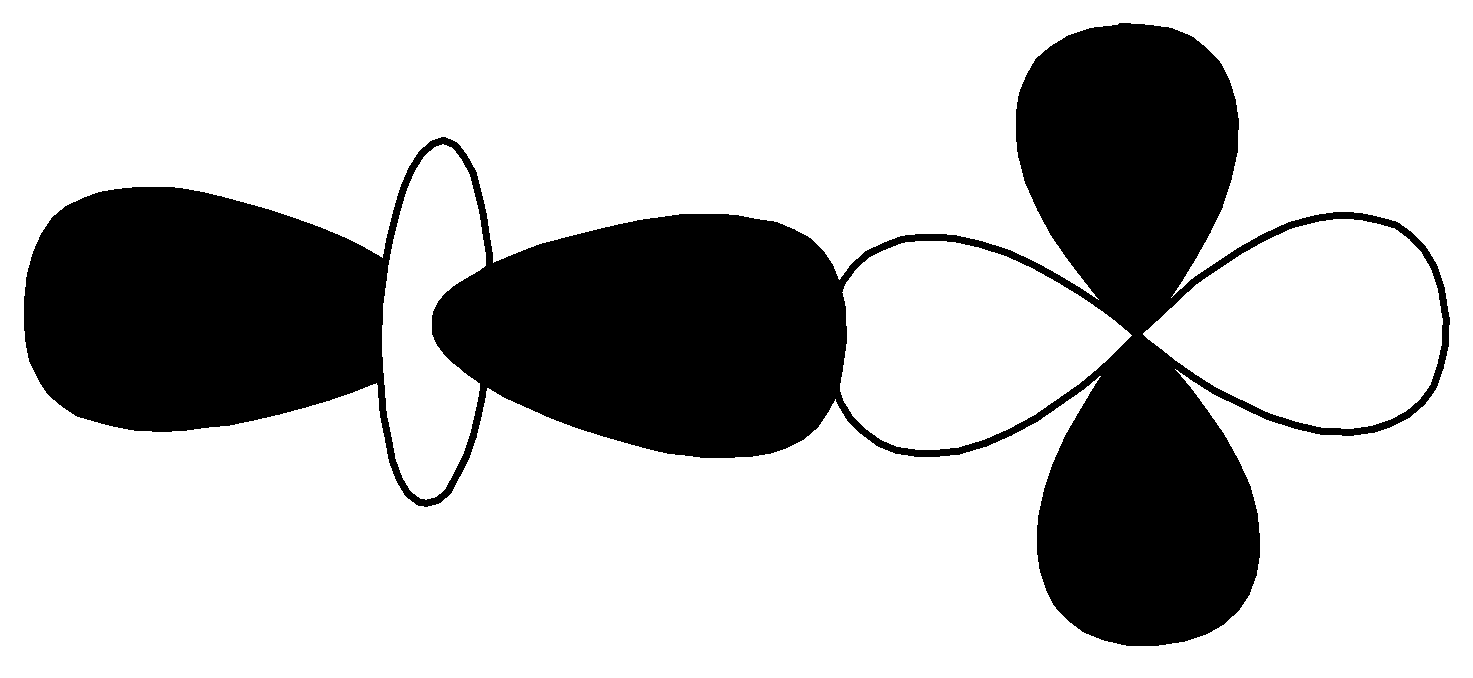
$d - d$ $\sigma\; antibonding$
A. \[P - 2,Q - 1,R - 3,S - 4\]
B. $P - 4,Q - 3,R - 1,S - 2$
C. $P - 2,Q - 3,R - 1,S - 4$
D. $P - 4,Q - 1,R - 3,S - 2$
| List-I | List-II |
P. 
| $p - d$ $\pi \;antibonding$ |
Q. 
| $d - d$ $\sigma\; bonding$ |
R.
| $p - d$ $\pi\; bonding$ |
S.
| $d - d$ $\sigma\; antibonding$ |
Answer
557.1k+ views
Hint: We must need to know that an orbital overlap is the concentration of orbitals on adjacent atoms in the same regions of space and the atoms combine by colliding with each other, and create chemical bonds. Overlapping of orbitals occurs in two ways, they are sigma \[\left( \sigma \right)\] bond and pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond, and these are giving rise to covalent bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that when the orbital overlap between the nuclei of two atoms, and also known as the internuclear axis, is known as sigma \[\left( \sigma \right)\] bond. And pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond occurs when two $p - $ orbitals overlap. Electrons in bonding orbitals will stabilize the molecule because they are between the nuclei and they have lower energies. When there is less electron density between the nuclei, then antibonding orbitals are placed.
$p$ and $d$ orbitals are,
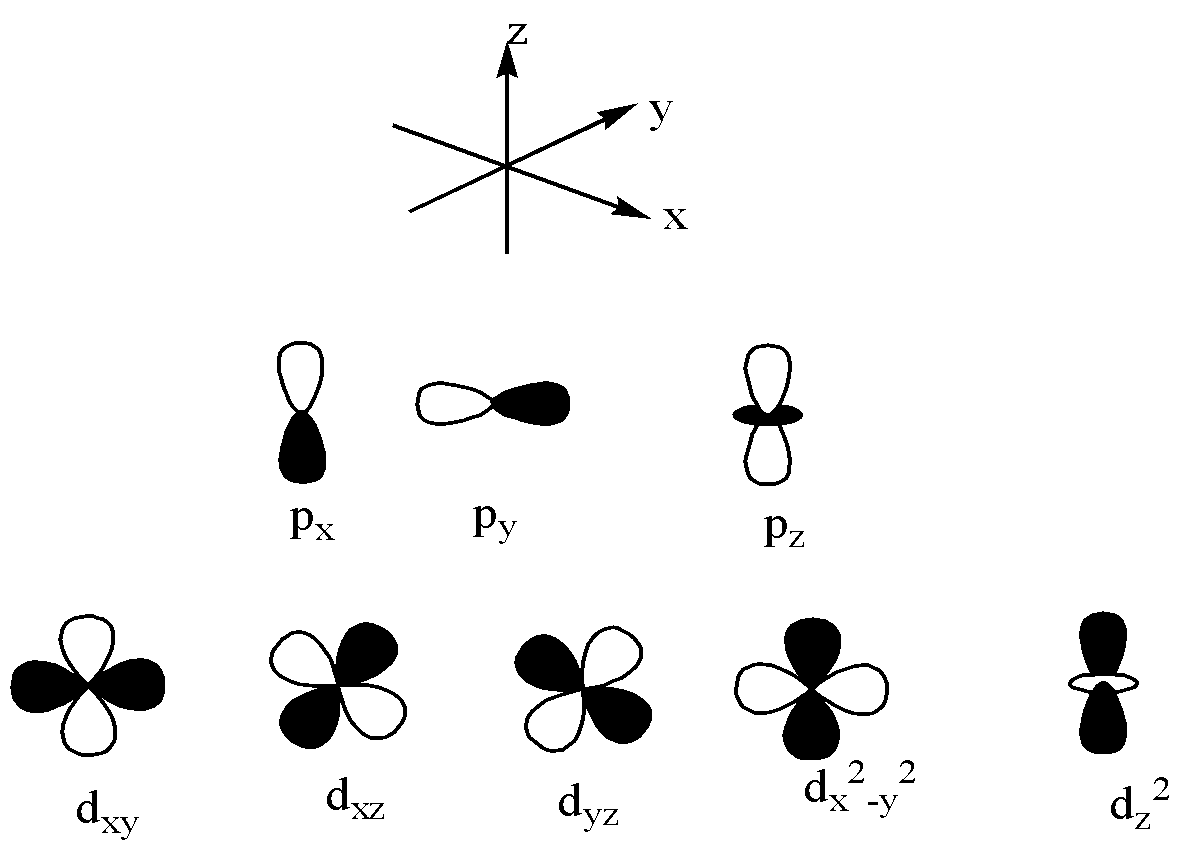
From the above information and the orbitals diagram, let us see the correct options one by one,
P.
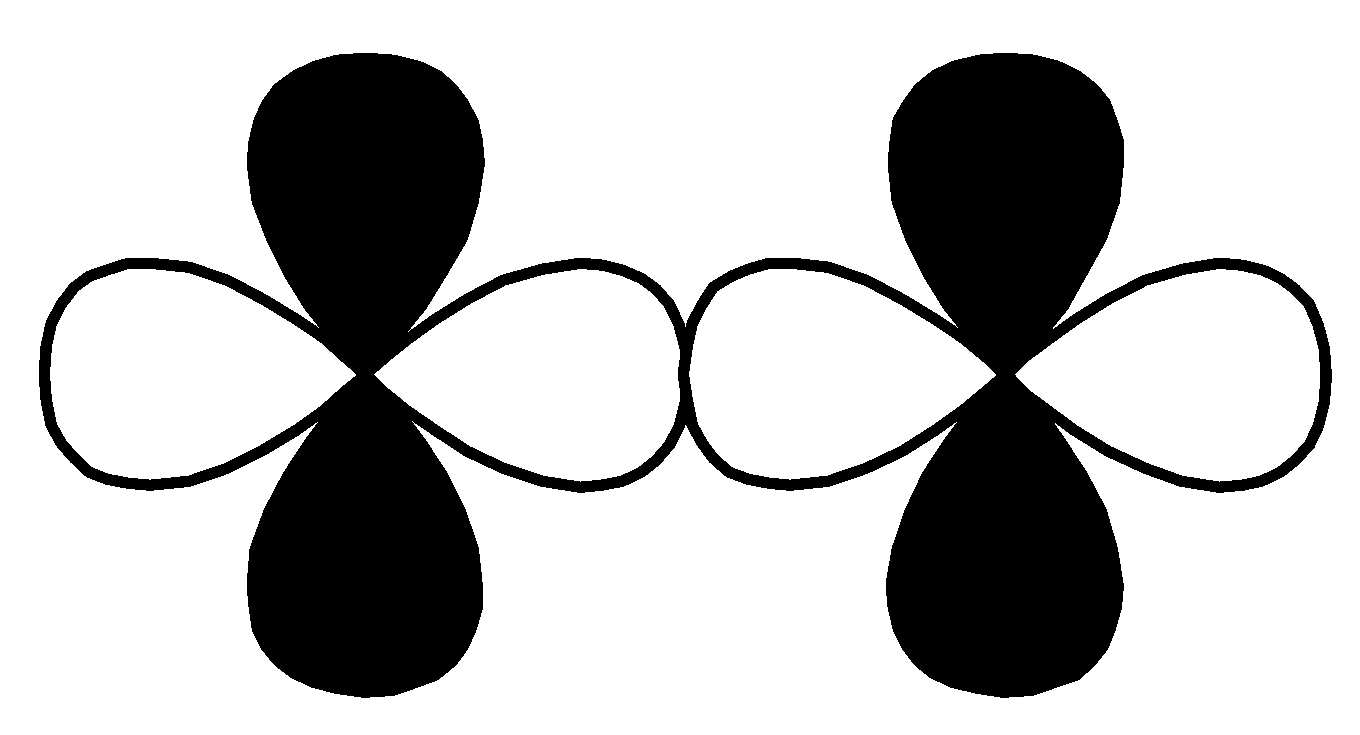 ,
,
This overlap is head-to-head overlapping, so this is a sigma bond.
So, option $\left( 2 \right)$ $d - d$ $\sigma $ bonding is the correct option for (P).
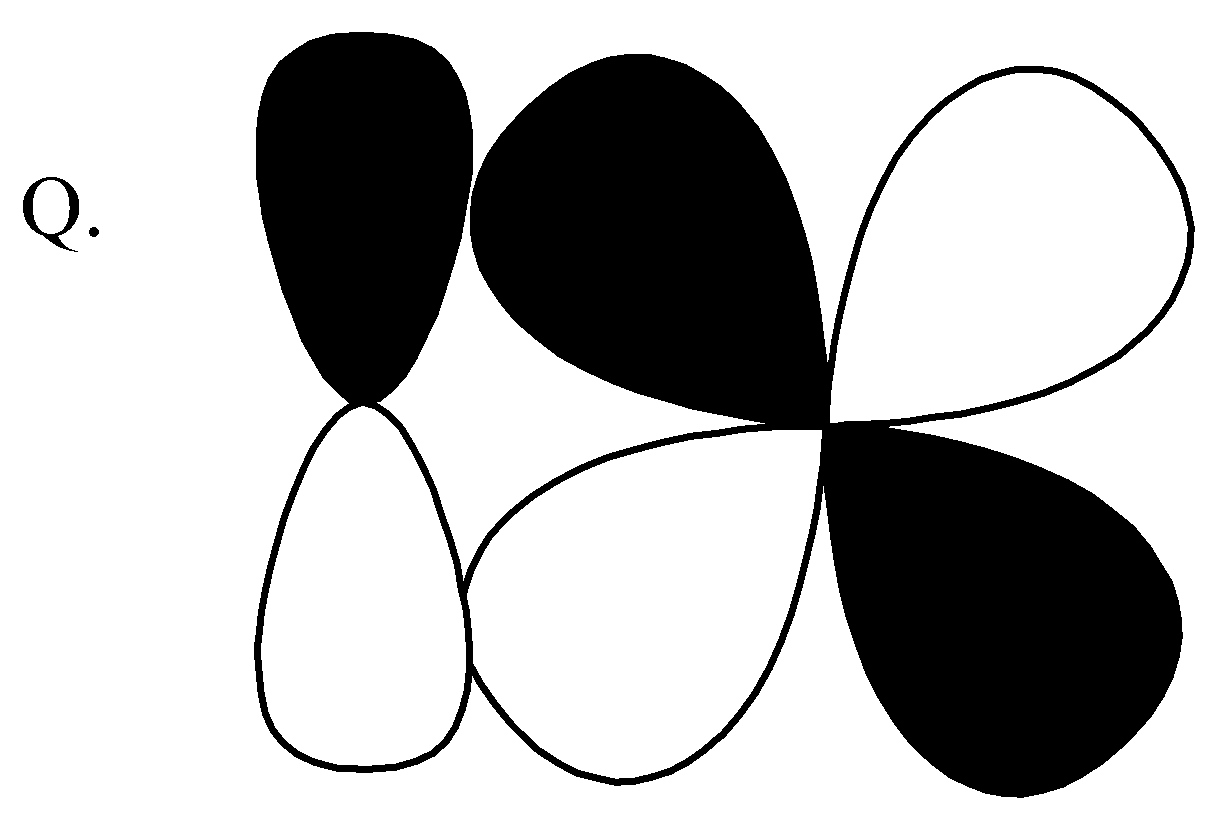 ,
,
This pi bond and this is formed by sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, the formed pi bond axes are parallel to each other and the overlapping is perpendicular to the internuclear axis. So, this is $p - d\;\pi \;bonding$. Correct option for (Q) is$\left( 3 \right)$ $p - d\;\pi \;bonding$.
 ,
,
This contains p, d orbitals and this is antibonding orbitals. So, the correct option for $\left( R \right)$is $\left( 1 \right)$ $p - d\;\pi {\text{ anti}}bonding$.
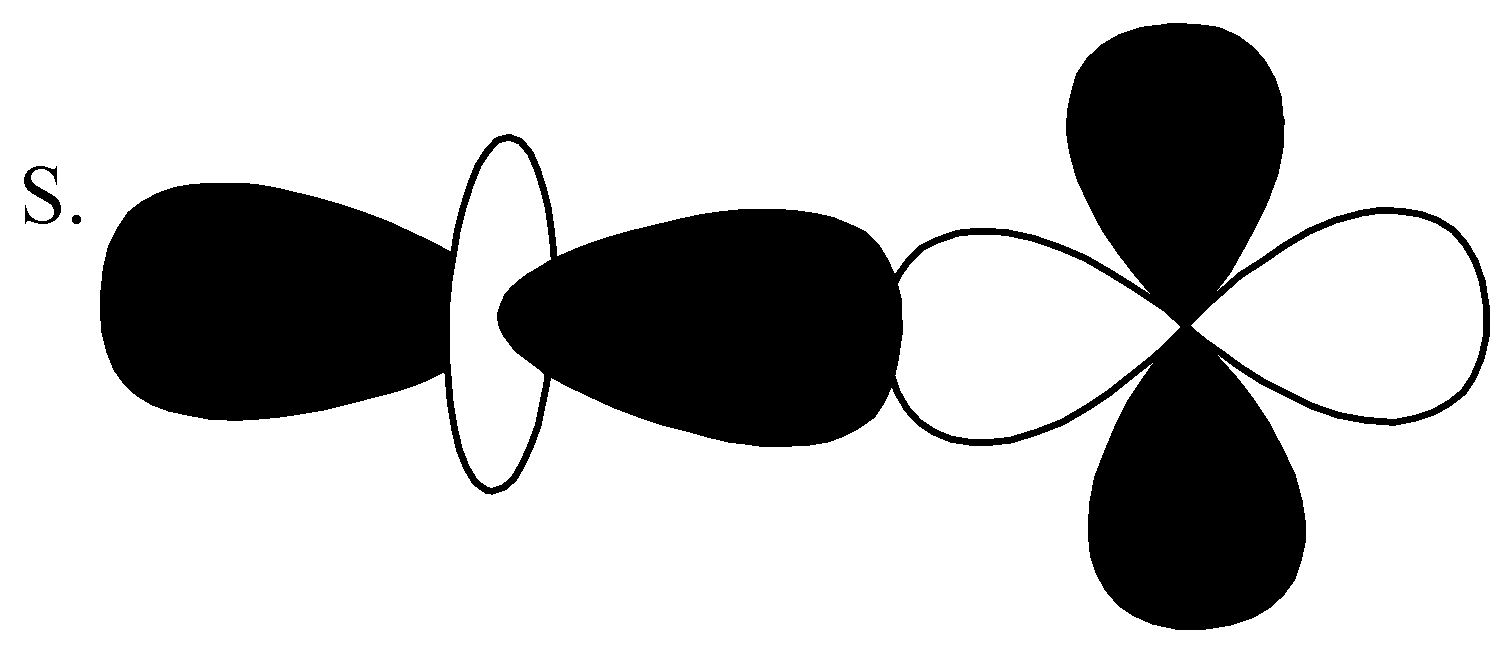 ,
,
From the above orbitals diagram, these two orbitals are $d - $ orbitals and the bonding is anti-bonding. So, the correct option is $(4)\;d - d\;\sigma \;anti - bonding$ .
Thus, the correct option is C. $P - 2,Q - 3,R - 1,S - 4$.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We have to remember that the $p - orbitals$ are dumbbell in shape whereas $d - orbitals$ are clover shape. Linus Pauling explained the importance of orbital overlap. This is explained by emphasizing the molecular bond angles are observed through the experiments and this is the basic concept for orbital hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that when the orbital overlap between the nuclei of two atoms, and also known as the internuclear axis, is known as sigma \[\left( \sigma \right)\] bond. And pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond occurs when two $p - $ orbitals overlap. Electrons in bonding orbitals will stabilize the molecule because they are between the nuclei and they have lower energies. When there is less electron density between the nuclei, then antibonding orbitals are placed.
$p$ and $d$ orbitals are,

From the above information and the orbitals diagram, let us see the correct options one by one,
P.

This overlap is head-to-head overlapping, so this is a sigma bond.
So, option $\left( 2 \right)$ $d - d$ $\sigma $ bonding is the correct option for (P).

This pi bond and this is formed by sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, the formed pi bond axes are parallel to each other and the overlapping is perpendicular to the internuclear axis. So, this is $p - d\;\pi \;bonding$. Correct option for (Q) is$\left( 3 \right)$ $p - d\;\pi \;bonding$.

This contains p, d orbitals and this is antibonding orbitals. So, the correct option for $\left( R \right)$is $\left( 1 \right)$ $p - d\;\pi {\text{ anti}}bonding$.

From the above orbitals diagram, these two orbitals are $d - $ orbitals and the bonding is anti-bonding. So, the correct option is $(4)\;d - d\;\sigma \;anti - bonding$ .
Thus, the correct option is C. $P - 2,Q - 3,R - 1,S - 4$.
| List-I | List-II |
P. 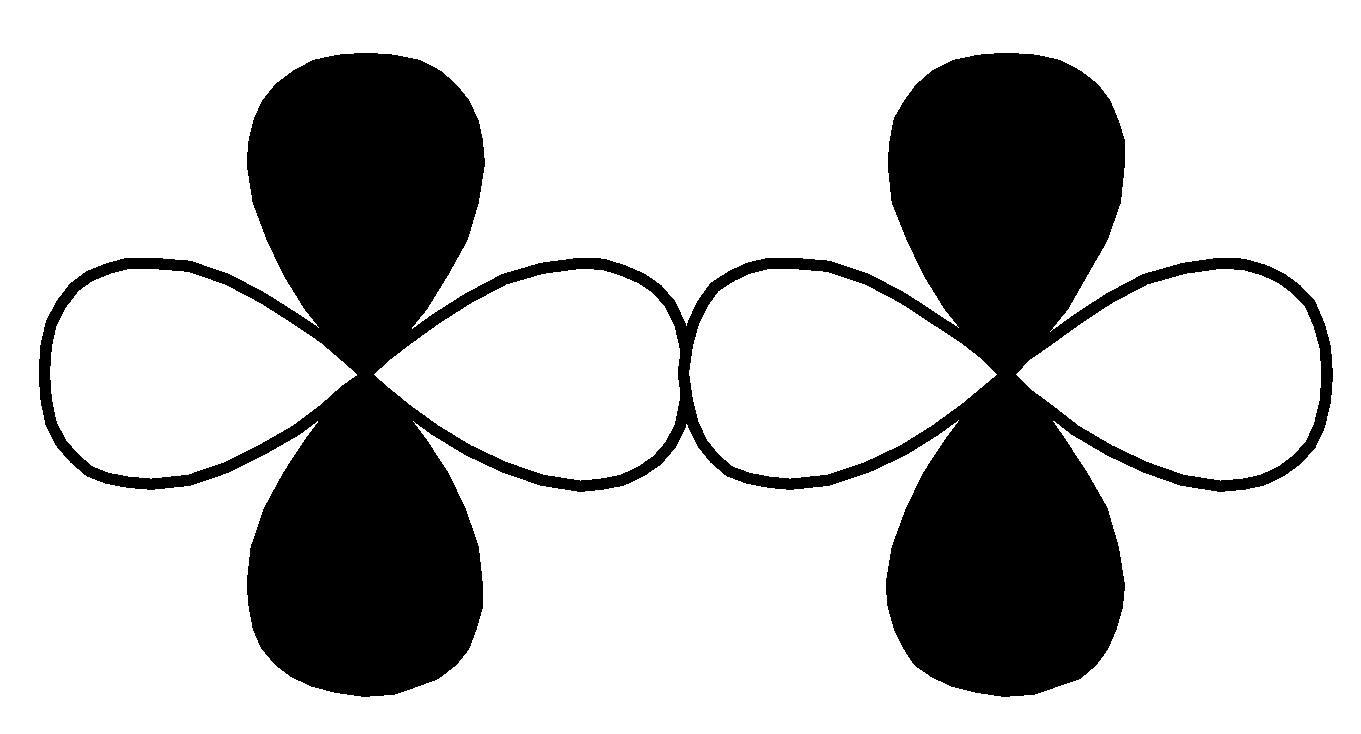
| $d - d$ $\sigma\; bonding$ |
Q. 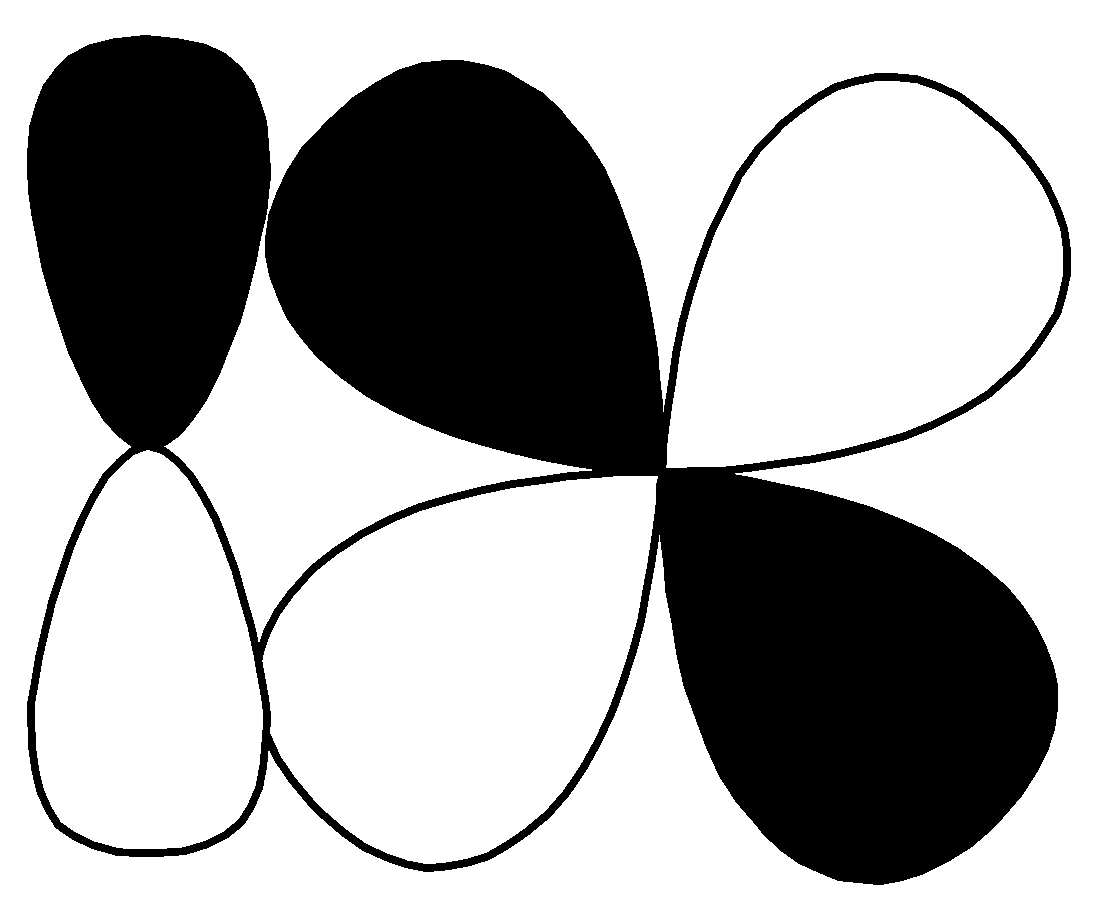
| $d - d$ $\pi \;bonding$ |
R. 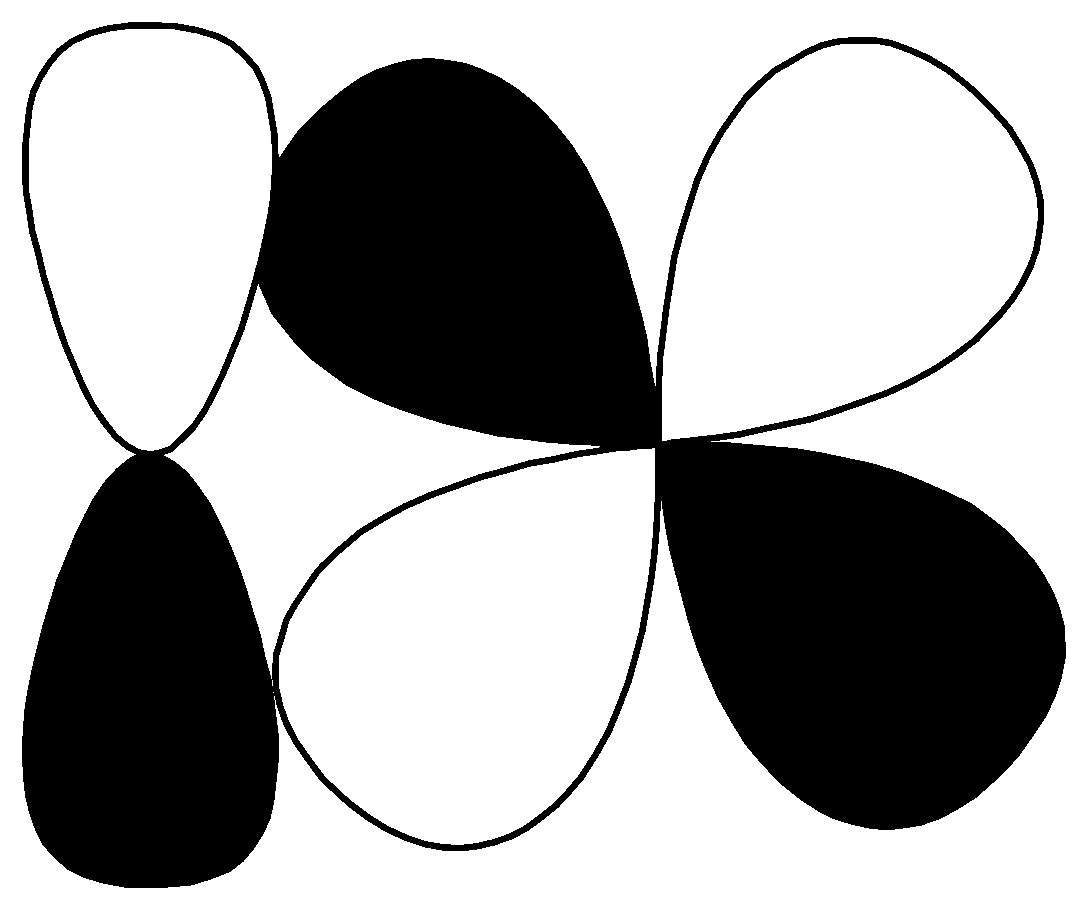
| $p - d$ $\pi \;antibonding$ |
S.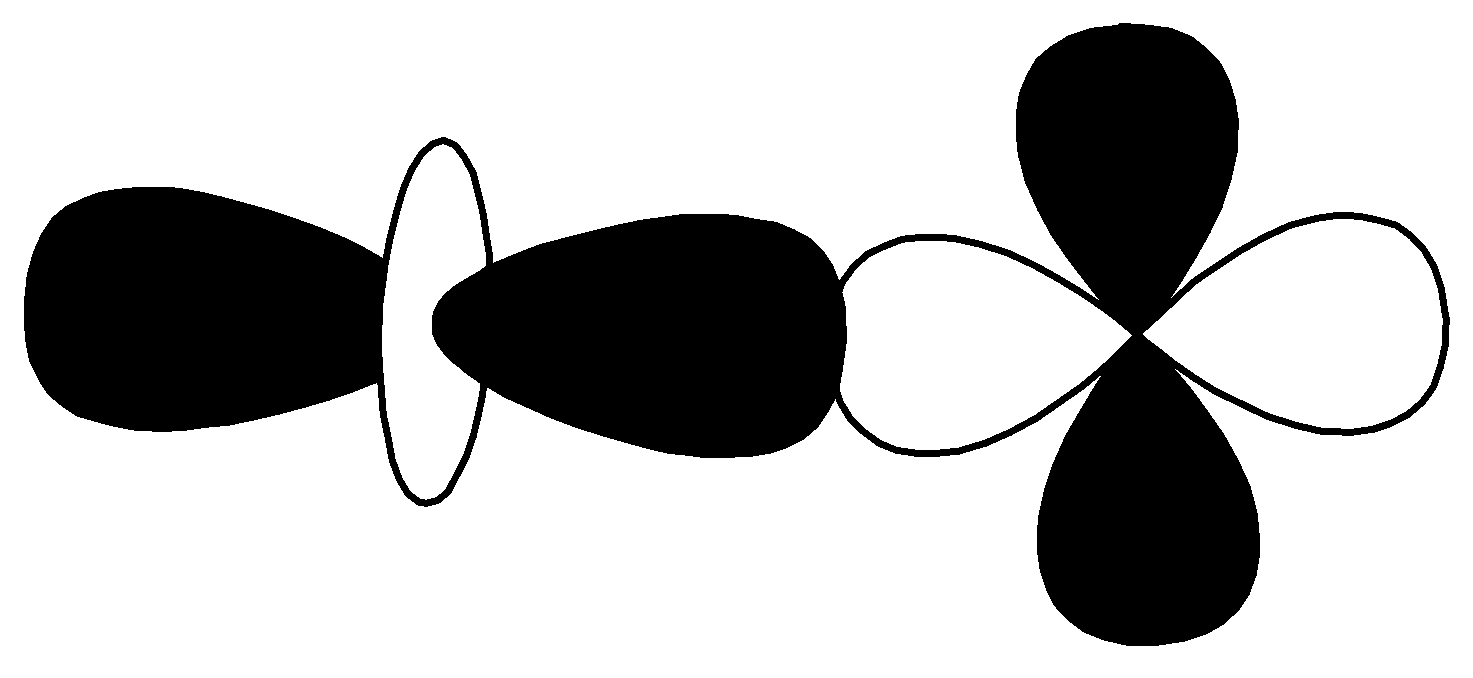
| $d - d$ $\sigma \;antibonding$ |
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: We have to remember that the $p - orbitals$ are dumbbell in shape whereas $d - orbitals$ are clover shape. Linus Pauling explained the importance of orbital overlap. This is explained by emphasizing the molecular bond angles are observed through the experiments and this is the basic concept for orbital hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




