
Mature mammalian RBC does not contain
A. Membrane bound cell organelles
B. Carbonic anhydrase
C. Haemoglobin
D. Enzymes of the glycolytic pathway
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: RBCs or Red blood corpuscles make the most abundant component of blood. They help in oxygen transfer throughout the body. The RBCs are composed of hemoglobin pigment. Haemoglobin needs a large space that is enough to eliminate the need for other organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.
Complete answer:
The RBCs are the cellular components of the blood among various immune cells. These are biconcave and red in color. The red color is due to the presence of the pigment named haemoglobin. The haemoglobin is a complex protein pigment that needs a large space to get fit into RBCs. Also, haemoglobin consists of four iron sites that carry oxygen. Thus, RBCs need to accommodate as much haemoglobin as possible. In the nascent RBC cells, some of the energy-producing organelles are present that get vanished as the RBC matures to accommodate hemoglobin molecules. The RBC in its mature forms needs to function as an oxygen carrier, thus it lacks membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum. This characteristic property of RBCs enables them to carry more hemoglobin, consequently leads to more oxygen transfer.
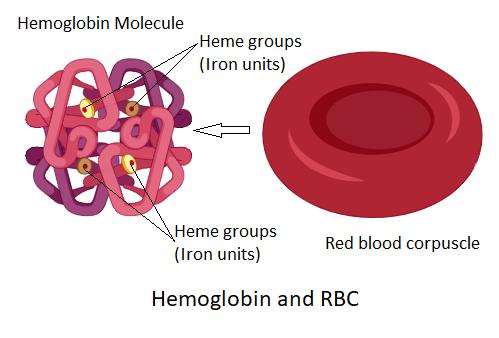
Now, let us study the other given options as well.
-Carbonic anhydrase enzyme is present inside the RBCs. As the haemoglobin is also attracted to carbon dioxide molecules, this enzyme converts carbon dioxide to carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions. These chemicals help in maintaining homeostasis in the blood acidity or alkalinity.
-Haemoglobin is the key component of the RBCs.
-Enzymes of the glycolytic pathway are present in RBCs as there is no Kreb’s cycle for energy production due to lack of mitochondria. This glycolytic pathway provides the required energy to RBCs to regulate in the blood.
Hence, from the above discussion, we can conclude that the right answer is option A.
Note: The RBCs are formed in the bone marrow by the stimulus provided by the erythropoietin hormone released by the kidney. The nascent RBCs consist of cellular organelles that help in protein synthesis and energy production. After entering the bloodstream, within 2 days the RBCs lose all of the cellular organelles required for protein and energy production. Thus, they survive only for 10 days based on the energy stored and made by the glycolytic pathway.
Complete answer:
The RBCs are the cellular components of the blood among various immune cells. These are biconcave and red in color. The red color is due to the presence of the pigment named haemoglobin. The haemoglobin is a complex protein pigment that needs a large space to get fit into RBCs. Also, haemoglobin consists of four iron sites that carry oxygen. Thus, RBCs need to accommodate as much haemoglobin as possible. In the nascent RBC cells, some of the energy-producing organelles are present that get vanished as the RBC matures to accommodate hemoglobin molecules. The RBC in its mature forms needs to function as an oxygen carrier, thus it lacks membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum. This characteristic property of RBCs enables them to carry more hemoglobin, consequently leads to more oxygen transfer.

Now, let us study the other given options as well.
-Carbonic anhydrase enzyme is present inside the RBCs. As the haemoglobin is also attracted to carbon dioxide molecules, this enzyme converts carbon dioxide to carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions. These chemicals help in maintaining homeostasis in the blood acidity or alkalinity.
-Haemoglobin is the key component of the RBCs.
-Enzymes of the glycolytic pathway are present in RBCs as there is no Kreb’s cycle for energy production due to lack of mitochondria. This glycolytic pathway provides the required energy to RBCs to regulate in the blood.
Hence, from the above discussion, we can conclude that the right answer is option A.
Note: The RBCs are formed in the bone marrow by the stimulus provided by the erythropoietin hormone released by the kidney. The nascent RBCs consist of cellular organelles that help in protein synthesis and energy production. After entering the bloodstream, within 2 days the RBCs lose all of the cellular organelles required for protein and energy production. Thus, they survive only for 10 days based on the energy stored and made by the glycolytic pathway.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




