
What do you mean by hysteresis? Explain hysteresis loop and hysteresis loss.
Answer
475.8k+ views
Hint: Hysteresis occurs In a system with a magnetic field. The hysteresis loop represents the magnetic flux density and the magnetizing field strength. As current flows in both directions, hysteresis loss is induced by the core's magnetization and demagnetization. As current flows in both directions, hysteresis loss is induced by the core's magnetization and demagnetization.
Complete answer:
Hysteresis- The hysteresis effect occurs when the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials lags behind that of the magnetic field. Whenever a ferromagnetic substance is inserted in a current-carrying coil, the substance becomes magnetized as a result of the magnetic field present. Hysteresis is the process of demagnetizing a substance by reversing the direction of the current.
Hysteresis loop- The loop is formed by continuously monitoring the magnetic flux released by the ferromagnetic substance as the external magnetizing field is altered.
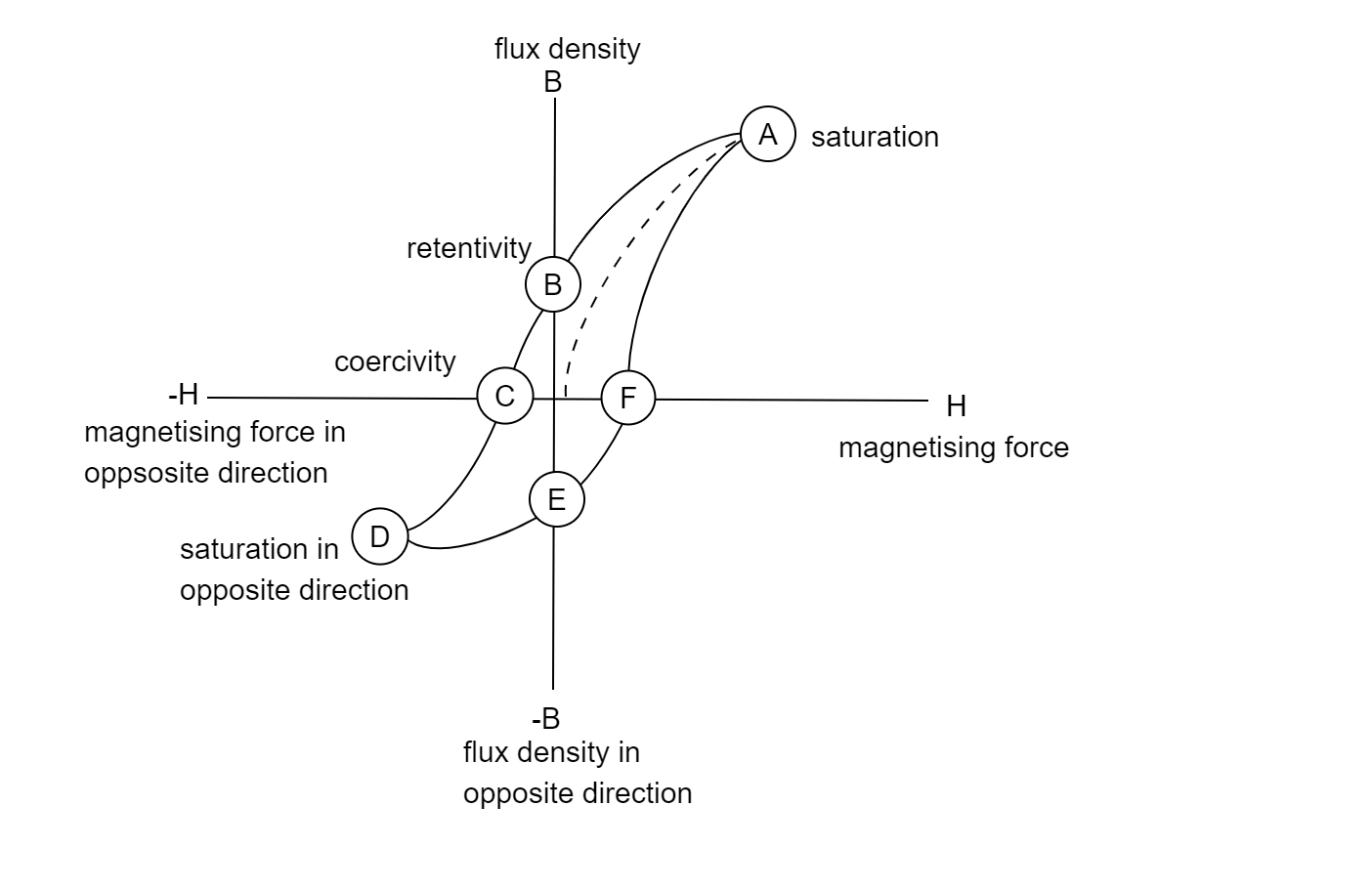
The graph is indicating a hysteresis loop.
When the magnetic field strength (H) is increased from zero to one, the magnetic flux density (B) increases.
The value of magnetism increases when the magnetic field is increased until it reaches point A, also known as the saturation point, where B remains constant.
As the magnetic field value diminishes, the value of magnetism lowers as well. However, the substance or material retains some magnetic retentivity, sometimes known as residual magnetism, when B and H are both zero.
When the magnetic field is shifted to the negative side, magnetism decreases as well. The material is totally demagnetized at point C.
Coercive force is the amount of force required to remove a material's retentivity (C).
The cycle is repeated in the opposite direction, with the saturation point D, retentivity point E, and coercive force F.
The forward and opposite direction processes complete the cycle, which is referred to as the hysteresis loop.
Hysteresis loss- Hysteresis can cause energy loss in electric machines' ferromagnetic cores. This is due to the fact that the alternating current's flow direction, and hence the direction of the magnetic field produced by it, is continually changing. This causes the molecules in the core to migrate in order to correct their alignment. These molecules collide with one other during this movement, causing friction and heat. Hysteresis loss is the energy loss induced by the friction of molecules in the core.
Note:
Ferromagnetic materials have a common feature called hysteresis. Hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs in all ferromagnetic materials. The amount of magnetism that persists after the external magnetizing field is removed is known as retentivity. The amount of reverse (negative H) external magnetizing field necessary to completely demagnetize a substance is known as coercivity.
Complete answer:
Hysteresis- The hysteresis effect occurs when the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials lags behind that of the magnetic field. Whenever a ferromagnetic substance is inserted in a current-carrying coil, the substance becomes magnetized as a result of the magnetic field present. Hysteresis is the process of demagnetizing a substance by reversing the direction of the current.
Hysteresis loop- The loop is formed by continuously monitoring the magnetic flux released by the ferromagnetic substance as the external magnetizing field is altered.

The graph is indicating a hysteresis loop.
When the magnetic field strength (H) is increased from zero to one, the magnetic flux density (B) increases.
The value of magnetism increases when the magnetic field is increased until it reaches point A, also known as the saturation point, where B remains constant.
As the magnetic field value diminishes, the value of magnetism lowers as well. However, the substance or material retains some magnetic retentivity, sometimes known as residual magnetism, when B and H are both zero.
When the magnetic field is shifted to the negative side, magnetism decreases as well. The material is totally demagnetized at point C.
Coercive force is the amount of force required to remove a material's retentivity (C).
The cycle is repeated in the opposite direction, with the saturation point D, retentivity point E, and coercive force F.
The forward and opposite direction processes complete the cycle, which is referred to as the hysteresis loop.
Hysteresis loss- Hysteresis can cause energy loss in electric machines' ferromagnetic cores. This is due to the fact that the alternating current's flow direction, and hence the direction of the magnetic field produced by it, is continually changing. This causes the molecules in the core to migrate in order to correct their alignment. These molecules collide with one other during this movement, causing friction and heat. Hysteresis loss is the energy loss induced by the friction of molecules in the core.
Note:
Ferromagnetic materials have a common feature called hysteresis. Hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs in all ferromagnetic materials. The amount of magnetism that persists after the external magnetizing field is removed is known as retentivity. The amount of reverse (negative H) external magnetizing field necessary to completely demagnetize a substance is known as coercivity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




