
What do you mean by leaf venation. Explain various types of leaf venation with examples.
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: Leaf consist of veins. Veins are made up of vascular tissues which help in transport of nutrients, food and water. The arrangement of veins differs in monocot and dicot plants.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we must know about the venation and its types.
The arrangement of veins and veinlets on the lamina or leaf-blade is known as venation. The veins are the vascular tissues that are xylem and phloem which supply food, water and nutrients to the leaves. The veins are connected to the petiole and the petiole is attached to the main stem. The arrangement to veins helps in determining whether the plant is monocot or dicot.
Types of Venation:
The venation is mostly of two types:
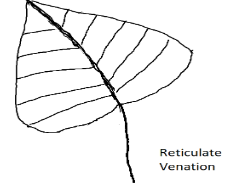
1)Reticulate venation: This type of venation is seen in the dicotyledonous angiosperm plants. In this type of arrangement, the veins form a network or a net like structure. The veins are interconnected like a web on either side of the mid rib. Example- Leaves of Oak, rose.
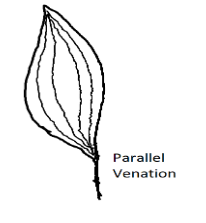
2)Parallel Venation: This type of venation is mostly seen in the monocotyledons like grasses, wheat etc. The veins are smaller and are parallel to one another. The midrib is not present in this type of leaves.
A rare pattern of vein arrangement is seen in gymnosperms like Ginkgo biloba. In this the veins branch off like the branches of a tree. This type of venation is known as Dichotomous venation.
Note: The leaf venation is significant in providing mechanical stability to the leaves. They also aid in gaseous exchange. The thicker veins help in transporting more waler and glucose. The venation of the leaves helps in identification and classification of plants. The veins also help in coordinating the leaves with different parts of the plant.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we must know about the venation and its types.
The arrangement of veins and veinlets on the lamina or leaf-blade is known as venation. The veins are the vascular tissues that are xylem and phloem which supply food, water and nutrients to the leaves. The veins are connected to the petiole and the petiole is attached to the main stem. The arrangement to veins helps in determining whether the plant is monocot or dicot.
Types of Venation:
The venation is mostly of two types:
1)Reticulate venation: This type of venation is seen in the dicotyledonous angiosperm plants. In this type of arrangement, the veins form a network or a net like structure. The veins are interconnected like a web on either side of the mid rib. Example- Leaves of Oak, rose.

2)Parallel Venation: This type of venation is mostly seen in the monocotyledons like grasses, wheat etc. The veins are smaller and are parallel to one another. The midrib is not present in this type of leaves.

A rare pattern of vein arrangement is seen in gymnosperms like Ginkgo biloba. In this the veins branch off like the branches of a tree. This type of venation is known as Dichotomous venation.
Note: The leaf venation is significant in providing mechanical stability to the leaves. They also aid in gaseous exchange. The thicker veins help in transporting more waler and glucose. The venation of the leaves helps in identification and classification of plants. The veins also help in coordinating the leaves with different parts of the plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




