
What do you mean by oxidation and reduction?
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two species. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron.
Complete step by step answer:
Oxidation means gaining oxygen in a chemical reaction.
In Chemistry, it is referred to as the loss of oxygen when it is with respect to the oxygen transfer. It is the job of the reducing agent to remove the oxygen from another substance.
Similarly, in the case of hydrogen transfer, it is the gain of hydrogen. That means it is reducing the agent’s work to remove oxygen from one substance and hydrogen to it.
We will be looking at oxidation and reduction from two different points of view.
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen transfer
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron transfer
Oxidation and reduction in terms of oxygen transfer:
\[2Mg(s) + {O_2}(g)\xrightarrow{{oxidation}}2MgO(s)\]
\[MgO(s) + C(s)\xrightarrow{{reduction}}Mg(s) + CO(g)\]
Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer: Oxidation and Reduction reactions are always interlinked. Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, oxidation and reduction always occur in pairs, it is impossible to have one without the other. In the below reaction Magnesium gets oxidized by losing two electrons to oxygen which gets reduced by accepting two electrons from magnesium.
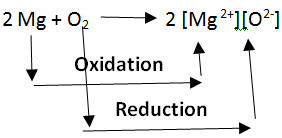
Note: Since oxidation and reduction cannot occur individually, they as a whole are called ‘Redox Reactions’. The reactant that oxidizes the other reactants is called the Oxidizing agent and the reactant that reduces is called the Reducing agent. There is quite some confusion about the aspect of whether oxidizing agents accept or give away electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Oxidation means gaining oxygen in a chemical reaction.
In Chemistry, it is referred to as the loss of oxygen when it is with respect to the oxygen transfer. It is the job of the reducing agent to remove the oxygen from another substance.
Similarly, in the case of hydrogen transfer, it is the gain of hydrogen. That means it is reducing the agent’s work to remove oxygen from one substance and hydrogen to it.
We will be looking at oxidation and reduction from two different points of view.
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen transfer
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron transfer
Oxidation and reduction in terms of oxygen transfer:
\[2Mg(s) + {O_2}(g)\xrightarrow{{oxidation}}2MgO(s)\]
\[MgO(s) + C(s)\xrightarrow{{reduction}}Mg(s) + CO(g)\]
Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer: Oxidation and Reduction reactions are always interlinked. Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, oxidation and reduction always occur in pairs, it is impossible to have one without the other. In the below reaction Magnesium gets oxidized by losing two electrons to oxygen which gets reduced by accepting two electrons from magnesium.

Note: Since oxidation and reduction cannot occur individually, they as a whole are called ‘Redox Reactions’. The reactant that oxidizes the other reactants is called the Oxidizing agent and the reactant that reduces is called the Reducing agent. There is quite some confusion about the aspect of whether oxidizing agents accept or give away electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




