
What is meant by nitrogen fixation? Explain biological nitrogen fixation in plants?
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen, a chemical compound is assimilated into organic compounds, this conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds with the help of certain microorganisms is part of the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen fixation is basically an industrial process, which converts free nitrogen into inert gas and combines with elements.
Complete answer-
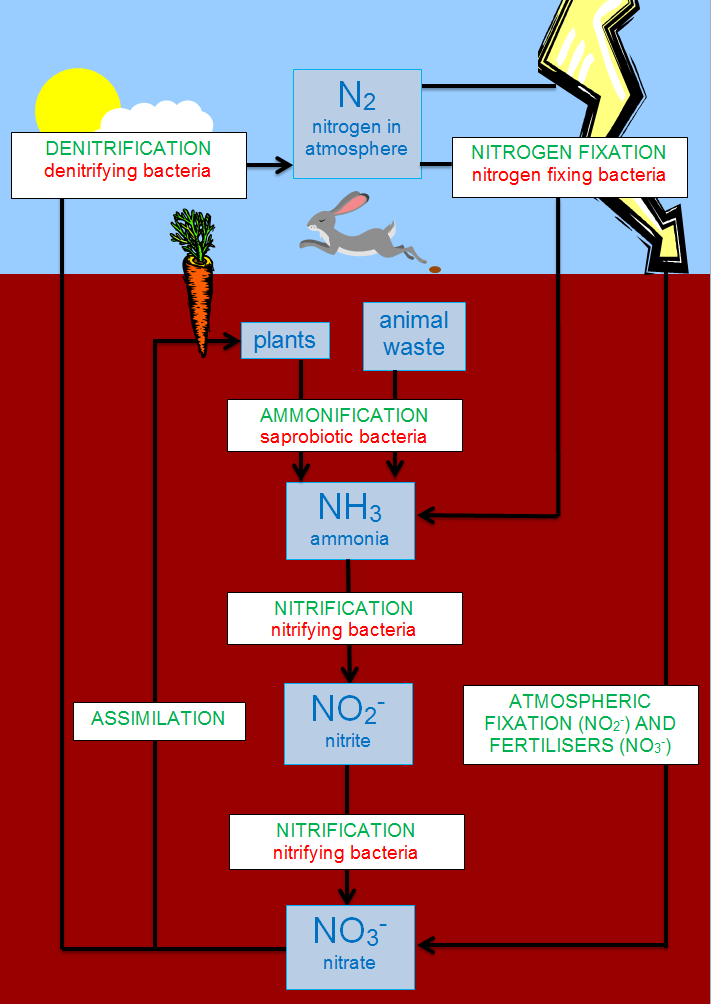
Biological nitrogen fixation occurs with the help of microorganisms.
Biological nitrogen fixation is where gases combine chemically with other elements and form more reactive nitrogen compounds like- ammonia nitrites etc. In all fertile soils, living things, food stuffs, and coal nitrogen compounds occur.
It is also found in the nucleus of living cells as a major component in DNA. In biological fixation, the nitrogen gas after being converted is incorporated into the tissue of plants. This process in which some crops are incorporated with N$_2$ from air with a host present in the plant is called microsymbiont.
Among the forage crops, legumes belonging to the Fabaceae family are well known for being able to convert Nitrogen from atmospheric nitrogen. In forage production, the method is often vital because it means nitrogen is often extracted from three sources, the atmosphere via biological fixation, the soil and fertilizers.
Note:
The microorganisms which are involved in conversion are- rhizobia, free-living (nonsymbiotic) bacteria, cyanobacteria, anabaena, nostoc and many heterotrophic bacteria. All reactions including the process of nitrogen fixation often be catalyzed by enzymes known as nitrogenases. Enzymes are used to fasten the reaction and also, they contain iron, molybdenum.
Complete answer-
Biological nitrogen fixation occurs with the help of microorganisms.
Biological nitrogen fixation is where gases combine chemically with other elements and form more reactive nitrogen compounds like- ammonia nitrites etc. In all fertile soils, living things, food stuffs, and coal nitrogen compounds occur.
It is also found in the nucleus of living cells as a major component in DNA. In biological fixation, the nitrogen gas after being converted is incorporated into the tissue of plants. This process in which some crops are incorporated with N$_2$ from air with a host present in the plant is called microsymbiont.
Among the forage crops, legumes belonging to the Fabaceae family are well known for being able to convert Nitrogen from atmospheric nitrogen. In forage production, the method is often vital because it means nitrogen is often extracted from three sources, the atmosphere via biological fixation, the soil and fertilizers.

Note:
The microorganisms which are involved in conversion are- rhizobia, free-living (nonsymbiotic) bacteria, cyanobacteria, anabaena, nostoc and many heterotrophic bacteria. All reactions including the process of nitrogen fixation often be catalyzed by enzymes known as nitrogenases. Enzymes are used to fasten the reaction and also, they contain iron, molybdenum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




