
Meiosis I is a reduction division. Meiosis II is equational division due to
(a)Separation of chromatids
(b)Crossing over
(c)Pairing of homologous chromosome
(d)Disjunction of homologous chromosome
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Meiosis I and II are given the names based upon the ploidy number of the cells in those stages and the ploidy number of the cells before the beginning of those stages. Meiosis I results in the formation of haploid cells.
Complete answer:
The cells before entering the process of meiosis are diploid.
The first meiotic division or the meiosis results in the formation of two cells, each with 46 chromosomes. Then, the second round of meiotic division takes place and each of these two cells divides further resulting in four haploid cells. Thus, Meiosis is called a reduction division, because, at the end of this special type of cell division, four haploid cells are formed.
On the other hand, in meiosis II, the two chromatids of each chromosome separate from each other and go to separate daughter cells. As a result, there is no increase or decrease in the number of chromosomes and it remains the same as produced by meiosis I.
Therefore, meiosis II is known as equational division or homotypic division.
So, the correct answer is, “Separation of chromatids”
Note:
-After both meiosis I and II, the cell is haploid with 23 chromosomes.
-The process meiosis II has the same steps as mitosis.
-The steps in meiosis I, are the main steps that are responsible for genetic variation, such as crossing over and separation of chromatids.
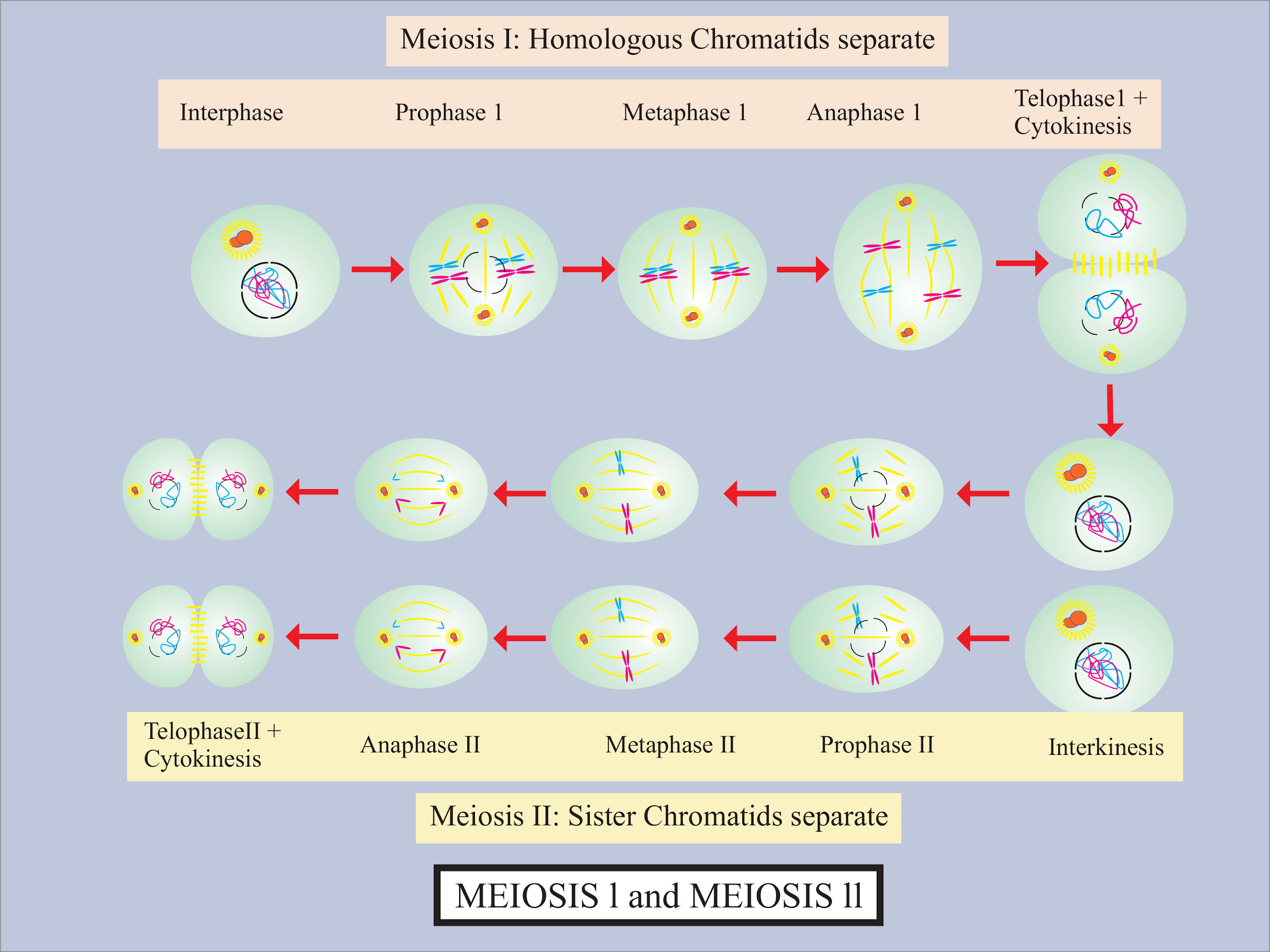
Complete answer:
The cells before entering the process of meiosis are diploid.
The first meiotic division or the meiosis results in the formation of two cells, each with 46 chromosomes. Then, the second round of meiotic division takes place and each of these two cells divides further resulting in four haploid cells. Thus, Meiosis is called a reduction division, because, at the end of this special type of cell division, four haploid cells are formed.
On the other hand, in meiosis II, the two chromatids of each chromosome separate from each other and go to separate daughter cells. As a result, there is no increase or decrease in the number of chromosomes and it remains the same as produced by meiosis I.
Therefore, meiosis II is known as equational division or homotypic division.
So, the correct answer is, “Separation of chromatids”
Note:
-After both meiosis I and II, the cell is haploid with 23 chromosomes.
-The process meiosis II has the same steps as mitosis.
-The steps in meiosis I, are the main steps that are responsible for genetic variation, such as crossing over and separation of chromatids.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




