
How can I memorize functional groups?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: We know that functional groups are the atoms or groups of atoms that decide the chemical reactivity of an organic compound. Some examples of functional groups are alkane, alkene, alcohol, aldehyde etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s learn about functional groups in detail. They are specific groups of atoms or bonds that decide the chemical reactions of that compound. In organic chemistry, the naming of compounds is based on the functional groups present in the compound. We have to memorize the names of the functional groups, such as, alkane, alkene, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, amide, amine etc.
Let’s understand the functional groups with the help of their structure.
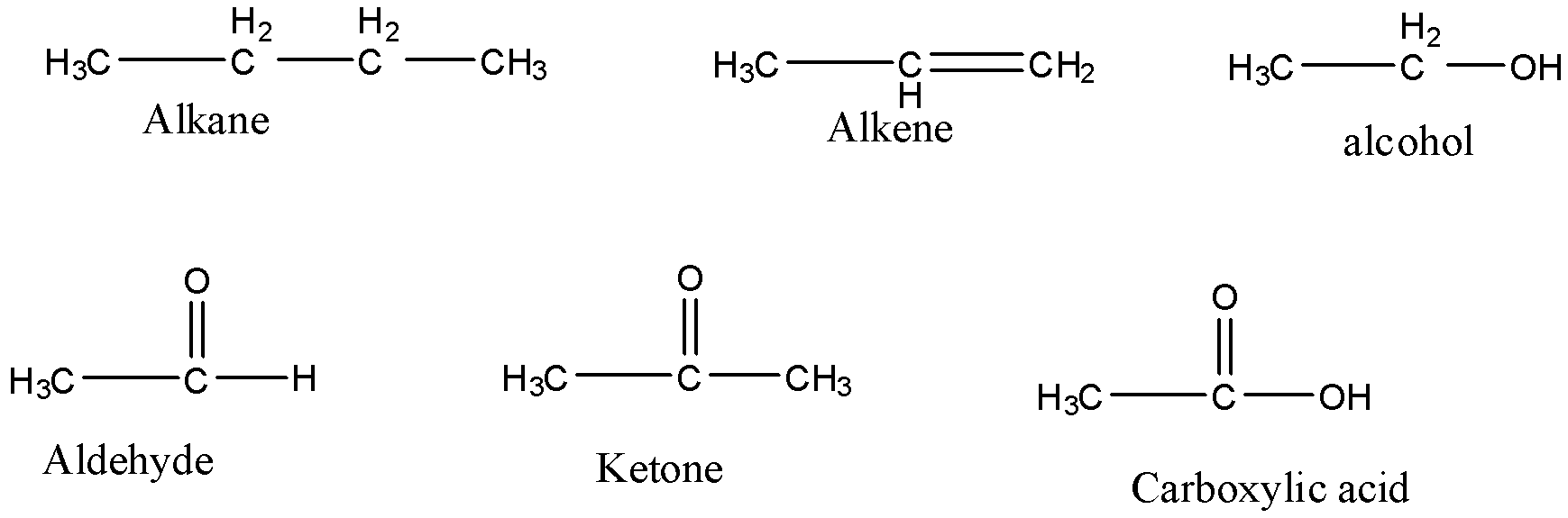
Alkane is a functional group which indicates that only single bonds are present in the compound.
Alkene is a functional group which indicates the presence of double bond in the compound
Alkyne is a functional group which indicates the presence of triple bond in the compound
Alcohol is a functional group composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms and it forms bonds with an alkyl group.
Aldehyde (-CHO) is a functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to an alkyl group and a hydrogen atom.
Ketone is another functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups.
Carboxylic group is another functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to an alkyl group and an alcohol group.
Note: The number of organic compounds present on Earth is in millions and that’s why memorizing chemical reactions of each compound is difficult. It is to be noted that molecules having identical functional groups undergo similar reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s learn about functional groups in detail. They are specific groups of atoms or bonds that decide the chemical reactions of that compound. In organic chemistry, the naming of compounds is based on the functional groups present in the compound. We have to memorize the names of the functional groups, such as, alkane, alkene, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, amide, amine etc.
Let’s understand the functional groups with the help of their structure.

Alkane is a functional group which indicates that only single bonds are present in the compound.
Alkene is a functional group which indicates the presence of double bond in the compound
Alkyne is a functional group which indicates the presence of triple bond in the compound
Alcohol is a functional group composed of oxygen and hydrogen atoms and it forms bonds with an alkyl group.
Aldehyde (-CHO) is a functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to an alkyl group and a hydrogen atom.
Ketone is another functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups.
Carboxylic group is another functional group in which a carbonyl group is bonded to an alkyl group and an alcohol group.
Note: The number of organic compounds present on Earth is in millions and that’s why memorizing chemical reactions of each compound is difficult. It is to be noted that molecules having identical functional groups undergo similar reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




