
Mention the bonds present in $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ .
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: While determining the type of bonds that are present in $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ , we must remember that the metal ion involved is copper. Copper is a transition metal capable of forming simple ionic salts as well as coordination complexes as water and sulphate both are capable of acting as ligands.
Complete answer:
In order to determine the bonding situation of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ , we must get an insight of its structure.
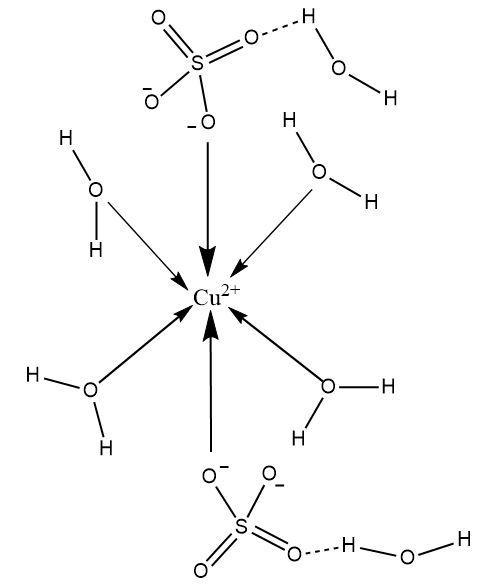
The structure of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ represents a coordination complex in which the copper cation serves as the central metal ion. It is an octahedral complex in which one coordination sphere includes a total of four water molecules present as ligands and two sulphate ions present at terminal positions. The sulphate ions are not just interacting with the central metal ion (copper) but also water molecules that are not part of the coordination sphere.
The different kinds of bonds that exist in the $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ complex are as follows:
A mixed interaction between the sulphate ion and the copper ion. The sulphate ion acts as ligand and is connected through a coordinate covalent bond but at the same time there are electrostatic forces of attraction between the negatively charged sulphate ions and positively charged copper ions. Thus the sulphate-copper bond is both ionic (electrovalent) and coordinate covalent in nature.
The negatively charged oxygens of sulphur molecules are engaged in forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules outside the coordination sphere.
There are coordinate covalent bonds between the copper ion and the water molecules acting as ligands.
There are covalent bonds present inside the sulphate as well as water molecules.
Hence, the bonds present in $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ are ionic, covalent, coordinate covalent and hydrogen bonds.
Note:
One may interpret the formula of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ as an ionic salt between copper and sulphate ions (charges are balanced as both have the same magnitude of charge) along with five molecules being present as water of crystallization. This interpretation is not wrong but does not provide a clear picture of the bonds formed between atoms.
Complete answer:
In order to determine the bonding situation of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ , we must get an insight of its structure.

The structure of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ represents a coordination complex in which the copper cation serves as the central metal ion. It is an octahedral complex in which one coordination sphere includes a total of four water molecules present as ligands and two sulphate ions present at terminal positions. The sulphate ions are not just interacting with the central metal ion (copper) but also water molecules that are not part of the coordination sphere.
The different kinds of bonds that exist in the $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ complex are as follows:
A mixed interaction between the sulphate ion and the copper ion. The sulphate ion acts as ligand and is connected through a coordinate covalent bond but at the same time there are electrostatic forces of attraction between the negatively charged sulphate ions and positively charged copper ions. Thus the sulphate-copper bond is both ionic (electrovalent) and coordinate covalent in nature.
The negatively charged oxygens of sulphur molecules are engaged in forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules outside the coordination sphere.
There are coordinate covalent bonds between the copper ion and the water molecules acting as ligands.
There are covalent bonds present inside the sulphate as well as water molecules.
Hence, the bonds present in $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ are ionic, covalent, coordinate covalent and hydrogen bonds.
Note:
One may interpret the formula of $ CuS{O_4}.5{H_2}O $ as an ionic salt between copper and sulphate ions (charges are balanced as both have the same magnitude of charge) along with five molecules being present as water of crystallization. This interpretation is not wrong but does not provide a clear picture of the bonds formed between atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




