
Mention the effect of altitude and depth on the value of acceleration due to gravity. Give the corresponding mathematical relation.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Recall that the acceleration due to gravity experienced by the all bodies on the surface of the earth is the same. In both cases, using the universal law of gravitation obtains the relation between the force experienced by the body and the height or depth at which the body is relative to the surface of the earth in terms of the acceleration due to gravity.
Formula used:
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth:
$\Rightarrow g_h = g\left(1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from the surface of the earth:
$\Rightarrow g_d = g\left(1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth is given as :
$g = \dfrac{GM}{R^2}$, where G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the earth, and R is the radius of the earth.
From the above relation, we see that all bodies on the surface of the earth experience the same acceleration due to gravity, irrespective of their mass. This means that the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body will only differ at different heights and depths from the surface of the earth. We will now look at each of these cases separately.
1) Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth:
Consider a mass m that is at a height h from the surface of the earth. The force acting on this mass due to gravity is given by the universal law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{(R+h)^2}$
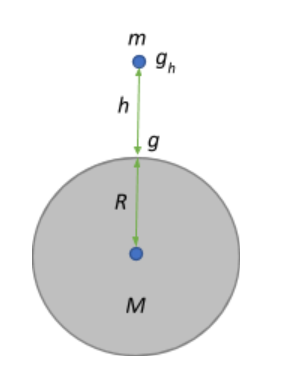
The acceleration due to gravity at a certain height is also given by $mg_h$.
Equating the two $mg_h = \dfrac{GMm}{(R+h)^2} \Rightarrow g_h = \dfrac{GM}{R^2(1+\dfrac{h}{R})^2} \Rightarrow g_h = \left(\dfrac{GM}{R^2}\right)\left( 1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
$\Rightarrow g_h = g\left(1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
This expression describes the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body at a certain height h from the surface of the earth. From the above relation we deduce that the acceleration due to gravity decreases with an increase in height and it becomes zero at an infinite distance from earth.
2) Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from the surface of the earth:
Consider a mass m that is at a depth d below the surface of the earth. The force acting on this mass due to gravity is given by the universal law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{(R-d)^2}$
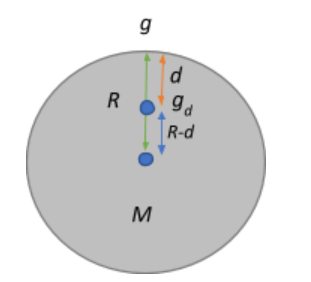
The acceleration due to gravity at a certain depth is also given by $mg_d$.
Equating the two $mg_d = \dfrac{GMm}{(R-d)^2} \Rightarrow g_d = \dfrac{GM}{R^2(1-\dfrac{d}{R})^2} \Rightarrow g_d = \left(\dfrac{GM}{R^2}\right)\left( 1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
$\Rightarrow g_d = g\left(1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
This expression describes the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body at a certain depth d from the surface of the earth. From the above relation we deduce that the acceleration due to gravity decreases with an increase in depth and it becomes zero at the centre of the earth.
Note: In addition to height and depth, the acceleration due to gravity varies due to the shape of the earth as well. Since the earth is an oblate spheroid, the radius at the equator of the earth is more than the radius of the earth near the poles. Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity is more at the equator and less at the poles. So, if a person moves from the equator to poles, his weight decreases as the value of g decreases.
Formula used:
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth:
$\Rightarrow g_h = g\left(1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from the surface of the earth:
$\Rightarrow g_d = g\left(1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth is given as :
$g = \dfrac{GM}{R^2}$, where G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the earth, and R is the radius of the earth.
From the above relation, we see that all bodies on the surface of the earth experience the same acceleration due to gravity, irrespective of their mass. This means that the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body will only differ at different heights and depths from the surface of the earth. We will now look at each of these cases separately.
1) Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth:
Consider a mass m that is at a height h from the surface of the earth. The force acting on this mass due to gravity is given by the universal law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{(R+h)^2}$

The acceleration due to gravity at a certain height is also given by $mg_h$.
Equating the two $mg_h = \dfrac{GMm}{(R+h)^2} \Rightarrow g_h = \dfrac{GM}{R^2(1+\dfrac{h}{R})^2} \Rightarrow g_h = \left(\dfrac{GM}{R^2}\right)\left( 1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
$\Rightarrow g_h = g\left(1+\dfrac{h}{R}\right)^{-2}$
This expression describes the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body at a certain height h from the surface of the earth. From the above relation we deduce that the acceleration due to gravity decreases with an increase in height and it becomes zero at an infinite distance from earth.
2) Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from the surface of the earth:
Consider a mass m that is at a depth d below the surface of the earth. The force acting on this mass due to gravity is given by the universal law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{(R-d)^2}$

The acceleration due to gravity at a certain depth is also given by $mg_d$.
Equating the two $mg_d = \dfrac{GMm}{(R-d)^2} \Rightarrow g_d = \dfrac{GM}{R^2(1-\dfrac{d}{R})^2} \Rightarrow g_d = \left(\dfrac{GM}{R^2}\right)\left( 1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
$\Rightarrow g_d = g\left(1-\dfrac{d}{R}\right)^{-2}$
This expression describes the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a body at a certain depth d from the surface of the earth. From the above relation we deduce that the acceleration due to gravity decreases with an increase in depth and it becomes zero at the centre of the earth.
Note: In addition to height and depth, the acceleration due to gravity varies due to the shape of the earth as well. Since the earth is an oblate spheroid, the radius at the equator of the earth is more than the radius of the earth near the poles. Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity is more at the equator and less at the poles. So, if a person moves from the equator to poles, his weight decreases as the value of g decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




