
Mention the location and function of the given parts:
a) Fovea centralis
b) Choroid
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: Fovea centralis and choroid are the important regions that are present in our eye. The Fovea is the area within the retina of the eye where more cone cells are connected and the choroid is the middle layer of the eye which has pigment, vascular and connective tissue.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about the structure of an eye. The human eye is made up of various parts which include Iris, pupil, cornea, lens, choroid, ciliary body, retina, macula, fovea, optic disc, optic nerves, sclera, rod cells and cone cells.
FOVEA CENTRALIS: -
Location (fovea): - it is small tiny parts of eye anatomy located at the centre of the macula and is the area with the great concentration of cone cells.
Function: -the fovea is responsible for sharp vision which is necessary for humans to do various activities such as reading, driving etc.
CHOROID: -
Location (choroid coat):- A thin layer of tissue that is the part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye between the retina and sclera .and it is filled with blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
Function: -it contains pigments that help to absorb excess light so it prevents the blurring of vision and nourishes the retina and also maintains the temperature and volume of the eye.
The diagram below shows the structure of the human eye.
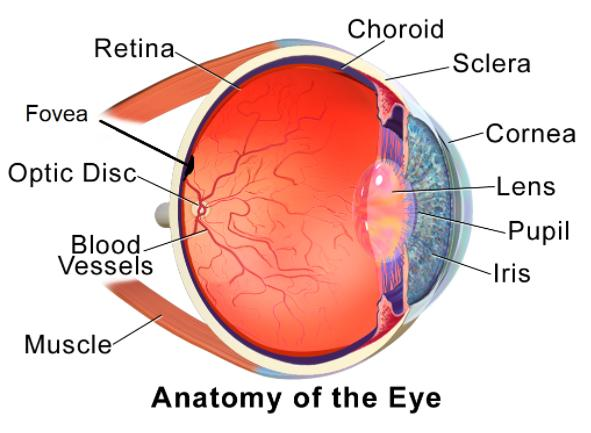
Note: The eye is a complex structure with many small organs that are essential for vision and movements of the eyes. More than 50% of the sensory receptors in the human body are located in the eyes, eyes absorb the visible light from 400 -700 nm. The eye is the source of injury, infection and multiple medical diseases.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about the structure of an eye. The human eye is made up of various parts which include Iris, pupil, cornea, lens, choroid, ciliary body, retina, macula, fovea, optic disc, optic nerves, sclera, rod cells and cone cells.
FOVEA CENTRALIS: -
Location (fovea): - it is small tiny parts of eye anatomy located at the centre of the macula and is the area with the great concentration of cone cells.
Function: -the fovea is responsible for sharp vision which is necessary for humans to do various activities such as reading, driving etc.
CHOROID: -
Location (choroid coat):- A thin layer of tissue that is the part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye between the retina and sclera .and it is filled with blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
Function: -it contains pigments that help to absorb excess light so it prevents the blurring of vision and nourishes the retina and also maintains the temperature and volume of the eye.
The diagram below shows the structure of the human eye.

Note: The eye is a complex structure with many small organs that are essential for vision and movements of the eyes. More than 50% of the sensory receptors in the human body are located in the eyes, eyes absorb the visible light from 400 -700 nm. The eye is the source of injury, infection and multiple medical diseases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




