
Meso Tartaric acid and d-tartaric acid are:
A.Position isomers
B.Racemic isomers
C.Enantiomers
D.Diastereomers
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: We must need to know that the same molecular formula but compounds are different, is called isomers. Same molecular formula compounds behave as different compounds are called isomerism. An achiral compound which contains a chiral center is called a meso compound. The mirror image of the meso compound is superimposed and it contains two or more stereocenters. Meso compound is optically inactive.
Complete answer:
Now we can discuss the position isomers as the groups are moved on that carbon skeleton, but the basic carbon skeleton of the compound is unchanged.
Let's know about the racemic isomers: A mixtures that contains equal amounts of enantiomers, also a solution that contains an equimolar, $50:50$ or $1:1$ enantiomeric mixtures, of a chiral compound.
Enantiomers: Optical isomers which rotate the plane polarized light in the opposite direction, mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Now we can see the concept of diastereomers: These are stereoisomers. When a molecule contains more than one chiral center (stereo centre) diastereomers occur. These are not mirror images of each other. $cis - trans$ isomers are always diastereomers.
Given meso tartaric acid and d-tartaric acid structural formula are respectively,
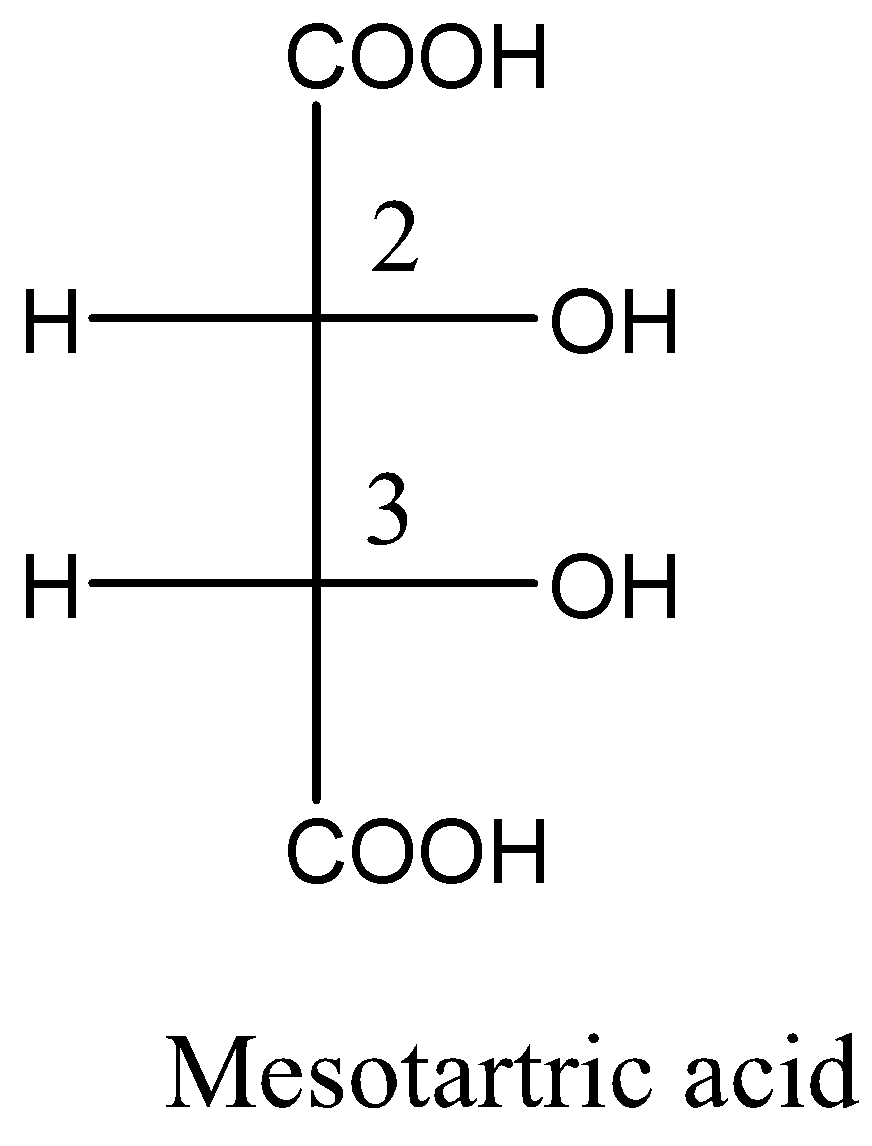
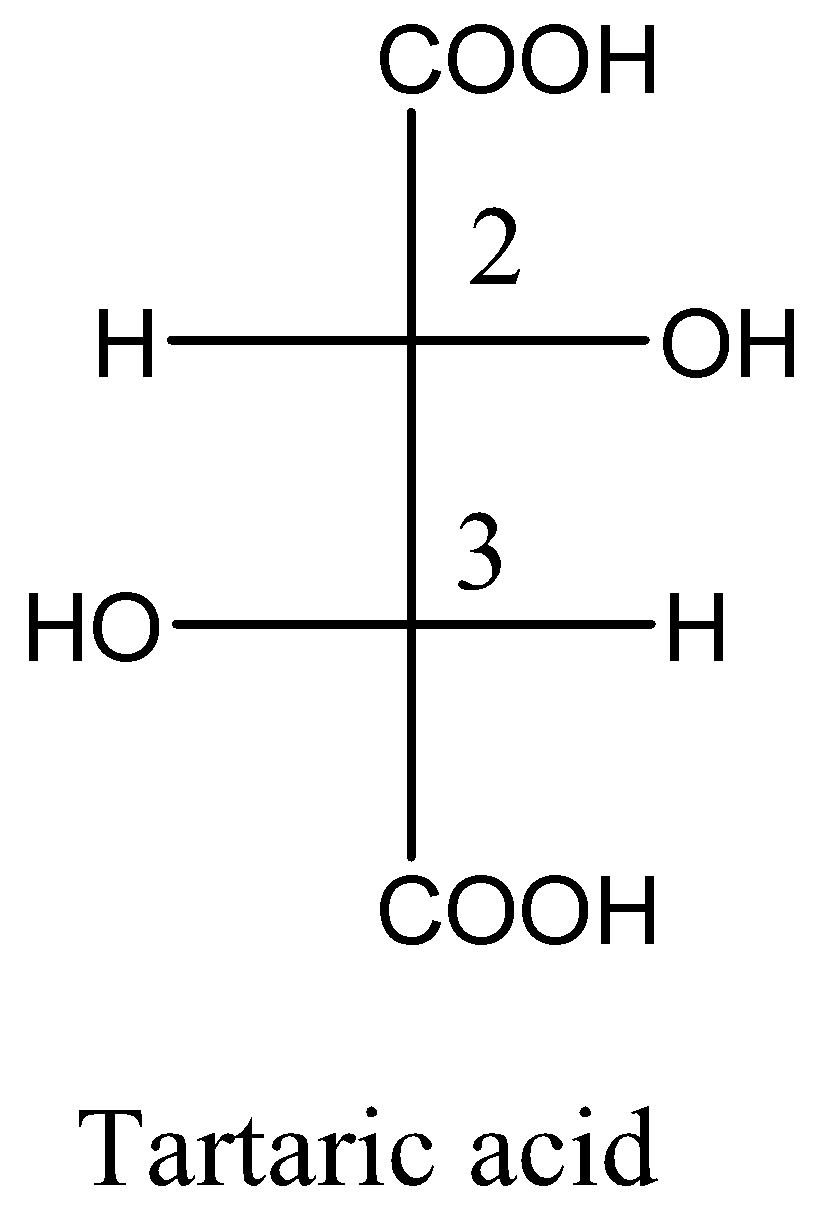
From the above structural formula, the carbon $ - 2$ and carbon $ - 3$ are not mirror images of each other and the stereocenters are not identical. So, these are called diastereomers.
The correct option is D. Diastereomers.
Note:
We need to know that the Diastereomers are optically active compounds and the rotation of plane polarized light between the diastereomers is unrelated. Enantiomeric compounds are always chiral but diastereomeric compounds can be chiral or achiral. The absolute configurations of diastereomeric compounds are opposite, if a compound is $R,S$ then the pair compound configuration is $S,R$ or $R,R$ configuration. But not the same configuration.
Complete answer:
Now we can discuss the position isomers as the groups are moved on that carbon skeleton, but the basic carbon skeleton of the compound is unchanged.
Let's know about the racemic isomers: A mixtures that contains equal amounts of enantiomers, also a solution that contains an equimolar, $50:50$ or $1:1$ enantiomeric mixtures, of a chiral compound.
Enantiomers: Optical isomers which rotate the plane polarized light in the opposite direction, mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Now we can see the concept of diastereomers: These are stereoisomers. When a molecule contains more than one chiral center (stereo centre) diastereomers occur. These are not mirror images of each other. $cis - trans$ isomers are always diastereomers.
Given meso tartaric acid and d-tartaric acid structural formula are respectively,


From the above structural formula, the carbon $ - 2$ and carbon $ - 3$ are not mirror images of each other and the stereocenters are not identical. So, these are called diastereomers.
The correct option is D. Diastereomers.
Note:
We need to know that the Diastereomers are optically active compounds and the rotation of plane polarized light between the diastereomers is unrelated. Enantiomeric compounds are always chiral but diastereomeric compounds can be chiral or achiral. The absolute configurations of diastereomeric compounds are opposite, if a compound is $R,S$ then the pair compound configuration is $S,R$ or $R,R$ configuration. But not the same configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




