
Meso tartaric acid is formed in
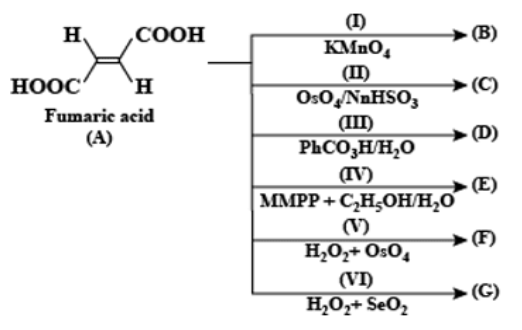
A. $\left( I \right),\left( II \right),\left( V \right)$
B. $\left( III \right),\left( IV \right),\left( VI \right)$
C. $\left( I \right),\left( II \right),\left( IV \right)$

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Tartaric acid is an organic acid which is white acid crystalline naturally occurring in fruits, mostly present in grapes. As we know tartaric acid is chiral and is useful raw material in organic chemical synthesis.
Let us discuss chiral in brief: In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superimposed by any mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations.
Complete answer:
The preferred IUPAC name of meso-tartaric acid is 2,3 -dihydroxybutanedioic acid which has meso configuration. Molecular formula of meso-tartaric acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{6}}$.
Let us see the structure of meso-tartaric acid:
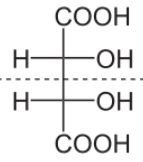
Now let us talk about meso configuration of tartaric acid: as we know a meso compound or meso isomer is a non- optically active member of a set of stereoisomers at least two of them actively active.
In the case of tartaric acid, the two chiral centres have the same four substituents and are equivalent and meso compounds are optically inactive diastereomers of chiral stereoisomers.
Now let us see the chemical reaction in which meso-tartaric acid is formed:
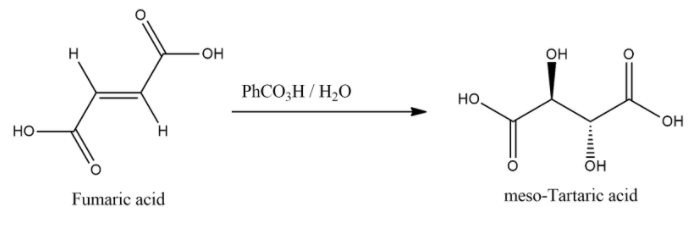
When fumaric acid is treated with $PhC{{O}_{3}}H/{{H}_{2}}O$ it will give meso-tartaric acid.
And the general chemical equation for this reaction:
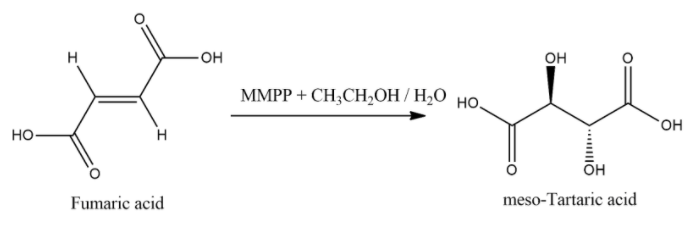
Now, when fumaric acid treated with Magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) then product will be meso tartaric acid and general equation for this reaction is:
Now, when fumaric acid is treated with hydrogen peroxide and silicon dioxide then it will form meso tartaric acid and chemical equation for this reaction is:
\[H{{O}_{2}}CCH=CHC{{O}_{2}}H+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+Se{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{{}}{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{6}}\] (meso tartaric acid)
Hence from the above chemical equations, it is concluded that meso tartaric acid formed in reactions (III), (IV), and (VI). The two -OH groups added to the carbon-carbon double bond.
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Now we will see in brief why other options are incorrect: When fumaric acid is treated with (I) $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ (II) $Os{{O}_{4}}/NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ and (V) ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+Os{{O}_{4}}$ then $\left( \pm \right)$Tartaric acid will form that is the two -OH groups are added across carbon-carbon double bonds from the same side.
Now let see what is $\left( \pm \right)$ represented here: the dextrorotatory compound is represented with (+) whereas, the laevorotatory compound is prefixed with ( – ).
Note:
Remember, don’t confuse here meso configuration with enantiomers because meso compounds have at least two chiral centres despite having chiral centre they are optically inactive they have a plane of symmetry whereas, enantiomers are optically active having chiral centres which are non-superimposable.
Let us discuss chiral in brief: In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superimposed by any mirror image by any combination of rotations and translations.
Complete answer:
The preferred IUPAC name of meso-tartaric acid is 2,3 -dihydroxybutanedioic acid which has meso configuration. Molecular formula of meso-tartaric acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{6}}$.
Let us see the structure of meso-tartaric acid:

Now let us talk about meso configuration of tartaric acid: as we know a meso compound or meso isomer is a non- optically active member of a set of stereoisomers at least two of them actively active.
In the case of tartaric acid, the two chiral centres have the same four substituents and are equivalent and meso compounds are optically inactive diastereomers of chiral stereoisomers.
Now let us see the chemical reaction in which meso-tartaric acid is formed:
When fumaric acid is treated with $PhC{{O}_{3}}H/{{H}_{2}}O$ it will give meso-tartaric acid.
And the general chemical equation for this reaction:

Now, when fumaric acid treated with Magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) then product will be meso tartaric acid and general equation for this reaction is:

Now, when fumaric acid is treated with hydrogen peroxide and silicon dioxide then it will form meso tartaric acid and chemical equation for this reaction is:
\[H{{O}_{2}}CCH=CHC{{O}_{2}}H+{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+Se{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{{}}{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{6}}\] (meso tartaric acid)
Hence from the above chemical equations, it is concluded that meso tartaric acid formed in reactions (III), (IV), and (VI). The two -OH groups added to the carbon-carbon double bond.
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Now we will see in brief why other options are incorrect: When fumaric acid is treated with (I) $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ (II) $Os{{O}_{4}}/NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ and (V) ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}+Os{{O}_{4}}$ then $\left( \pm \right)$Tartaric acid will form that is the two -OH groups are added across carbon-carbon double bonds from the same side.
Now let see what is $\left( \pm \right)$ represented here: the dextrorotatory compound is represented with (+) whereas, the laevorotatory compound is prefixed with ( – ).
Note:
Remember, don’t confuse here meso configuration with enantiomers because meso compounds have at least two chiral centres despite having chiral centre they are optically inactive they have a plane of symmetry whereas, enantiomers are optically active having chiral centres which are non-superimposable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




