
How many metamers are possible for a molecule formula ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{11}}N$ ?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Metamerism occurs among the members of the same homologous family. Sometimes metamers are also called position isomers. The compound which exhibits metamerism having the same molecular weight but the difference in chemical properties.
Complete Solution:
The phenomenon of existence with the same molecular formula of two or more compounds but different properties is known as isomerism and which compounds exhibit this phenomenon is called isomers.
The following flow chart shows different types of isomerism.
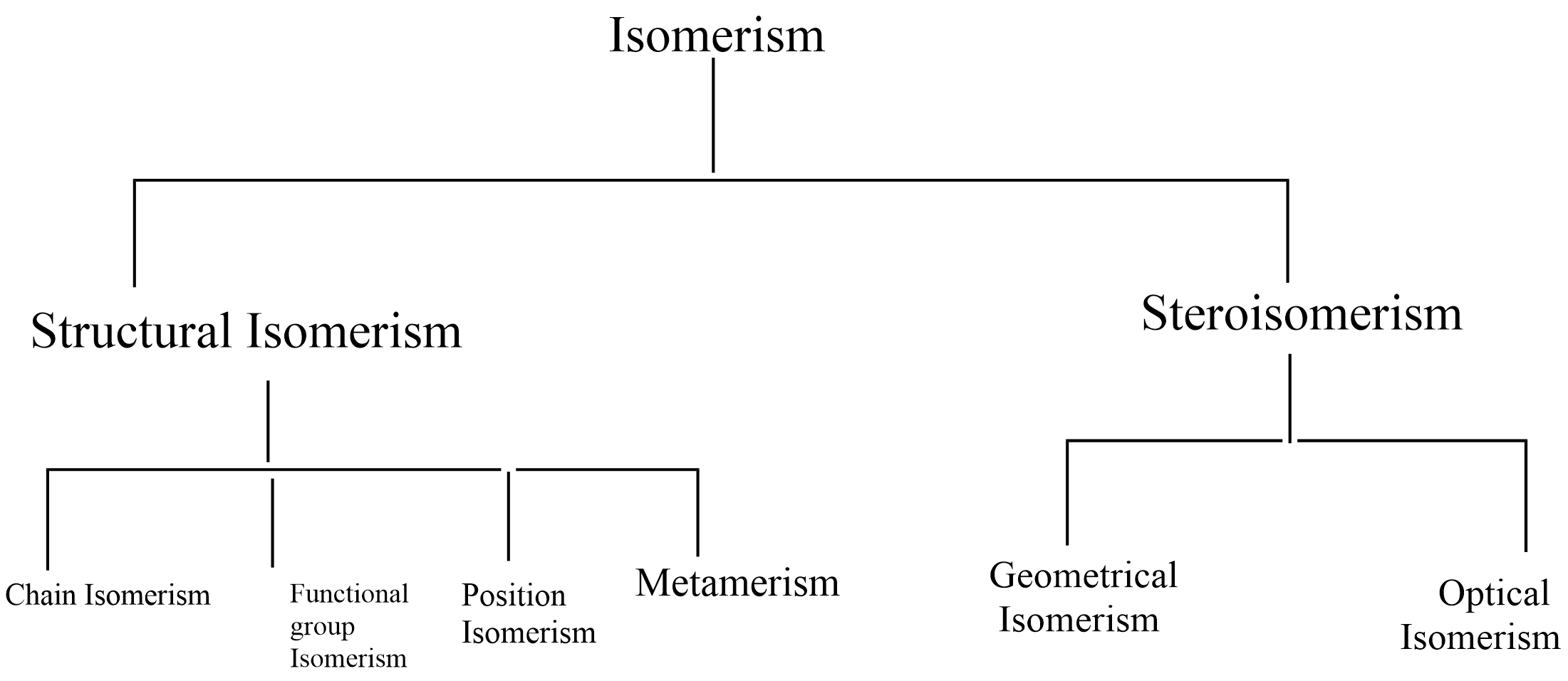
Structural isomerism: compounds with different structures with the same molecular formula are classified as structural isomers. Different types of structural isomers are,
(1) Chain isomerism
(2) Position isomerism
(3) Functional group isomerism
(4) Metamerism
Metamerism:
This isomerism observed in compounds having the same molecular formula but different alkyl chains on either side of the functional group of the molecule.
For example, diethyl ether and methyl propyl ethers, ethoxyethane and 1- methoxy propane, pentane-2-one and pentan-3-one represent a pair of metamers.
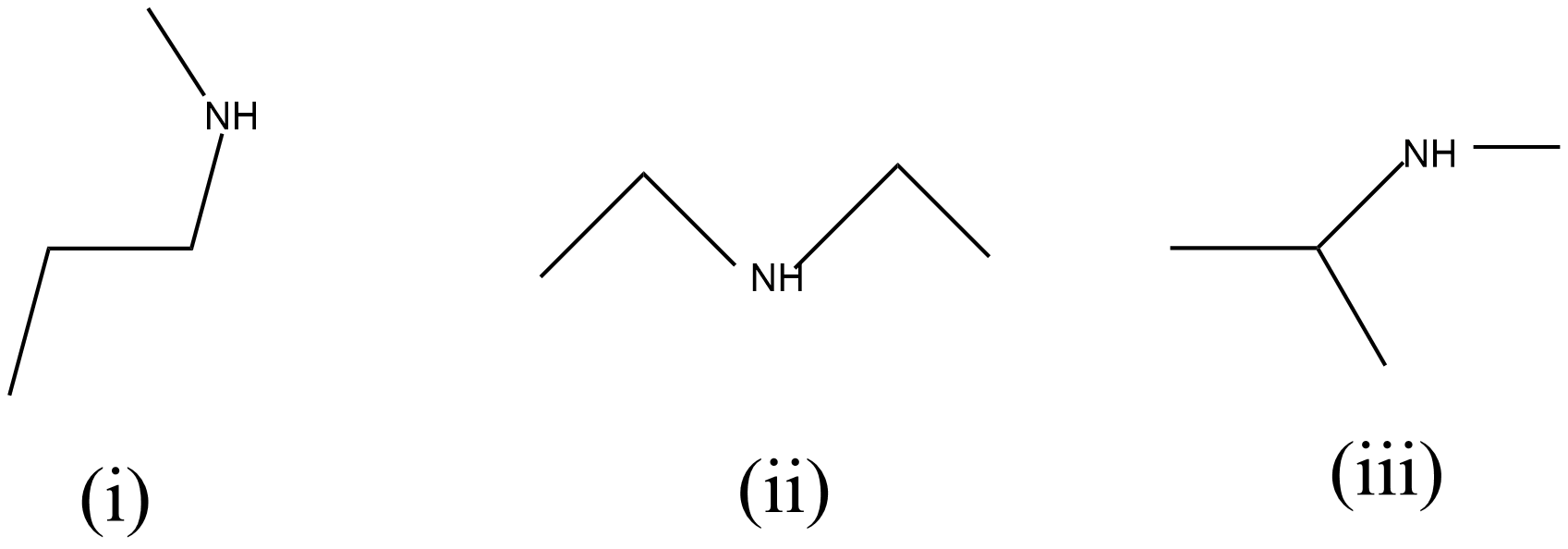
Given compound molecular structure is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{11}}N$, this same molecular formula with compound exhibits three metamers as shown below:
(i) N-methylpropan-1-amine
(ii) diethylamine
(iii) N-methyl propane-2-amine.
The three structure of the above metamers of the same molecular formula ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{11}}N$ as shown below respectively:
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Hydrocarbons show conformational isomerism by alkanes due to C - C rotation along with sigma bonds. Metamerism is a type of chain or position isomerism observed with same functional group and different alkyl groups attached to hetero atom.
Complete Solution:
The phenomenon of existence with the same molecular formula of two or more compounds but different properties is known as isomerism and which compounds exhibit this phenomenon is called isomers.
The following flow chart shows different types of isomerism.

Structural isomerism: compounds with different structures with the same molecular formula are classified as structural isomers. Different types of structural isomers are,
(1) Chain isomerism
(2) Position isomerism
(3) Functional group isomerism
(4) Metamerism
Metamerism:
This isomerism observed in compounds having the same molecular formula but different alkyl chains on either side of the functional group of the molecule.
For example, diethyl ether and methyl propyl ethers, ethoxyethane and 1- methoxy propane, pentane-2-one and pentan-3-one represent a pair of metamers.
Given compound molecular structure is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{11}}N$, this same molecular formula with compound exhibits three metamers as shown below:
(i) N-methylpropan-1-amine
(ii) diethylamine
(iii) N-methyl propane-2-amine.
The three structure of the above metamers of the same molecular formula ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{11}}N$ as shown below respectively:

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Hydrocarbons show conformational isomerism by alkanes due to C - C rotation along with sigma bonds. Metamerism is a type of chain or position isomerism observed with same functional group and different alkyl groups attached to hetero atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




