
Microtubules are constituents of
A) Centrosome, nucleosome, and centrioles
B) Cilia, flagella and peroxisomes
C) Spindle fibers, centrioles and cilia
D) Centrioles, spindle fibers and chromatin
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Microtubules are hollow cylinders with diameter approximately equal to 25nm and they vary in length from 200 nanometer to 25 micrometers. The lateral association between 12 and 17 protofilaments into a regular helical lattice is the reason behind the formation of them.
Complete answer:
Microtubules are the un-branched hollow submicroscopic tubules of protein tubulin and they develop on specific nucleating regions. It can undergo quick dissolution or growth at their ends by disassembly or assembly of monomers. Microtubules occur widely in eukaryotic cells except in Slime Moulds and Amoebae. They are present in cytoplasm as well as in the specialized structures like basal bodies, cilia or flagella, centrioles, spindle fibres, chromosome fibres, sensory hair, equatorial ring of thrombocytes etc. And they are responsible for the cell movement.
Spindle fibers form the protein structure which helps in meiosis and mitosis. The cell organelle called centrosome has two two cylindrical structures known as Centrioles. Flagella and Cilia are fine hair-like outgrowths of the membrane, but peroxisomes are the microbodies.
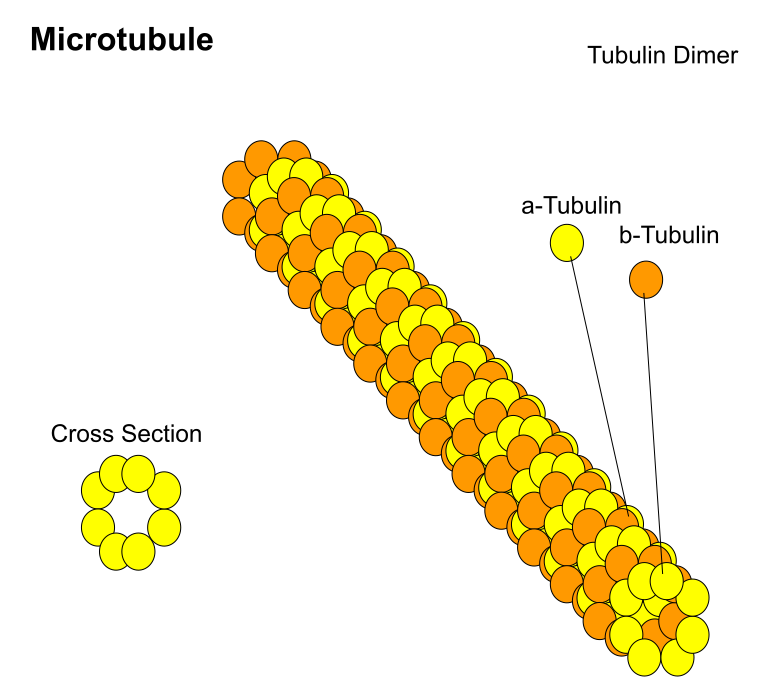
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: A microtubule may appear to be completely stable under steady state, however there is action taking place constantly. Populations of microtubules usually consist of some that are growing and some that are shrinking. A single microtubule can oscillate between shortening and growth phases. During its growth phase, heterodimers are added on to the end of a microtubule, and during the shrinkage phase they come off as intact subunits.
Complete answer:
Microtubules are the un-branched hollow submicroscopic tubules of protein tubulin and they develop on specific nucleating regions. It can undergo quick dissolution or growth at their ends by disassembly or assembly of monomers. Microtubules occur widely in eukaryotic cells except in Slime Moulds and Amoebae. They are present in cytoplasm as well as in the specialized structures like basal bodies, cilia or flagella, centrioles, spindle fibres, chromosome fibres, sensory hair, equatorial ring of thrombocytes etc. And they are responsible for the cell movement.
Spindle fibers form the protein structure which helps in meiosis and mitosis. The cell organelle called centrosome has two two cylindrical structures known as Centrioles. Flagella and Cilia are fine hair-like outgrowths of the membrane, but peroxisomes are the microbodies.

Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: A microtubule may appear to be completely stable under steady state, however there is action taking place constantly. Populations of microtubules usually consist of some that are growing and some that are shrinking. A single microtubule can oscillate between shortening and growth phases. During its growth phase, heterodimers are added on to the end of a microtubule, and during the shrinkage phase they come off as intact subunits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




