
Microvilli of the intestinal epithelium are similar in function with -
(a)Typhlosole of earthworm
(b)Hepatic caecum in cockroach
(c)Intestinal caecum in earthworm
(d)Malpighian tubules in cockroach
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The function of the microvilli is to aid in the absorption of nutrients in the small intestine efficiently. Their anatomy aids in maximum absorption of all nutrients from the digestive tract. Hence, we must find organs that carry out a similar system in the given organisms.
Complete answer:
- The microvilli of the intestine are small and finger-like projections present on the intestinal villus and are made of columnar epithelium.
- They increase the surface area of the intestinal walls hence increasing its surface area for absorption.
- Thousands of microvilli form a structure called the brush border that is present on the apical area of the epithelium intestines.
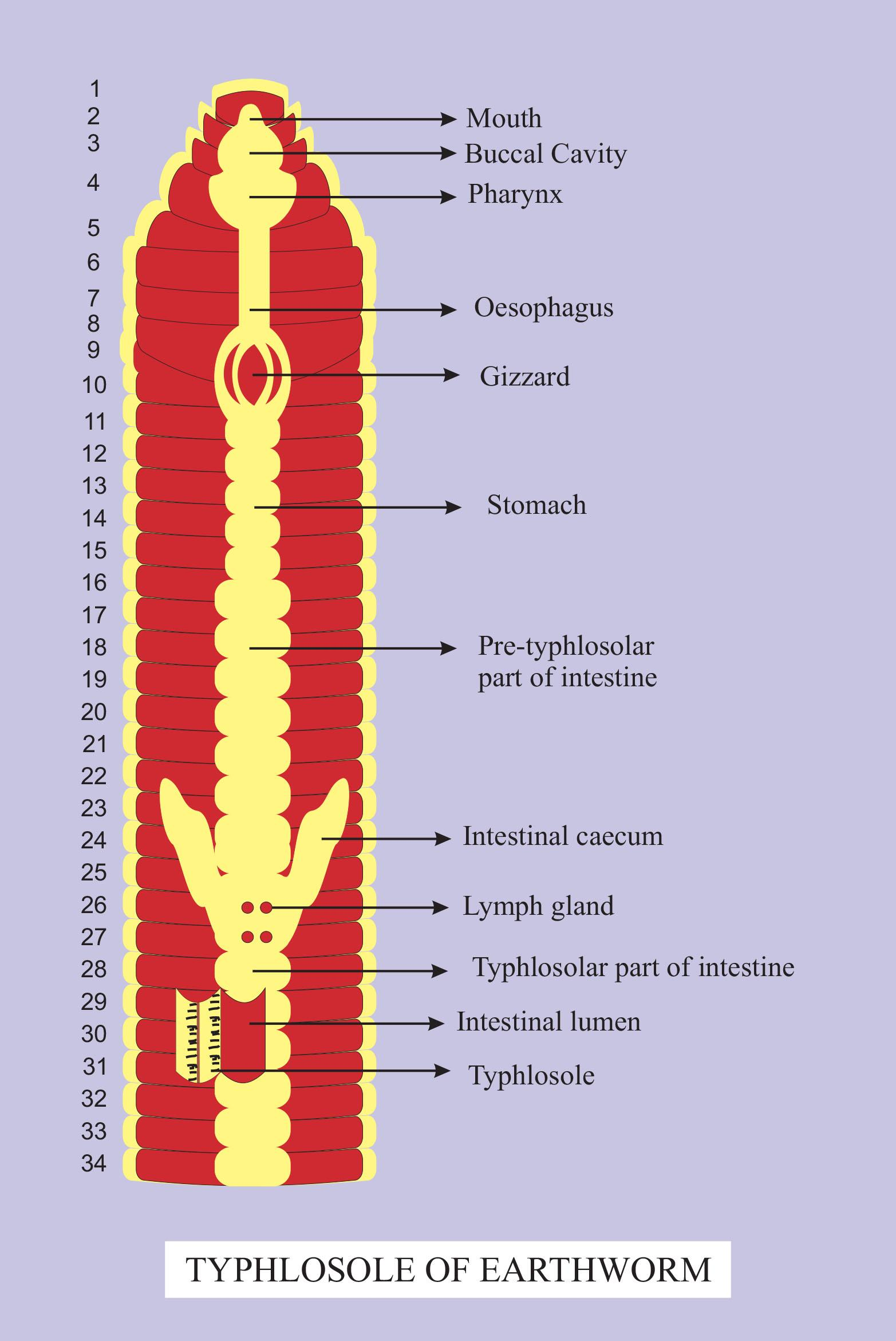
- In the digestive system of the earthworm is the intestine where instead of coiling, the mid-dorsal wall of the intestine forms a longitudinal, tongue-like fold which is known as typhlosole. The structure helps in making the absorption of nutrients more efficient.
Additional Information: - Microvilli of other tissues carry out processes such as absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion, and mechanotransduction.
- The difference between villi and microvilli is that villi are made of many cells and each cell has numerous microvilli.
- The hepatic caecum of the cockroach secretes digestive juices to help in digestion. Hence, they can be compared to the liver and the pancreas in humans.
- The intestinal caecum of the earthworm is present in the pre-typhlosolar region of the intestine. It specifically secretes amylase to digest carbohydrates.
- The Malpighian tubules in cockroach are the excretory units.
So, the correct answer is ‘typhlosole of earthworm’.
Note: - The increased surface area of the intestine aids in more effective diffusion of nutrients that pass through the villi and enter the blood vessels.
- In coeliac (celiac) disease and other inflammatory diseases of the intestines, the villi may flatten or entirely disappear.
- Microvilli are also present on the surface of white blood cells to aid in their movement.
Complete answer:
- The microvilli of the intestine are small and finger-like projections present on the intestinal villus and are made of columnar epithelium.
- They increase the surface area of the intestinal walls hence increasing its surface area for absorption.
- Thousands of microvilli form a structure called the brush border that is present on the apical area of the epithelium intestines.
- In the digestive system of the earthworm is the intestine where instead of coiling, the mid-dorsal wall of the intestine forms a longitudinal, tongue-like fold which is known as typhlosole. The structure helps in making the absorption of nutrients more efficient.
Additional Information: - Microvilli of other tissues carry out processes such as absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion, and mechanotransduction.
- The difference between villi and microvilli is that villi are made of many cells and each cell has numerous microvilli.
- The hepatic caecum of the cockroach secretes digestive juices to help in digestion. Hence, they can be compared to the liver and the pancreas in humans.
- The intestinal caecum of the earthworm is present in the pre-typhlosolar region of the intestine. It specifically secretes amylase to digest carbohydrates.
- The Malpighian tubules in cockroach are the excretory units.
So, the correct answer is ‘typhlosole of earthworm’.

Note: - The increased surface area of the intestine aids in more effective diffusion of nutrients that pass through the villi and enter the blood vessels.
- In coeliac (celiac) disease and other inflammatory diseases of the intestines, the villi may flatten or entirely disappear.
- Microvilli are also present on the surface of white blood cells to aid in their movement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




