
Middle lamella occurs
(a)Inner to the primary wall
(b)Inner to secondary wall
(c)Outer to secondary wall
(d)Outer to the primary wall
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The cellulose-containing layer laid down by cells that are dividing and developing is the main wall. Primary walls are thinner to allow for cell wall expansion during development. Secondary cell walls are responsible for much of the mechanical support of the plant as well as for the mechanical properties valued in wood.
Complete answer:
Calcium and magnesium pectates form the middle lamella. It's the outermost layer of the cell wall in a mature plant cell. In such instances, a compound middle lamella can be called the two neighbouring primary walls and the middle lamella, and maybe the first layer of each cell's secondary wall.
Two membranes, the middle lamella and the primary cell wall are present in all cell walls, and several cells create an additional layer, called the secondary wall. The middle lamella acts between the primary walls of neighbouring cells as a cementing sheet. The cellulose-containing layer laid down by cells that are dividing and developing is the main wall. Primary walls are thinner and less rigid than those of cells that have stopped growing, to allow for cell wall expansion during development. A fully grown plant cell may maintain (sometimes thicken) its primary cell wall or an additional, rigidizing layer of different composition may be deposited; this is the secondary wall. Some of the mechanical support of the plant as well as the mechanical properties valued in the wood are responsible for secondary cell walls. In comparison to the permanent stiffness and load-bearing capability of thick secondary walls, only when the vacuoles inside the cell are filled with water to the point that they exert a turgor pressure against the cell wall are the thin primary walls capable of serving a structural, supporting function. Turgor-induced primary wall stiffening is similar to air pressure stiffening of the sides of a pneumatic tyre. The loss of turgor pressure induces the wilting of flowers and leaves, resulting in the loss of water from the plant cells.
So, the correct answer is ‘outer to the primary wall’.
Note: The middle lamella is the portion of the cell wall between the cells that is the outermost layer. It is rich in pectin, which cements together the primary cell walls of neighbouring cells. It provides continuity and creates plasmodesmata between cells. It is also the first layer that, particularly from the cell plate that divides the two cells during cell division, is deposited at the time of cytokinesis. Calcium and magnesium pectates are located in the middle lamella.
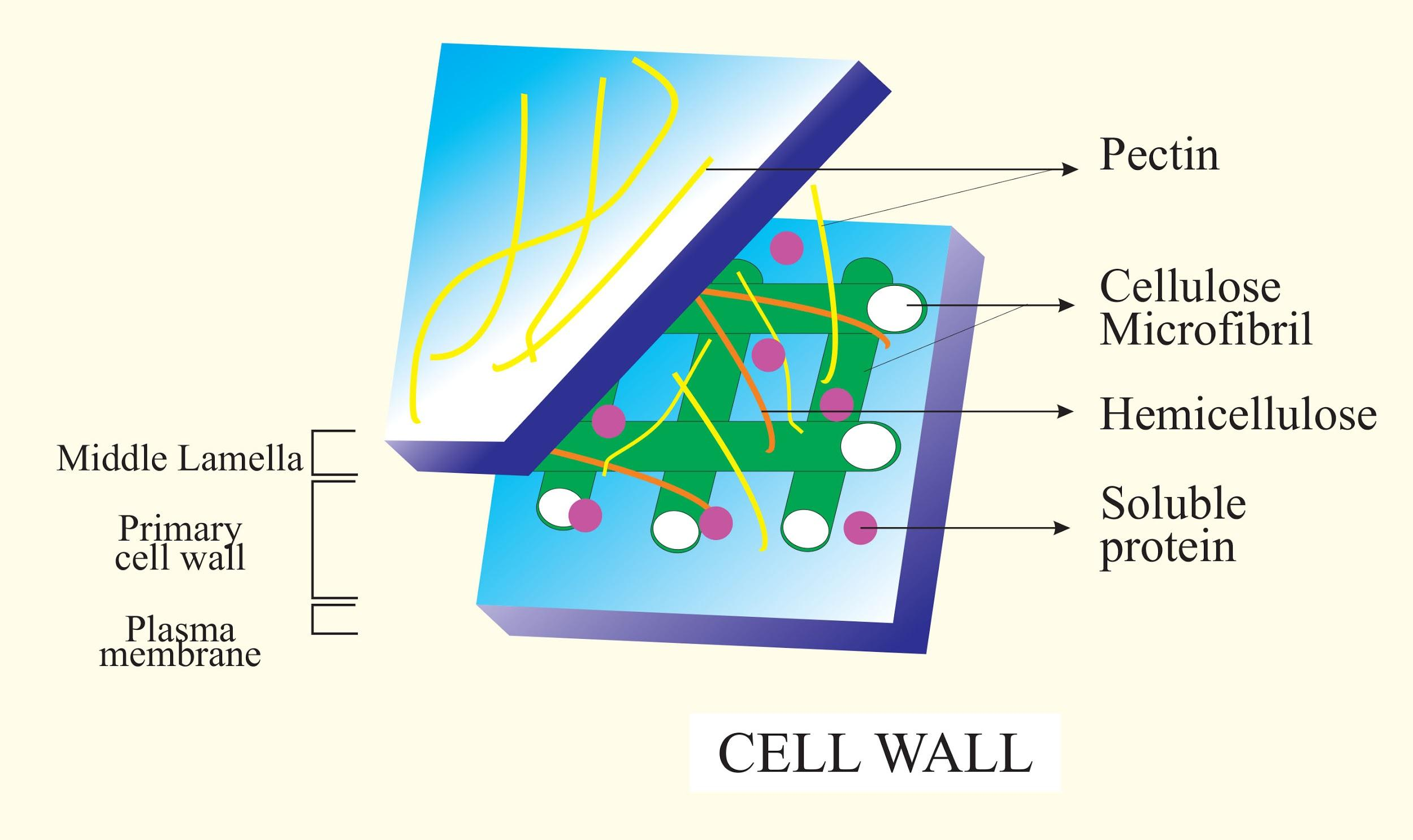
Complete answer:
Calcium and magnesium pectates form the middle lamella. It's the outermost layer of the cell wall in a mature plant cell. In such instances, a compound middle lamella can be called the two neighbouring primary walls and the middle lamella, and maybe the first layer of each cell's secondary wall.
Two membranes, the middle lamella and the primary cell wall are present in all cell walls, and several cells create an additional layer, called the secondary wall. The middle lamella acts between the primary walls of neighbouring cells as a cementing sheet. The cellulose-containing layer laid down by cells that are dividing and developing is the main wall. Primary walls are thinner and less rigid than those of cells that have stopped growing, to allow for cell wall expansion during development. A fully grown plant cell may maintain (sometimes thicken) its primary cell wall or an additional, rigidizing layer of different composition may be deposited; this is the secondary wall. Some of the mechanical support of the plant as well as the mechanical properties valued in the wood are responsible for secondary cell walls. In comparison to the permanent stiffness and load-bearing capability of thick secondary walls, only when the vacuoles inside the cell are filled with water to the point that they exert a turgor pressure against the cell wall are the thin primary walls capable of serving a structural, supporting function. Turgor-induced primary wall stiffening is similar to air pressure stiffening of the sides of a pneumatic tyre. The loss of turgor pressure induces the wilting of flowers and leaves, resulting in the loss of water from the plant cells.
So, the correct answer is ‘outer to the primary wall’.
Note: The middle lamella is the portion of the cell wall between the cells that is the outermost layer. It is rich in pectin, which cements together the primary cell walls of neighbouring cells. It provides continuity and creates plasmodesmata between cells. It is also the first layer that, particularly from the cell plate that divides the two cells during cell division, is deposited at the time of cytokinesis. Calcium and magnesium pectates are located in the middle lamella.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




