
Midrib is observed in which part of the leaf?
(a)Leaf base
(b)Lamina
(c)Petiole
(d)Stipule
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Throughout the leaf, a midrib provides support, holding it upright and durable in the wind. The green pigment that absorbs sunlight is chlorophyll. Water and glucose are transported through veins throughout the plant. The petiole affixes the leaf to the stem of the plant.
Complete answer:
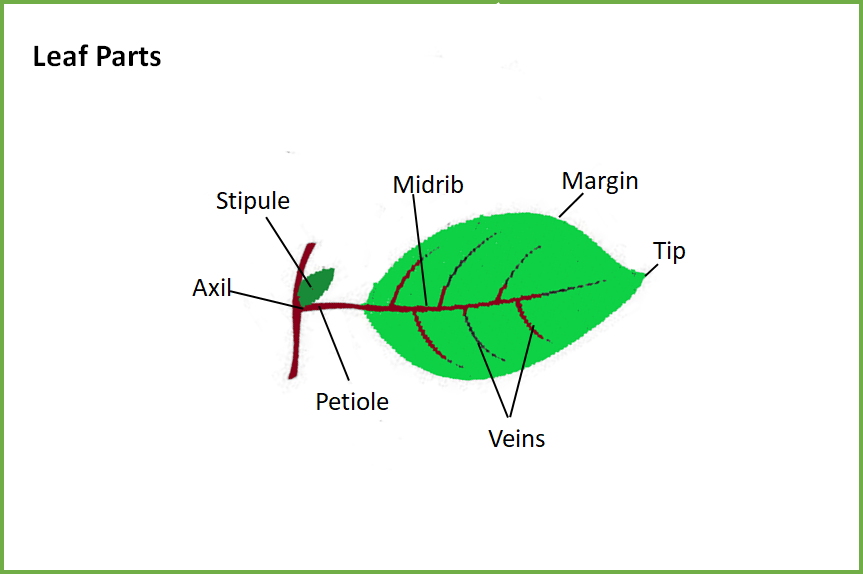
The leaf consists of the parts that follow—
1) The leaf blade (lamina) is also known as the epipodium, the wide and flat portion of the leaf where photosynthesis occurs.
The midrib is the central prominent vein on the lamina that contributes to the transport of water, minerals, and various leaf cells.
2) The lowermost section of the leaf is the leaf base and is also known as hypopodium.
3) The stalk-like portion of the leaf that links the leaf blade to the stem is the petiole.
A stipule is a tiny flap-like structure that develops and protects the developing petioles at the base of the petioles or falls off.
Additional Information: A general anatomical word meaning "plate" or "layer" is Lamina. It is used to describe structures in both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Such examples include The thyroid cartilage lamina: two leaf-like cartilage plates that make up the structure's walls.
A stalk that connects a leaf to the stem of the plant is the petiole. The leaf stalk (petiole) may be long, as in the celery and rhubarb leaves, short or entirely absent in the petiolate leaves, in which case the blade attaches directly to the stem and is said to be sessile.
A stipule is an outgrowth that is carried on either side of a leafstalk's foundation. A pair of stipules is known to be part of the leaf anatomy of a typical flowering plant, even though the stipules are inconspicuous or totally absent in many species.
The slightly enlarged area where the leaf sticks to the stem is the leaf foundation. When present, the paired stipules are located on either side of the base of the leaf and may resemble scales, spines, and glands.
So, the correct answer is ‘lamina’.
Note: The leaf blade, or lamina, is made up of a central tissue called the mesophyll, surrounded by the upper and lower epidermis on either side. Leaf vein patterns are often characteristic of plant taxa and may include one primary vein and different orders of smaller veins, the finest infiltrating veinlets.
Complete answer:
The leaf consists of the parts that follow—
1) The leaf blade (lamina) is also known as the epipodium, the wide and flat portion of the leaf where photosynthesis occurs.
The midrib is the central prominent vein on the lamina that contributes to the transport of water, minerals, and various leaf cells.
2) The lowermost section of the leaf is the leaf base and is also known as hypopodium.
3) The stalk-like portion of the leaf that links the leaf blade to the stem is the petiole.
A stipule is a tiny flap-like structure that develops and protects the developing petioles at the base of the petioles or falls off.
Additional Information: A general anatomical word meaning "plate" or "layer" is Lamina. It is used to describe structures in both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Such examples include The thyroid cartilage lamina: two leaf-like cartilage plates that make up the structure's walls.
A stalk that connects a leaf to the stem of the plant is the petiole. The leaf stalk (petiole) may be long, as in the celery and rhubarb leaves, short or entirely absent in the petiolate leaves, in which case the blade attaches directly to the stem and is said to be sessile.
A stipule is an outgrowth that is carried on either side of a leafstalk's foundation. A pair of stipules is known to be part of the leaf anatomy of a typical flowering plant, even though the stipules are inconspicuous or totally absent in many species.
The slightly enlarged area where the leaf sticks to the stem is the leaf foundation. When present, the paired stipules are located on either side of the base of the leaf and may resemble scales, spines, and glands.
So, the correct answer is ‘lamina’.
Note: The leaf blade, or lamina, is made up of a central tissue called the mesophyll, surrounded by the upper and lower epidermis on either side. Leaf vein patterns are often characteristic of plant taxa and may include one primary vein and different orders of smaller veins, the finest infiltrating veinlets.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




