
Milky water in green coconut is
(a)Liquid female gametophyte
(b)Liquid endosperm
(c)Liquid Nucleus
(d)Liquid Chalaza
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Coconut is a drupe fruit. The milky water present inside the green coconut is responsible for providing nutrition to the developing embryo and is triploid in nature. It is formed due to triple fusion.
Complete answer:
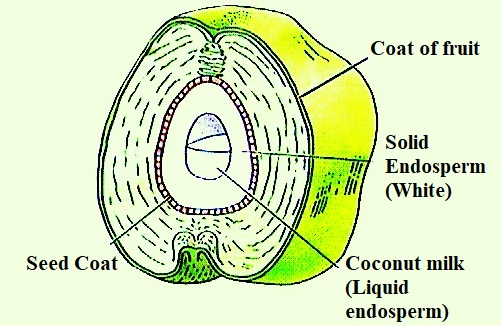
The endosperm is produced inside the seeds after fertilization in almost all flowering plants.
Its main function is to provide nourishment and support to the developing embryo supplying nutrients and protecting it.
The endosperm surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of carbohydrate (starch).
During the early development of liquid endosperm in coconut fruits, the nuclei divide before cytokinesis resulting in the free nuclear endosperm or the liquid endosperm of the coconut. The karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis.
Additional Information:
In angiosperms, the endosperm is of three types
Nuclear type-
It is the most common type of endosperm formed by the free nuclear division of the primary endosperm nucleus. It is found in coconut.
Cellular type-
In this type of endosperm, the division of the primary endosperm nucleus is followed by wall formation. Example-Datura.
Helobial type-
It is the intermediate of cellular and nuclear type of endosperm, in which the primary endosperm nucleus divides unequally into two parts, one half of the endosperm develops in the cellular pattern while the other half develops in the nuclear pattern. It is found in monocotyledons.
So, the correct answer is, “Liquid Endosperm.”
Note: On maturation of the coconut, the liquid endosperm will be fully consumed by the embryo during development. Coconut water is highly used as a nutritional drink as it is rich in carbohydrates such as potassium sodium and magnesium. Because of this, it is used as an electrolyte to treat and prevent dehydration.
Complete answer:
The endosperm is produced inside the seeds after fertilization in almost all flowering plants.
Its main function is to provide nourishment and support to the developing embryo supplying nutrients and protecting it.
The endosperm surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of carbohydrate (starch).
During the early development of liquid endosperm in coconut fruits, the nuclei divide before cytokinesis resulting in the free nuclear endosperm or the liquid endosperm of the coconut. The karyokinesis is not followed by cytokinesis.
Additional Information:

In angiosperms, the endosperm is of three types
Nuclear type-
It is the most common type of endosperm formed by the free nuclear division of the primary endosperm nucleus. It is found in coconut.
Cellular type-
In this type of endosperm, the division of the primary endosperm nucleus is followed by wall formation. Example-Datura.
Helobial type-
It is the intermediate of cellular and nuclear type of endosperm, in which the primary endosperm nucleus divides unequally into two parts, one half of the endosperm develops in the cellular pattern while the other half develops in the nuclear pattern. It is found in monocotyledons.
So, the correct answer is, “Liquid Endosperm.”
Note: On maturation of the coconut, the liquid endosperm will be fully consumed by the embryo during development. Coconut water is highly used as a nutritional drink as it is rich in carbohydrates such as potassium sodium and magnesium. Because of this, it is used as an electrolyte to treat and prevent dehydration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




