
Mitochondria is present in which of the following organisms?
(a)Aerobic organism only
(b)Obligate anaerobic organism
(c)Aerobic and obligate anaerobic organism
(d)Angiosperm only
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Mitochondria is the organelle in which the Krebs cycle and ETS reactions of the cellular respiration take place. A structure analogous to mitochondria is seen in prokaryotic organisms known as the mesosome which is the extension of the cell membrane into the cytoplasm.
Complete answer:
Mitochondria is present in the aerobic organisms only as the aerobic part of the cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria. ATP is formed by the reactions of the Krebs cycle in the mitochondrial matrix and Electron Transport System (ETS) in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. ETS builds an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane which store potential energy in them. When a proton flows out of this inner membrane, energy is released which is trapped by the ATP synthetase complex to produce ATP. This process only takes place in aerobic organisms.
Additional Information:
Let us know more about the cell organelle mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion).
-Mitochondria is not easily seen in the microscope unless stained by special stains like Janus green.
-The number of mitochondria in a cell depends upon the physiological activity it has to perform.
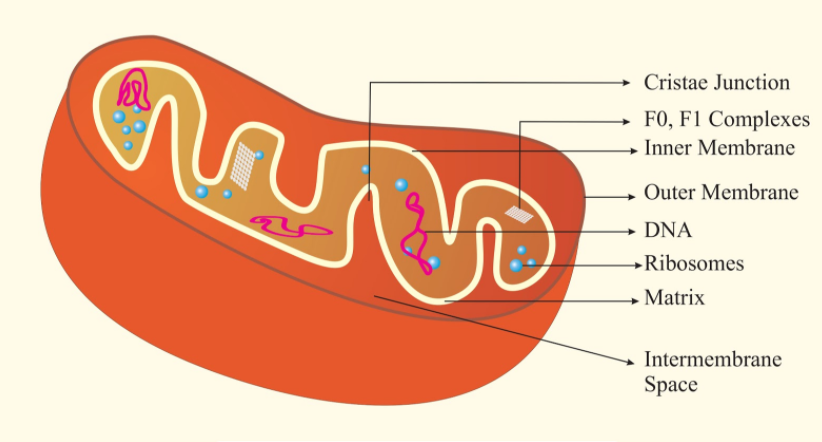
-The mitochondrion is made up of a double membrane structure known as the outer membrane and inner membrane.
-These membranes divide the mitochondria into an outer compartment and an inner compartment.
-The inner compartment is filled with a dense homogeneous substance known as the matrix whereas the outer compartment has infoldings towards the matrix known as the cristae.
-Different types of enzymes are present on each of the membranes according to the functions they need to perform.
So, the correct option is ‘Aerobic organism only’.
Note: -Mitochondria and chloroplasts are semiautonomous organelles which means they have their own DNA and protein synthesis machinery but are dependent on the nucleus for some functions.
-Mitochondria and chloroplasts are known as endosymbionts which means that they are prokaryotic bacteria that started living inside the eukaryotic cells as symbionts.
-A structure analogous to mitochondria is seen in prokaryotes known as mesosomes.
Complete answer:
Mitochondria is present in the aerobic organisms only as the aerobic part of the cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria. ATP is formed by the reactions of the Krebs cycle in the mitochondrial matrix and Electron Transport System (ETS) in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. ETS builds an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane which store potential energy in them. When a proton flows out of this inner membrane, energy is released which is trapped by the ATP synthetase complex to produce ATP. This process only takes place in aerobic organisms.
Additional Information:
Let us know more about the cell organelle mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion).
-Mitochondria is not easily seen in the microscope unless stained by special stains like Janus green.
-The number of mitochondria in a cell depends upon the physiological activity it has to perform.
-The mitochondrion is made up of a double membrane structure known as the outer membrane and inner membrane.
-These membranes divide the mitochondria into an outer compartment and an inner compartment.
-The inner compartment is filled with a dense homogeneous substance known as the matrix whereas the outer compartment has infoldings towards the matrix known as the cristae.
-Different types of enzymes are present on each of the membranes according to the functions they need to perform.
So, the correct option is ‘Aerobic organism only’.

Note: -Mitochondria and chloroplasts are semiautonomous organelles which means they have their own DNA and protein synthesis machinery but are dependent on the nucleus for some functions.
-Mitochondria and chloroplasts are known as endosymbionts which means that they are prokaryotic bacteria that started living inside the eukaryotic cells as symbionts.
-A structure analogous to mitochondria is seen in prokaryotes known as mesosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




