
What is the molecular orbital diagram for $ C_{2}^{-} $ ?
Answer
530.7k+ views
Hint :We know that $ {{C}_{2}} $ is a component of vapours of carbon. According to a research paper, carbon vapours contain around $ 28% $ but this depends on the temperature and pressure. The electrons are distributed among the atomic orbitals according to Aufbau’s principle. This produces unique quantum states, with corresponding energy levels.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The quantum state which has the lowest energy level is known as the ground state. The ground state is a singlet state. There are several excited singlet and triplet states that are relatively similar energy to the ground state. Molecular orbital theory shows that it has two sets of paired electrons in a degenerate bonding set of orbitals. This gives a bond order of two, which means that there should exist a double bond between the two carbons in a $ {{C}_{2}} $ .
As you know, a neutral carbon atom has a total of six electrons. This, of course, implies that a $ {{C}_{2~}} $ molecule has a total of $ 2\times 6{{e}^{-}}=12{{e}^{-}} $
Thus follows that the $ C_{2~}^{-} $ species will have; $ 12{{e}^{-}}+1{{e}^{-}}=13{{e}^{-}} $
It will be added to lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital/lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, LUMO, that follows that the highest energy occupied molecular orbital/highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO. The diagram below shows the two $ 2p\pi $ orbitals, let's say $ 2p\pi x $ and $ 2p\pi y $ , are the highest energy occupied molecular orbitals. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is $ 2p\sigma $ , so that is where extra electrons will be added.
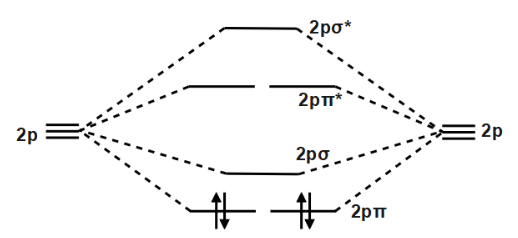
Also, an unpaired electron will make the $ C_{2}^{-} $ ion paramagnetic, i.e. it is attracted by an externally applied magnetic field. On the other hand, the neutral $ {{C}_{2}} $ molecule has no unpaired electrons, so it is diamagnetic, i.e. it is not attracted by an externally applied magnetic field.
Note :
The various quantum states of dicarbon form significant proportions of dicarbon under ambient conditions. The problem provides you with a MO diagram for the $ {{C}_{2~}} $ molecule, so all we really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. We need to add an electron and not remove one because of overall negative charge that exists on molecule
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The quantum state which has the lowest energy level is known as the ground state. The ground state is a singlet state. There are several excited singlet and triplet states that are relatively similar energy to the ground state. Molecular orbital theory shows that it has two sets of paired electrons in a degenerate bonding set of orbitals. This gives a bond order of two, which means that there should exist a double bond between the two carbons in a $ {{C}_{2}} $ .
As you know, a neutral carbon atom has a total of six electrons. This, of course, implies that a $ {{C}_{2~}} $ molecule has a total of $ 2\times 6{{e}^{-}}=12{{e}^{-}} $
Thus follows that the $ C_{2~}^{-} $ species will have; $ 12{{e}^{-}}+1{{e}^{-}}=13{{e}^{-}} $
It will be added to lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital/lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, LUMO, that follows that the highest energy occupied molecular orbital/highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO. The diagram below shows the two $ 2p\pi $ orbitals, let's say $ 2p\pi x $ and $ 2p\pi y $ , are the highest energy occupied molecular orbitals. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is $ 2p\sigma $ , so that is where extra electrons will be added.

Also, an unpaired electron will make the $ C_{2}^{-} $ ion paramagnetic, i.e. it is attracted by an externally applied magnetic field. On the other hand, the neutral $ {{C}_{2}} $ molecule has no unpaired electrons, so it is diamagnetic, i.e. it is not attracted by an externally applied magnetic field.

Note :
The various quantum states of dicarbon form significant proportions of dicarbon under ambient conditions. The problem provides you with a MO diagram for the $ {{C}_{2~}} $ molecule, so all we really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. We need to add an electron and not remove one because of overall negative charge that exists on molecule
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




