
Molecule having a non zero dipole moment?
a) $ S{F_4} $
b) $ Si{F_4} $
c) $ Xe{F_4} $
d) $ B{F_3}^{} $
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: The dipole moment is the product of negative or positive charge and the distance between the centers of positive and negative charges. The dipole moment is directly towards the more electronegative atom in the compound. The opposite direction of the dipole moment in the molecule cancels each other.
Complete answer:
Let us see all the options.
The structure of $ Si{F_4} $ is :
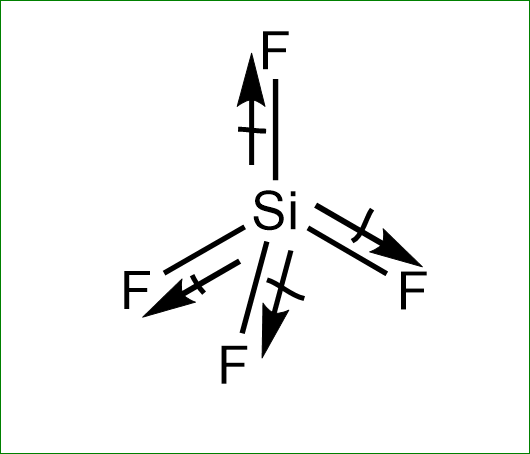
The fluorine is more electronegative than the silicon atom. hence, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other three fluorine. Hence it has zero dipole moment.
ii) $ Xe{F_4} $
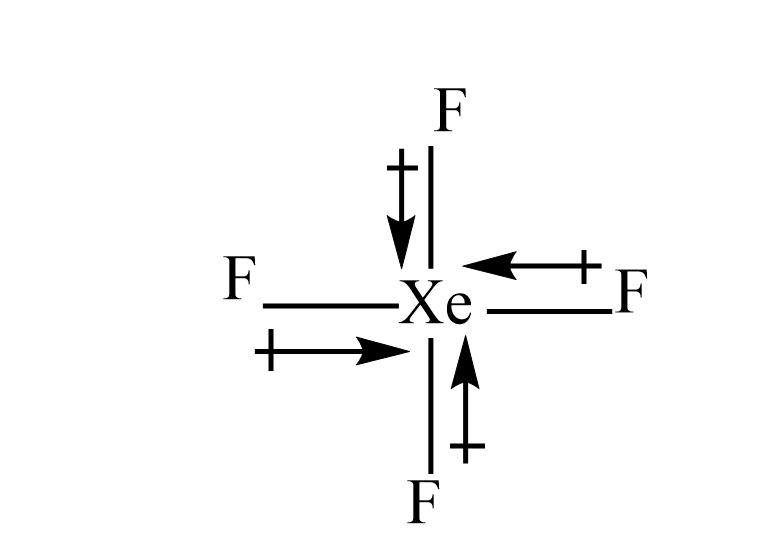
The fluorine is more electronegative than the xenon atom. hence, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since, the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other three fluorine. Hence even this will have zero dipole moment.
iii) $ S{F_4} $
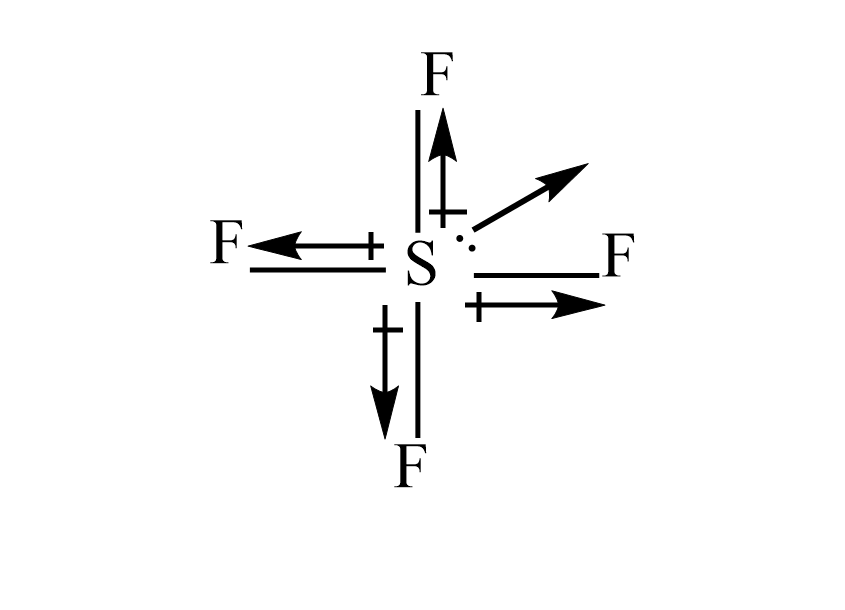
The fluorine is more electronegative than the sulphur atom. so, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other fluorine, and the lone pair does not get cancelled out. Hence it has a non zero dipole moment.
iv) $ B{F_3}^{} $
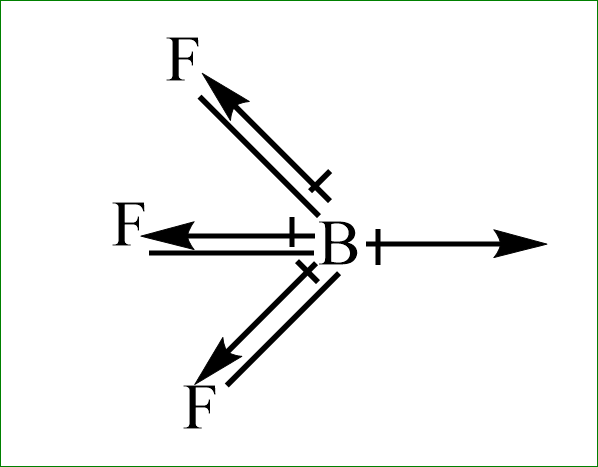
Even here, the fluorine is more electronegative than the boron atom. the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since, the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other two fluorine. Hence this will have zero dipole moment.
Note:
The dipole moment is the product of the positive or negative charge and the distance between centers of the positive and negative charges. It is denoted by the dipole moment directed towards the more electronegative atom.
Complete answer:
Let us see all the options.
The structure of $ Si{F_4} $ is :

The fluorine is more electronegative than the silicon atom. hence, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other three fluorine. Hence it has zero dipole moment.
ii) $ Xe{F_4} $

The fluorine is more electronegative than the xenon atom. hence, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since, the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other three fluorine. Hence even this will have zero dipole moment.
iii) $ S{F_4} $

The fluorine is more electronegative than the sulphur atom. so, the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other fluorine, and the lone pair does not get cancelled out. Hence it has a non zero dipole moment.
iv) $ B{F_3}^{} $

Even here, the fluorine is more electronegative than the boron atom. the dipole moment will direct towards the fluorine atom. Since, the dipole moment of one fluorine atom is cancelled by resultant dipole moments of the other two fluorine. Hence this will have zero dipole moment.
Note:
The dipole moment is the product of the positive or negative charge and the distance between centers of the positive and negative charges. It is denoted by the dipole moment directed towards the more electronegative atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




