
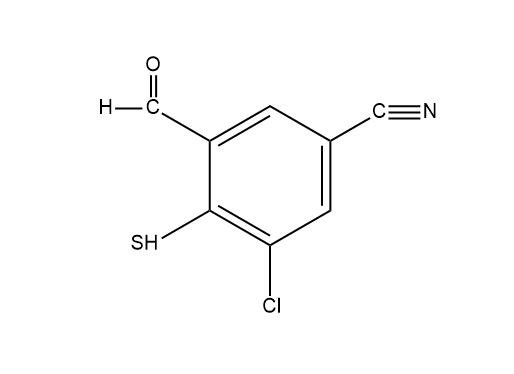
How many moles of Grignard react with the following compound?
\[
A.\;\;\;\;\;2 \\
B.\;\;\;\;\;3 \\
C.\;\;\;\;\;4 \\
D.\;\;\;\;\;5 \\
\]

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: Grignard reagent is an organomagnesium compound having a chemical formula \[R - Mg - X\](where R is an alkyl or aryl group and X is a halogen). Different groups react differently with Grignard’s reagent. For reaction, only the functional group are going to react so the other groups for one particular reaction can be taken as R.
Complete answer:
The question says to find out the total number mole of Grignard reacting with the following compound. This means we have to individually find out how many moles of Grignard will be required for one group to react and then adding the individual moles will give us the total moles.
For this question, you should know how Grignard will react with different types of groups.
We have three different groups here which are \[CN,{\text{ }}HS,{\text{ }}CHO\], so there will be three different reactions taking place. So let us see the reaction below along with the moles Grignard used.
(For every reaction we will only consider the main group which will react and the entire left out part will be written as R)
Our first reaction is with cyanide:
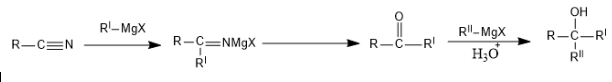
$2$ Moles of Grignard are used.
Next reaction is with aldehyde group:
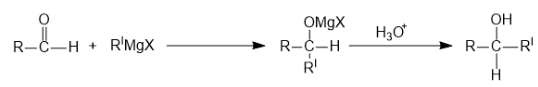
$1$ Mole of Grignard is used.
And the final reaction is with \[HS\]

$1$ Mole of Grignard is used.
Now just add up all the moles $2 + 1 + 1 = 4$. And we see that in total $4$ moles of Grignard is used.
Therefore the correct option is \[C.{\text{ }}4\]
Note:
In some questions, there might be more than $3$ or $4$ groups, all of those questions are to be done in the same manner. Grignard reagent does not react with a single halogen attached to benzene. The Grignard reagent is important for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
Complete answer:
The question says to find out the total number mole of Grignard reacting with the following compound. This means we have to individually find out how many moles of Grignard will be required for one group to react and then adding the individual moles will give us the total moles.
For this question, you should know how Grignard will react with different types of groups.
We have three different groups here which are \[CN,{\text{ }}HS,{\text{ }}CHO\], so there will be three different reactions taking place. So let us see the reaction below along with the moles Grignard used.
(For every reaction we will only consider the main group which will react and the entire left out part will be written as R)
Our first reaction is with cyanide:

$2$ Moles of Grignard are used.
Next reaction is with aldehyde group:

$1$ Mole of Grignard is used.
And the final reaction is with \[HS\]

$1$ Mole of Grignard is used.
Now just add up all the moles $2 + 1 + 1 = 4$. And we see that in total $4$ moles of Grignard is used.
Therefore the correct option is \[C.{\text{ }}4\]
Note:
In some questions, there might be more than $3$ or $4$ groups, all of those questions are to be done in the same manner. Grignard reagent does not react with a single halogen attached to benzene. The Grignard reagent is important for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




