
What is the moment of inertia of a triangular plate $ABC$ of mass $M$ and side $BC = 'a'$ about an axis passing through $A$ and perpendicular to the plane of paper?
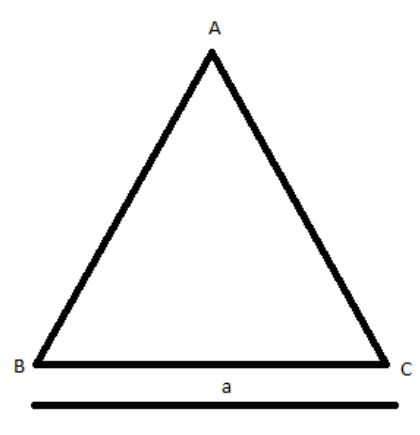
A. $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{6}$
B. $\dfrac{{3M{a^2}}}{4}$
C. $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{24}}$
D. $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{{12}}$

Answer
477k+ views
Hint:To simplify the question, imagine the triangle to be a part of a square. As the triangle has two angles of ${45^0}$ then by the property of the sum of angles, the third angle would be ${90^o}$. When the diagonals are drawn in a square, it is divided into $4$ right-angled triangles as the diagonals bisect each other at ${90^o}$.
Complete step by step answer:
When a force is applied to a rigid body, it tends to resist any change in its translational and rotational state. The measure of the tendency to oppose any change in the translational state when a force is applied is called mass. When the body opposes any change in the rotational state (i.e. angular acceleration) on the application of force, then it is known as moment of inertia.
The formula for the moment of inertia can be as the sum of the product of all the masses and the square of perpendicular distance from the axis of all the particles. The moment of inertia depends on the amount of matter in a body as well as its distribution.
$I = \sum\limits_i {{m_i}} {r_i}^2$
Where $I = $ Moment of inertia, ${m_i} = $ mass of ${i^{th}}$ particle and $r = $ perpendicular distance is taken from the axis to the ${i^{th}}$ particle having mass ${m_i}$.
To calculate the moment of inertia about any axis, the following two theorems on the moment of inertia is used:
- Theorem of Parallel Axes
- Theorem of Perpendicular Axes
According to the question, we assumed the triangle is a part of a square as shown in the figure:
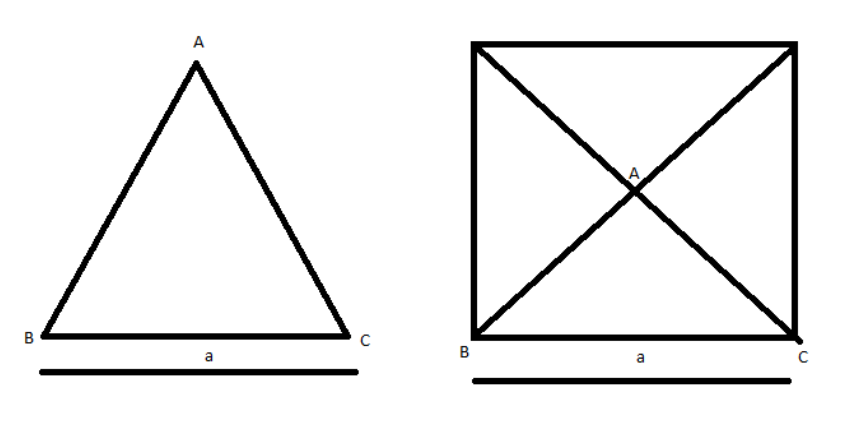
The axis is passing through the point $A$. This implies that for a square it is passing through its centre and is perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Moment of Inertia of the square for the axis passing through its centre is given by:
${I_{Square}} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{6}$
Where $m = $ The mass of square and $l = $ sides of square.
The square is made up of four triangles, each triangle having mass $M$ and one side $a$ . So, the mass of the square, $m = 4M$ and side $l = a$ .
${I_{Square}} = \dfrac{{4M{a^2}}}{6}$
So, the moment of inertia of one triangle will be:
${I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times {I_{Square}}\,\,\, \\
\Rightarrow {I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times \dfrac{{4M{a^2}}}{6} \\
\Rightarrow {I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{6} $
So, the moment of inertia of the triangle is $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{6}$.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:While solving the question, the axis plays a very important role. If the axis gets changed then the whole solution will be different. There are a few standard moments of inertia like the moment of inertia of a ring, circular plate etc. which helps in solving the moment of inertia of complicated figures. Simple geometrical assumptions can simplify the question.
Complete step by step answer:
When a force is applied to a rigid body, it tends to resist any change in its translational and rotational state. The measure of the tendency to oppose any change in the translational state when a force is applied is called mass. When the body opposes any change in the rotational state (i.e. angular acceleration) on the application of force, then it is known as moment of inertia.
The formula for the moment of inertia can be as the sum of the product of all the masses and the square of perpendicular distance from the axis of all the particles. The moment of inertia depends on the amount of matter in a body as well as its distribution.
$I = \sum\limits_i {{m_i}} {r_i}^2$
Where $I = $ Moment of inertia, ${m_i} = $ mass of ${i^{th}}$ particle and $r = $ perpendicular distance is taken from the axis to the ${i^{th}}$ particle having mass ${m_i}$.
To calculate the moment of inertia about any axis, the following two theorems on the moment of inertia is used:
- Theorem of Parallel Axes
- Theorem of Perpendicular Axes
According to the question, we assumed the triangle is a part of a square as shown in the figure:

The axis is passing through the point $A$. This implies that for a square it is passing through its centre and is perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Moment of Inertia of the square for the axis passing through its centre is given by:
${I_{Square}} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{6}$
Where $m = $ The mass of square and $l = $ sides of square.
The square is made up of four triangles, each triangle having mass $M$ and one side $a$ . So, the mass of the square, $m = 4M$ and side $l = a$ .
${I_{Square}} = \dfrac{{4M{a^2}}}{6}$
So, the moment of inertia of one triangle will be:
${I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times {I_{Square}}\,\,\, \\
\Rightarrow {I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times \dfrac{{4M{a^2}}}{6} \\
\Rightarrow {I_{Triangle}} = \dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{6} $
So, the moment of inertia of the triangle is $\dfrac{{M{a^2}}}{6}$.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:While solving the question, the axis plays a very important role. If the axis gets changed then the whole solution will be different. There are a few standard moments of inertia like the moment of inertia of a ring, circular plate etc. which helps in solving the moment of inertia of complicated figures. Simple geometrical assumptions can simplify the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




