
Moss plant is a
a) Gametophyte
b) Sporophyte
c) gametophyte and sporophyte
d)Predominantly gametophyte with sporophyte attached to it.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Moss belongs to the non-vascular plants. They are the land plants and are adapted to live on land. They have a thin cuticle layer present on them which helps them against the water loss. It has rhizoids present as the root structure.
Complete answer:
The mosses undergo alternation of generation. In the gametophyte stage of the moss, the leafy shoot takes part. The shoots formed in the moss are of a female, which develops the archegonia at their tip and leads to the formation of the archegonium. The other shoot formed is of the male which develops the antheridia and leads to the formation of the motile sperm formed in each archegonium. The male sperm is transported to the female for fertilization which leads to starting off the sporophyte stage in the moss. The zygote formed from the development of the fertilization leads to produce an embryo that grows and matures into a sporophyte. It consists of foot and stalk. The foot of the sporophyte absorbs the nutrients from the parent and the stalk forms the sporangium. The sporangium is filled with the spore mother cells. It is covered by the calyptra which is the layer of the gametophyte stage of the archegonium. Each SMC undergoes meiosis to produce the haploid spores which would start the gametophyte stage. The tiny spores are dispersed by the wind and when they reach a suitable habitat, they germinate to form protonema. The gametophytic generation is responsible for sexual reproduction and the sporophyte generation is responsible for the dispersal.
So, the answer is ‘gametophyte and sporophyte’.
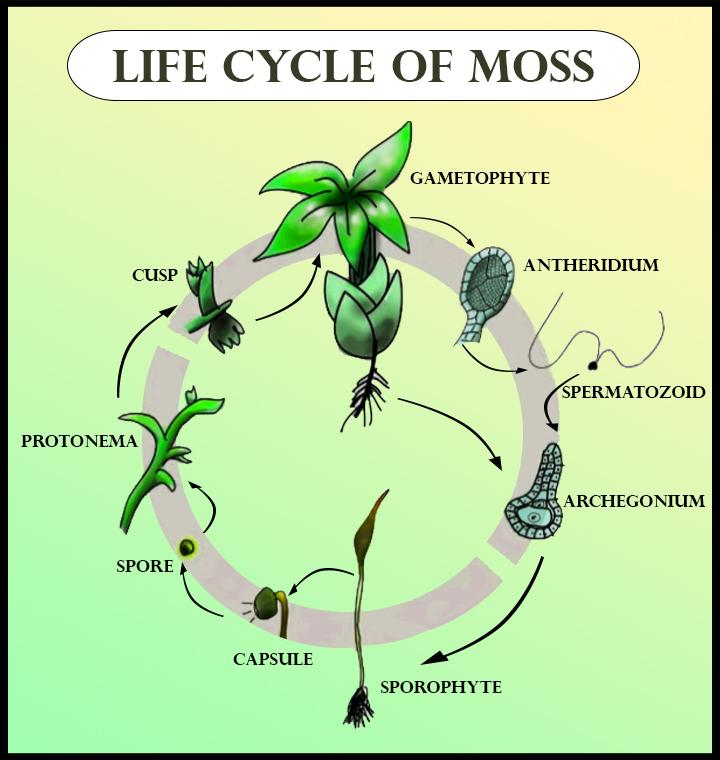
Note: The spores of the sporophyte stage of the moss plant gives rise to the gametes. The gametes then lead to the fertilization which gives rise to the spores and then starts the sporophyte stage. The dispersal of spores occurs through the water.
Complete answer:
The mosses undergo alternation of generation. In the gametophyte stage of the moss, the leafy shoot takes part. The shoots formed in the moss are of a female, which develops the archegonia at their tip and leads to the formation of the archegonium. The other shoot formed is of the male which develops the antheridia and leads to the formation of the motile sperm formed in each archegonium. The male sperm is transported to the female for fertilization which leads to starting off the sporophyte stage in the moss. The zygote formed from the development of the fertilization leads to produce an embryo that grows and matures into a sporophyte. It consists of foot and stalk. The foot of the sporophyte absorbs the nutrients from the parent and the stalk forms the sporangium. The sporangium is filled with the spore mother cells. It is covered by the calyptra which is the layer of the gametophyte stage of the archegonium. Each SMC undergoes meiosis to produce the haploid spores which would start the gametophyte stage. The tiny spores are dispersed by the wind and when they reach a suitable habitat, they germinate to form protonema. The gametophytic generation is responsible for sexual reproduction and the sporophyte generation is responsible for the dispersal.
So, the answer is ‘gametophyte and sporophyte’.

Note: The spores of the sporophyte stage of the moss plant gives rise to the gametes. The gametes then lead to the fertilization which gives rise to the spores and then starts the sporophyte stage. The dispersal of spores occurs through the water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




