
Myopia is corrected by
(a)Cylindrical lens
(b)Bifocal lens
(c)Biconvex lens
(d)Biconcave lens
(e)Plain glass
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Myopia is also known as nearsightedness. This is because, in this disorder, the person can only see things that are kept near to him. Objects that are at infinity appear blurry or out of focus to a person with myopia.
Complete answer:
Myopia is caused when the lens of a person is too converging or if the diameter of the eyeball is too long. In the case of an over-converging lens, the rays that come from infinity are converged at a point before the retina thus not giving a sharp image. Similarly, in the case of a large eyeball, the image is formed in front of the retina. This defect can be correct by using a biconcave lens as it is a diverging lens which will diverge the rays enough to make them meet on the retina.
Additional Information: Now, let us learn about the other lenses mentioned in the options.
Cylindrical lens: This lens is used to cure astigmatism which occurs due to the improper shape of the cornea. The cylindrical lens refracts light into a line instead of a point thus correcting the disorder.
Bifocal lens: It is a lens made up of two lenses i.e. both concave and convex lens.
Biconvex lens: This lens is used to cure hypermetropia or farsightedness.
Plain glass: This is used in glasses as eye protection from dust etc.
So, the correct option is ‘Biconcave lens’.
Note: A bifocal lens is worn by old people who have a rigid eye lens that cannot focus on both near and far objects.
Hypermetropia is caused when the eye lens is not converging enough or the eyeball is too small.
Images formed on the retina are inverted which are then flipped back by our brain.
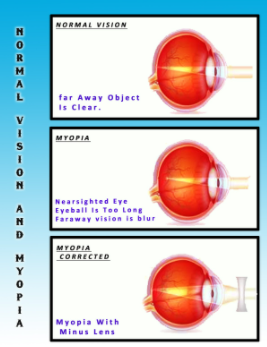
Complete answer:
Myopia is caused when the lens of a person is too converging or if the diameter of the eyeball is too long. In the case of an over-converging lens, the rays that come from infinity are converged at a point before the retina thus not giving a sharp image. Similarly, in the case of a large eyeball, the image is formed in front of the retina. This defect can be correct by using a biconcave lens as it is a diverging lens which will diverge the rays enough to make them meet on the retina.
Additional Information: Now, let us learn about the other lenses mentioned in the options.
Cylindrical lens: This lens is used to cure astigmatism which occurs due to the improper shape of the cornea. The cylindrical lens refracts light into a line instead of a point thus correcting the disorder.
Bifocal lens: It is a lens made up of two lenses i.e. both concave and convex lens.
Biconvex lens: This lens is used to cure hypermetropia or farsightedness.
Plain glass: This is used in glasses as eye protection from dust etc.
So, the correct option is ‘Biconcave lens’.
Note: A bifocal lens is worn by old people who have a rigid eye lens that cannot focus on both near and far objects.
Hypermetropia is caused when the eye lens is not converging enough or the eyeball is too small.
Images formed on the retina are inverted which are then flipped back by our brain.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




