
NADPH is produced in photosynthesis during
A) Dark reaction
B) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
C) Pseudocyclic photophosphorylation
D) Cyclic photophosphorylation
Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: NADPH is a cofactor which is used to donate electrons and hydrogen to reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. Typically, enzymes involved in anabolic pathways that result in large molecules use NADPH.
Complete Answer:
NADPH stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen. It is a product of the first stage of photosynthesis and is used to fuel reactions in the second stage of photosynthesis. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is infused into already existing organic carbon compounds, like ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, like glucose. The phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation.
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is a two-stage process involving two different chlorophyll photosystems. Initially, a water molecule is broken down into ${2}{H+ }+{1/2}{O}_{2}+{2}{e− }$ by a process called photolysis. Only the two electrons from the water molecule are kept in photosystem II. Then a photon is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments. The light excites the electrons of each pigment initiating a chain reaction which eventually transfers energy to the core of photosystem II. This excites the two electrons that were transferred to the primary electron acceptor, pheophytin. The deficit of electrons is compensated by taking electrons from another molecule of water. The highly excited electrons are transferred to the acceptor molecule, but this time are passed on to an enzyme called Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase which uses them to catalyse the reaction:
${NADP+ }+{2}{H+ }+{2}{e− }→ {NADPH}+{H+}$
Hence option B) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation, is the correct answer
Note:
Chloroplasts in plants also use NADPH as a part of the pathway to synthesize sugars from sunlight and carbon dioxide. As in other reactions, NADPH helps carry electrons and protons driven by sunlight into new carbon-carbon bonds leading to the creation of sugar molecules.
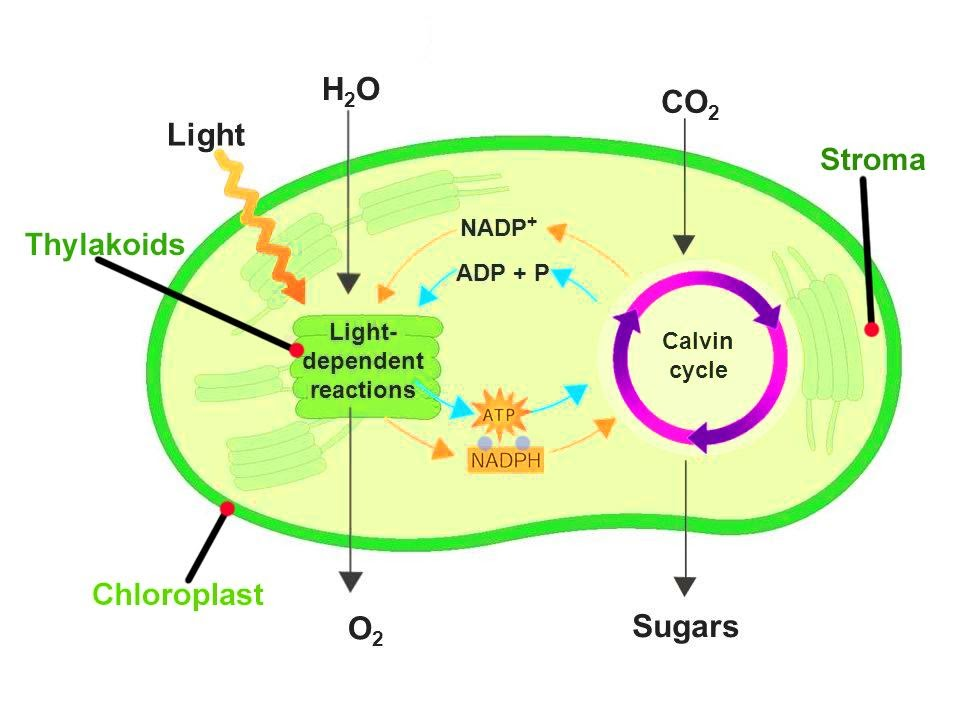
Figure: NADPH generation in photosynthesis
Complete Answer:
NADPH stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen. It is a product of the first stage of photosynthesis and is used to fuel reactions in the second stage of photosynthesis. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is infused into already existing organic carbon compounds, like ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, like glucose. The phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation.
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is a two-stage process involving two different chlorophyll photosystems. Initially, a water molecule is broken down into ${2}{H+ }+{1/2}{O}_{2}+{2}{e− }$ by a process called photolysis. Only the two electrons from the water molecule are kept in photosystem II. Then a photon is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments. The light excites the electrons of each pigment initiating a chain reaction which eventually transfers energy to the core of photosystem II. This excites the two electrons that were transferred to the primary electron acceptor, pheophytin. The deficit of electrons is compensated by taking electrons from another molecule of water. The highly excited electrons are transferred to the acceptor molecule, but this time are passed on to an enzyme called Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase which uses them to catalyse the reaction:
${NADP+ }+{2}{H+ }+{2}{e− }→ {NADPH}+{H+}$
Hence option B) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation, is the correct answer
Note:
Chloroplasts in plants also use NADPH as a part of the pathway to synthesize sugars from sunlight and carbon dioxide. As in other reactions, NADPH helps carry electrons and protons driven by sunlight into new carbon-carbon bonds leading to the creation of sugar molecules.

Figure: NADPH generation in photosynthesis
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




