
How do you name alkenes with alcohols?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint Alkenes are those species which possess double bonds between the carbon atoms. For alcohols a suffix –ol is given while naming the compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
We have explained the rules regarding the nomenclature of compounds which have a C-C double bond and also an alcohol attached to the C as the functional group.
We are familiar with the fact that for the nomenclature of the organic compounds, IUPAC has set some rules to maintain the homogeneity of naming the compounds in different places and to avoid confusion.
So the name given for a compound according to the rules set by the IUPAC is called the IUPAC names or IUPAC nomenclature of the molecules.
Now we have to discuss the rules that are to be followed for naming an alkene compound with alcohol.
From the time we are dealing with organic chemistry we are familiar with a class of hydrocarbons which possess double bonds between the C atoms i.e. $ C=C$ and are referred to as alkenes.
The compounds with the hydroxyl group $ -OH$ as the functional group are called alcohols.
Let’s discuss the rules for naming the compounds:
-First identify the longest chain possible which includes the $ C=C$ group.If there are two possibilities to take the long chain and both having the $ C=C$ chain, then go for the longest chain which has more number of substituents.
-Then number the C in the parent chain in such a fashion that the carbon having double bond should have the least possible number.
-Now identify the name of the parent chain with respect to the number of C present.And it should be named with the suffix as – ene.
-Then give the numbering for the substituents attached.The numbering should be in such a fashion that the sum of the numbers assigned for the substituents must have the least possible number.
-Name the substituents along with the assigned number in the alphabetical order before naming the parent chain. Here as in the question a functional group is also given, the functional group has more preference than the double bonds. And the suffix –ol is given by removing the e from –ene the suffix used for the parent carbon chain and the position to which the $ -OH$ group is attached must also be mentioned.
Therefore the functional group should be given preference and the least number should be given for the functional groups while naming the compounds.
The rules set are quite confusing to memorize and confusing,so let’s do the nomenclature of a compound for having better clarity.
Let’s consider an organic compound which has the structure,
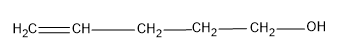
-Here we have 5 carbon atoms and it is the longest carbon chain possible.
-Number the C chain such that the functional group gets the least number.
-Now name the compound, the main chain is pentene. Since the double bond is on C-4 and the $ -OH$ group is on C-1. The IUPAC name of the compound will be Pent-4-en-1-ol.
Note:
The functional groups which have least priority than the $ C=C$ group are halogens, alkynes and $ -N{{O}_{2}}$ .
For representing the isomers of alkenes we will name the compounds by giving the prefix cis and trans which is commonly used. But the proper way and the IUPAC accepted way of representing the isomers is by following the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog $ {}^{E}/{}_{Z}$ sy
-Now name the compound, the main chain is pentene. Since the double bond is on C-4 and the $ -OH$ group is on C-1. The IUPAC name of the compound will be Pent-4-en-1-ol.
Note: The functional groups which have least priority than the $ C=C$ group are halogens, alkynes and $ -N{{O}_{2}}$ .
For representing the isomers of alkenes we will name the compounds by giving the prefix cis and trans which is commonly used. But the proper way and the IUPAC accepted way of representing the isomers is by following the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog $ {}^{E}/{}_{Z}$ system.
Complete step by step solution:
We have explained the rules regarding the nomenclature of compounds which have a C-C double bond and also an alcohol attached to the C as the functional group.
We are familiar with the fact that for the nomenclature of the organic compounds, IUPAC has set some rules to maintain the homogeneity of naming the compounds in different places and to avoid confusion.
So the name given for a compound according to the rules set by the IUPAC is called the IUPAC names or IUPAC nomenclature of the molecules.
Now we have to discuss the rules that are to be followed for naming an alkene compound with alcohol.
From the time we are dealing with organic chemistry we are familiar with a class of hydrocarbons which possess double bonds between the C atoms i.e. $ C=C$ and are referred to as alkenes.
The compounds with the hydroxyl group $ -OH$ as the functional group are called alcohols.
Let’s discuss the rules for naming the compounds:
-First identify the longest chain possible which includes the $ C=C$ group.If there are two possibilities to take the long chain and both having the $ C=C$ chain, then go for the longest chain which has more number of substituents.
-Then number the C in the parent chain in such a fashion that the carbon having double bond should have the least possible number.
-Now identify the name of the parent chain with respect to the number of C present.And it should be named with the suffix as – ene.
-Then give the numbering for the substituents attached.The numbering should be in such a fashion that the sum of the numbers assigned for the substituents must have the least possible number.
-Name the substituents along with the assigned number in the alphabetical order before naming the parent chain. Here as in the question a functional group is also given, the functional group has more preference than the double bonds. And the suffix –ol is given by removing the e from –ene the suffix used for the parent carbon chain and the position to which the $ -OH$ group is attached must also be mentioned.
Therefore the functional group should be given preference and the least number should be given for the functional groups while naming the compounds.
The rules set are quite confusing to memorize and confusing,so let’s do the nomenclature of a compound for having better clarity.
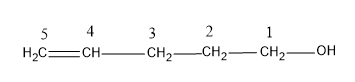
Let’s consider an organic compound which has the structure,
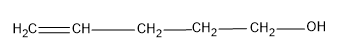
-Here we have 5 carbon atoms and it is the longest carbon chain possible.
-Number the C chain such that the functional group gets the least number.

-Now name the compound, the main chain is pentene. Since the double bond is on C-4 and the $ -OH$ group is on C-1. The IUPAC name of the compound will be Pent-4-en-1-ol.
Note:
The functional groups which have least priority than the $ C=C$ group are halogens, alkynes and $ -N{{O}_{2}}$ .
For representing the isomers of alkenes we will name the compounds by giving the prefix cis and trans which is commonly used. But the proper way and the IUPAC accepted way of representing the isomers is by following the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog $ {}^{E}/{}_{Z}$ sy
-Now name the compound, the main chain is pentene. Since the double bond is on C-4 and the $ -OH$ group is on C-1. The IUPAC name of the compound will be Pent-4-en-1-ol.
Note: The functional groups which have least priority than the $ C=C$ group are halogens, alkynes and $ -N{{O}_{2}}$ .
For representing the isomers of alkenes we will name the compounds by giving the prefix cis and trans which is commonly used. But the proper way and the IUPAC accepted way of representing the isomers is by following the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog $ {}^{E}/{}_{Z}$ system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




