
Name any two ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants. Give anatomical characters of these plants.
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: The plants that use the ${ C } _ { 4 }$ pathway of photorespiration are known as ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants. These are common in hot areas where sunlight is of high intensity.
Complete answer:
The Names of two ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are sugarcane and maize.
The anatomical characters of these plants are:
-${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are adapted to dry tropical regions and have the C4 pathway. Therefore it's called ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants.
-They have a special type of leaf anatomy known as Kranz anatomy.
-These plants are designed in such a way that they can tolerate higher temperatures and show a response to the high intensity of light.
-The large cells surrounding the vascular bundle of ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are called bundle sheath cells. They form several layers around the vascular bundle and have a large number of dimorphic chloroplasts.
-The other type of cells present in these plants are called mesophyll cells.
-${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants have thick walls impervious to gaseous exchange and no intercellular space.
Additional Information: -${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are known for their distinct anatomy and photorespiration process.
-They minimize photorespiration by separating initial ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ fixation and the Calvin cycle in space.
-In the case of these plants, Light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle are physically separated. The light reactions occur in the Mesophyll cells whereas the Calvin cycle occurs in special cells around the leaf veins, called bundle sheath cells.
-About 3% of all vascular plants use the ${ C } _ { 4 }$ pathway. It is common in hot habitats as the benefits of reduced photosynthesis likely exceed the ATP cost of moving ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ from the Mesophyll cells to the bundle sheath cells.
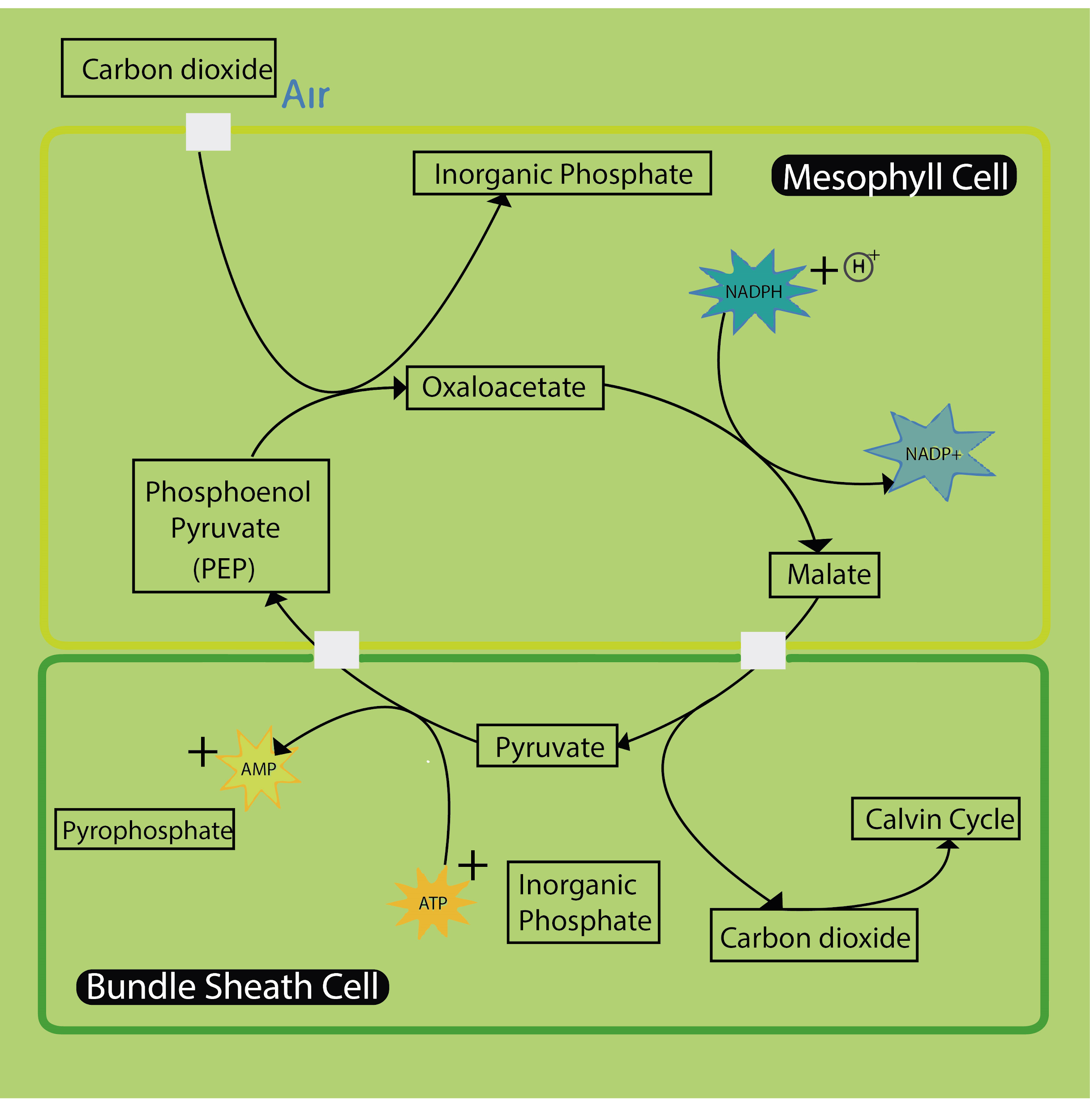
Note: To understand the c4 plants, we must understand the process of the ${ C } _ { 4 }$ pathway. The Mesophyll cells fix ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ to form oxaloacetate with the help of non-rubisco enzyme PEP carboxylase. The oxaloacetate transforms into malate and gets transported to bundle sheath cells. Their malate breaks down and releases ${ CO } _ { 2 }$. The ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ then get fixed by rubisco and made into sugars via the Calvin cycle.
Complete answer:
The Names of two ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are sugarcane and maize.
The anatomical characters of these plants are:
-${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are adapted to dry tropical regions and have the C4 pathway. Therefore it's called ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants.
-They have a special type of leaf anatomy known as Kranz anatomy.
-These plants are designed in such a way that they can tolerate higher temperatures and show a response to the high intensity of light.
-The large cells surrounding the vascular bundle of ${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are called bundle sheath cells. They form several layers around the vascular bundle and have a large number of dimorphic chloroplasts.
-The other type of cells present in these plants are called mesophyll cells.
-${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants have thick walls impervious to gaseous exchange and no intercellular space.
Additional Information: -${ C } _ { 4 }$ plants are known for their distinct anatomy and photorespiration process.
-They minimize photorespiration by separating initial ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ fixation and the Calvin cycle in space.
-In the case of these plants, Light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle are physically separated. The light reactions occur in the Mesophyll cells whereas the Calvin cycle occurs in special cells around the leaf veins, called bundle sheath cells.
-About 3% of all vascular plants use the ${ C } _ { 4 }$ pathway. It is common in hot habitats as the benefits of reduced photosynthesis likely exceed the ATP cost of moving ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ from the Mesophyll cells to the bundle sheath cells.
Note: To understand the c4 plants, we must understand the process of the ${ C } _ { 4 }$ pathway. The Mesophyll cells fix ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ to form oxaloacetate with the help of non-rubisco enzyme PEP carboxylase. The oxaloacetate transforms into malate and gets transported to bundle sheath cells. Their malate breaks down and releases ${ CO } _ { 2 }$. The ${ CO } _ { 2 }$ then get fixed by rubisco and made into sugars via the Calvin cycle.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




