
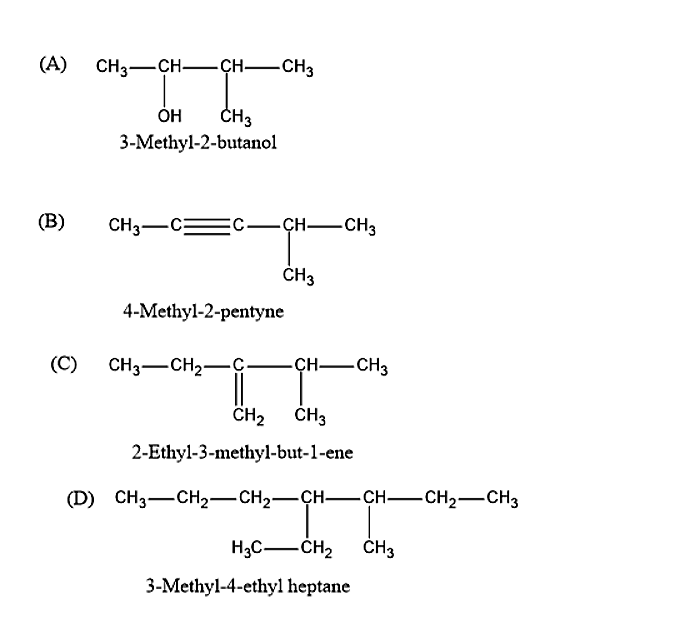
Name of some compounds are given. Which one is not correct in the IUPAC system?

Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: In order to find which name is not in the IUPAC system, we must first know what an IUPAC system is and what are the different rules for naming the organic compounds. IUPAC is abbreviated as International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. This system is useful for naming the organic compounds in a systematic way.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand about the IUPAC nomenclature. IUPAC nomenclature is the systematic way of naming the organic compounds. IUPAC is abbreviated as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Now let us see what are the different rules or steps for naming the organic compounds.
- we have to first identify the longest chain, i.e., the parent compound must be identified.
- The Carbon atom in the parent hydrocarbon must be numbered using the natural numbers. Beginning from that end where the carbon atom which is having the substituent can be given the lowest number.
- When there are many numbers of the same substituent in the given organic compound, then it will be given with a prefix such as di, tri, etc.
- When there are multiple substituents in the same compound, then the substituents are arranged according to the alphabetical order.
- When there are two substituents on the same position of the carbon atom, then these substituents are arranged in the alphabetical order.
From the above given rules, we can say that the option (D) is not in the correct IUPAC system, because there are more substituents in the given organic compound and these substituents are not arranged in the alphabetical order.
The option (D) can be correctly written in the IUPAC system as 4-Ethyl-3-methyl heptane.
Hence the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
We have to remember that there are different IUPAC nomenclature methods such as:
- Compositional nomenclature
- Substitutive nomenclature
- Additive nomenclature
Complete answer:
Let us first understand about the IUPAC nomenclature. IUPAC nomenclature is the systematic way of naming the organic compounds. IUPAC is abbreviated as the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Now let us see what are the different rules or steps for naming the organic compounds.
- we have to first identify the longest chain, i.e., the parent compound must be identified.
- The Carbon atom in the parent hydrocarbon must be numbered using the natural numbers. Beginning from that end where the carbon atom which is having the substituent can be given the lowest number.
- When there are many numbers of the same substituent in the given organic compound, then it will be given with a prefix such as di, tri, etc.
- When there are multiple substituents in the same compound, then the substituents are arranged according to the alphabetical order.
- When there are two substituents on the same position of the carbon atom, then these substituents are arranged in the alphabetical order.
From the above given rules, we can say that the option (D) is not in the correct IUPAC system, because there are more substituents in the given organic compound and these substituents are not arranged in the alphabetical order.
The option (D) can be correctly written in the IUPAC system as 4-Ethyl-3-methyl heptane.
Hence the correct answer is option (D).
Note:
We have to remember that there are different IUPAC nomenclature methods such as:
- Compositional nomenclature
- Substitutive nomenclature
- Additive nomenclature
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




