
Name the first organic acid produced by microbial fermentation
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: It is a chemical byproduct of the anaerobic respiration process in human beings by which the cells produce energy without oxygen. Mainly found in blood vessels and stored by muscles and RBC. The body produces it when there is a lack of oxygen in the body thus converts glucose to energy.
Complete step by step answer:
- During microbial fermentation lactic acid is the first organic acid that is produced.
- Lactic acid was first manufactured on a commercial scale in the United States by lactic acid bacterial fermentation of sugar substrate in 1883.
- The production of lactic acid is an anoxic process. The substrate used is glucose taken $12\%-15\%$ which produces lactic acid as a product, here Bacteria used is lactobacillus mainly Lactobacillus bulgaricus or delbrueckii.
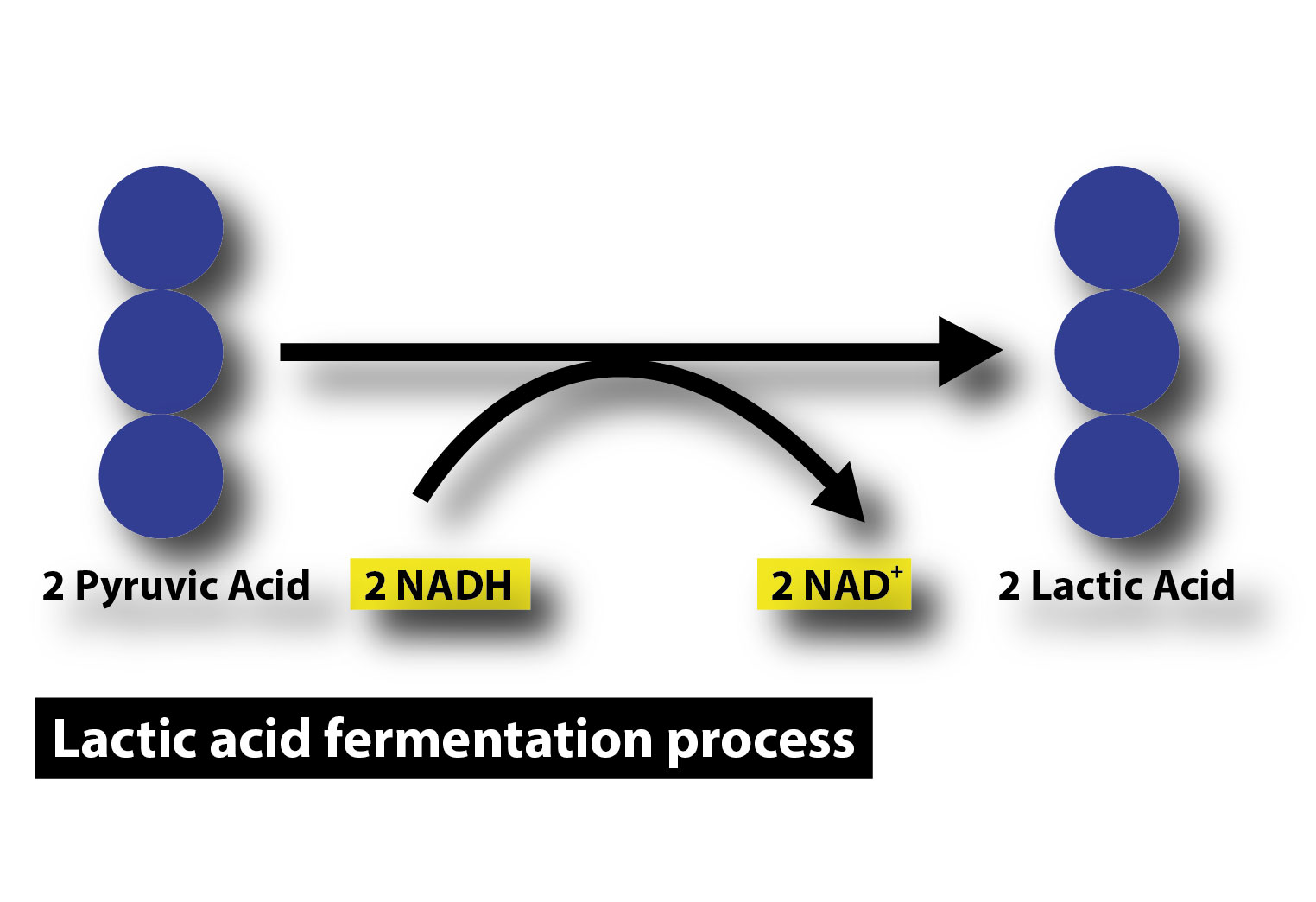
- Stages of Glycolysis
1) First glucose is converted to glucose - 1- phosphate, then glucose- 1 - phosphate is converted to glucose 1- 6 bisphosphate and at this stage we require NAD, NAD Energy is converted to $NADH{ H }^{ + }$
2) Glucose 1- 6 bisphosphate then converted to pyruvate and pyruvate converted into lactic acid. For this conversion, NAD is required which is carried out by pyruvate dehydrogenase.
- Oxygen has no role in this process. fermentation is carried out 72 hours temperature and maintained at 45 to 50 degree Celsius for the conversion of glucose into lactic acid
- In lactic acid fermentation NADH transfers its electron directly to pyruvate generating lactate as a by- product.
- The bacteria that make yogurt carry out lactic acid fermentation, as do the Red blood cells in our body which don't have mitochondria and thus can’t perform cellular respiration.
- Muscles cells also carry out lactic acid fermentation only when they have two little oxygen for aerobic respiration to continue
Note: The bloodstreams act as a carrier that carries the Lactic acid produced to the liver. The acts on this and converts it to pyruvate which gets processed as usual in the other cellular respiration. Lactic acid fermentation of glucose is of two types: Homolactic fermentation, where one molecule of glucose yields only two molecules of lactic acid, and heterolactic fermentation where one molecule of glucose yields carbon dioxide and ethanol in addition to lactic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
- During microbial fermentation lactic acid is the first organic acid that is produced.
- Lactic acid was first manufactured on a commercial scale in the United States by lactic acid bacterial fermentation of sugar substrate in 1883.
- The production of lactic acid is an anoxic process. The substrate used is glucose taken $12\%-15\%$ which produces lactic acid as a product, here Bacteria used is lactobacillus mainly Lactobacillus bulgaricus or delbrueckii.

- Stages of Glycolysis
1) First glucose is converted to glucose - 1- phosphate, then glucose- 1 - phosphate is converted to glucose 1- 6 bisphosphate and at this stage we require NAD, NAD Energy is converted to $NADH{ H }^{ + }$
2) Glucose 1- 6 bisphosphate then converted to pyruvate and pyruvate converted into lactic acid. For this conversion, NAD is required which is carried out by pyruvate dehydrogenase.
- Oxygen has no role in this process. fermentation is carried out 72 hours temperature and maintained at 45 to 50 degree Celsius for the conversion of glucose into lactic acid
- In lactic acid fermentation NADH transfers its electron directly to pyruvate generating lactate as a by- product.
- The bacteria that make yogurt carry out lactic acid fermentation, as do the Red blood cells in our body which don't have mitochondria and thus can’t perform cellular respiration.
- Muscles cells also carry out lactic acid fermentation only when they have two little oxygen for aerobic respiration to continue
Note: The bloodstreams act as a carrier that carries the Lactic acid produced to the liver. The acts on this and converts it to pyruvate which gets processed as usual in the other cellular respiration. Lactic acid fermentation of glucose is of two types: Homolactic fermentation, where one molecule of glucose yields only two molecules of lactic acid, and heterolactic fermentation where one molecule of glucose yields carbon dioxide and ethanol in addition to lactic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




