
Name the lens that always forms a virtual and erect image.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: We know that in the case of the lens when a ray of light incident on it, after refraction it diverges or converges and we can get an image. A concave lens is that lens that gives a virtual and erect image.
Complete answer:
A lens is an optical medium bounded by two surfaces of which at least one surface is spherical. lenses commonly used either two spherical surfaces or one spherical surface and one plane surface. These lenses are called spherical lenses. there are different types of lenses, namely biconvex lens, a plano-convex lens, biconcave lens, plano-concave lens, etc.,
A lens that diverges a parallel beam of light passing through it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges. It diverges parallel rays of light on refraction through it.
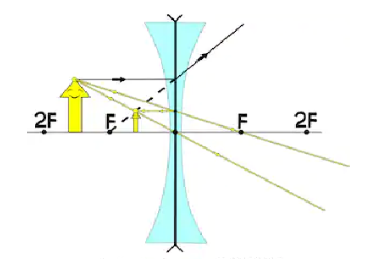
The ray diagram of we can say at any point that object distance, concave lens always produces a virtual and erect image.
From the diagram of the lens passing through the concave lens, we can say that a Virtual image is formed when the rays of light appear to be coming from a point but do not meet. This is because of its type of surface on which light falls. Depending on the surface pattern a light ray is converging or diverging. Virtual images cannot be formed on the screen. It is always erect, which means an upright image.
Additional information:
Cartesian sign convention for the lens:
All distances are measured from the optic center of the lens and along the principal axis.
The distances measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive while those measured in the direction opposite to the incident light are taken as negative.
A focal length of a convex lens is positive and that of a concave lens is negative.
Heights or distances measured upward and perpendicular to the principal axis are considered positive while those measured downwards are considered negative.
Note:
When a ray of light incident on a lens after refraction all the refracted ray meets at one point is called convergence.
When rays of light incident on a lens after refraction all the refracted rays appear to meet at one point are called divergence.
Complete answer:
A lens is an optical medium bounded by two surfaces of which at least one surface is spherical. lenses commonly used either two spherical surfaces or one spherical surface and one plane surface. These lenses are called spherical lenses. there are different types of lenses, namely biconvex lens, a plano-convex lens, biconcave lens, plano-concave lens, etc.,
A lens that diverges a parallel beam of light passing through it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges. It diverges parallel rays of light on refraction through it.

The ray diagram of we can say at any point that object distance, concave lens always produces a virtual and erect image.
From the diagram of the lens passing through the concave lens, we can say that a Virtual image is formed when the rays of light appear to be coming from a point but do not meet. This is because of its type of surface on which light falls. Depending on the surface pattern a light ray is converging or diverging. Virtual images cannot be formed on the screen. It is always erect, which means an upright image.
Additional information:
Cartesian sign convention for the lens:
All distances are measured from the optic center of the lens and along the principal axis.
The distances measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive while those measured in the direction opposite to the incident light are taken as negative.
A focal length of a convex lens is positive and that of a concave lens is negative.
Heights or distances measured upward and perpendicular to the principal axis are considered positive while those measured downwards are considered negative.
Note:
When a ray of light incident on a lens after refraction all the refracted ray meets at one point is called convergence.
When rays of light incident on a lens after refraction all the refracted rays appear to meet at one point are called divergence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




