
Name three types of levers found in the human skeleton.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: A lever is a simple mechanical arrangement that employs the collective participation of different parts to magnify a particular movement. It is represented by the presence of well-articulated joints in the human skeleton.
Complete step by step answer:
The three types of levers found in the human skeleton are as follows:
- Class I lever: It is found between the attachment of the skull to the first vertebra of our vertebral column. The attachment is in the form of an atlanto occipital joint.
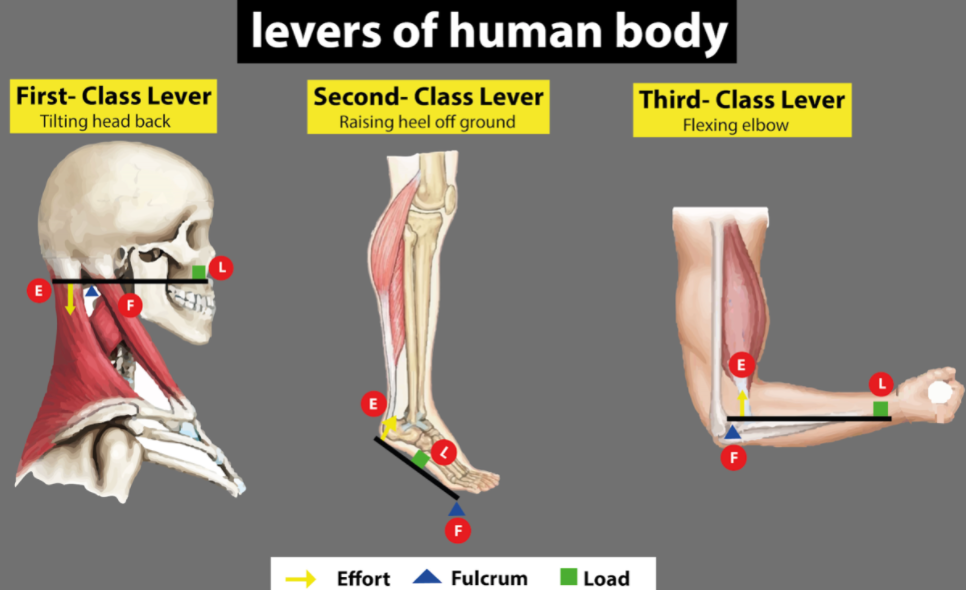
- Class II lever: Such types of levers are represented by the metatarsophalangeal joints or MTP joints. These are located between the phalanges of toes and the metatarsals of the foot.
Class III lever: In the human body, the elbow joint formed between the distal end of the humerus of the upper arm and the proximal ends of the radius and ulna of the forearm.
Additional Information:
- A lever is composed of four parts namely a lever arm, pivot, an effort, and a load. In our human body, the muscles and bones together form levers in our bodies.
- Bones act as lever arms, joints act as pivots, muscles provide effort while loads are the weights of the body parts that require to be pushed, lifted, or to be pulled.
- Coordinated participation of all these parts produce a desired magnified result as required. E.g While kicking a ball, a collective effort of muscles and bones produces a larger movement at the end of the leg.
Note:
- Joints are that part of our body where two or more bones are attached to allow free movement. They are further divided into movable and immovable joints.
- Movable joints in the adult body are freely movable joints due to the presence of some lubricating fluid.
- There are six sorts of freely movable joints - ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot, and gliding.
Complete step by step answer:
The three types of levers found in the human skeleton are as follows:
- Class I lever: It is found between the attachment of the skull to the first vertebra of our vertebral column. The attachment is in the form of an atlanto occipital joint.

- Class II lever: Such types of levers are represented by the metatarsophalangeal joints or MTP joints. These are located between the phalanges of toes and the metatarsals of the foot.
Class III lever: In the human body, the elbow joint formed between the distal end of the humerus of the upper arm and the proximal ends of the radius and ulna of the forearm.
Additional Information:
- A lever is composed of four parts namely a lever arm, pivot, an effort, and a load. In our human body, the muscles and bones together form levers in our bodies.
- Bones act as lever arms, joints act as pivots, muscles provide effort while loads are the weights of the body parts that require to be pushed, lifted, or to be pulled.
- Coordinated participation of all these parts produce a desired magnified result as required. E.g While kicking a ball, a collective effort of muscles and bones produces a larger movement at the end of the leg.
Note:
- Joints are that part of our body where two or more bones are attached to allow free movement. They are further divided into movable and immovable joints.
- Movable joints in the adult body are freely movable joints due to the presence of some lubricating fluid.
- There are six sorts of freely movable joints - ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot, and gliding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




