
Nastic movement differ from tropical movement in being
(a) Directional with respect to stimulus
(b) Non-directional with respect to stimulus
(c) Controlled by turgor pressure
(d) Controlled by chemicals
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: It is found virtually in all plants but nastic movements are mostly found in specialized organs and plants. There is a directional movement of plants in response to the surrounding like gravity or light but is independent in other movements. It controls the orientation of growth.
Complete answer:
Additional Information:
Types of tropic movement
1. Phototropism
2. Gravitropism
3. Chemotropism
4. Thigmotropism
5. Hydrotropism
6. Thermotropism
Phototropism: In phototropism, plants grow towards or away from the light, the type of tropism in the response to light
Gravitropism: It is the process in which a type of tropism where plants show some growth in response to gravity.
Chemotropism: There are some chemical substances, which are actively responsible for bringing a curvature movement in plant organs.
Thigmotropism: It is the process in which the growing or developing movements made through plants in response to contact with a solid object.
Hydrotropism: It is the process in which the movement or the growth of a plant in relation to the stimulus of water movements, and the equivalent response to the stimulus of water is called hydrotropism.
Thermotropism: It is the type of tropic movement in which a plant or a part of the plant responds to the changing atmospheric temperature.
So the correct answer is ‘Non-directional with respect to stimulus’.
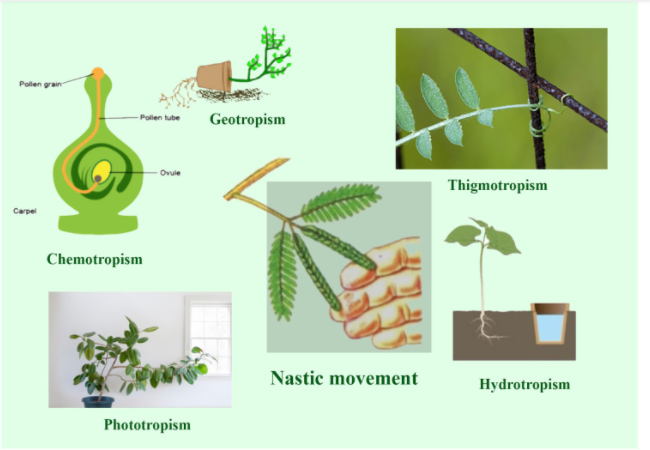
Note: Nostic movement may be induced by touch (seismonastic), temperature (Thermonastic), light and chemicals. But in tropical movement, if the movement of the plant part is towards the stimulus, then it is known as positive tropism. In the event that the movement of the plant part is away from the stimulus, then it is known as negative tropism.
Complete answer:
| Nastic movement | Tropical movement |
| The nastic movements are non-directional reactions to stimuli and are generally connected with plants. | In tropic movement, it is the response to stimuli that comes from one direction. |
| Nastic movements are fast. | Tropical movements are slow. |
| These movements are expressed by the flat organs (like leaves and petals of flowers) of a plant. For instance, the bending and drooping of leaves in the 'Touch-me-not' plant. | These movements are expressed by all parts of a plant. Such as movement of a shoot towards the light and not towards gravity. |
Additional Information:
Types of tropic movement
1. Phototropism
2. Gravitropism
3. Chemotropism
4. Thigmotropism
5. Hydrotropism
6. Thermotropism
Phototropism: In phototropism, plants grow towards or away from the light, the type of tropism in the response to light
Gravitropism: It is the process in which a type of tropism where plants show some growth in response to gravity.
Chemotropism: There are some chemical substances, which are actively responsible for bringing a curvature movement in plant organs.
Thigmotropism: It is the process in which the growing or developing movements made through plants in response to contact with a solid object.
Hydrotropism: It is the process in which the movement or the growth of a plant in relation to the stimulus of water movements, and the equivalent response to the stimulus of water is called hydrotropism.
Thermotropism: It is the type of tropic movement in which a plant or a part of the plant responds to the changing atmospheric temperature.
So the correct answer is ‘Non-directional with respect to stimulus’.

Note: Nostic movement may be induced by touch (seismonastic), temperature (Thermonastic), light and chemicals. But in tropical movement, if the movement of the plant part is towards the stimulus, then it is known as positive tropism. In the event that the movement of the plant part is away from the stimulus, then it is known as negative tropism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




