
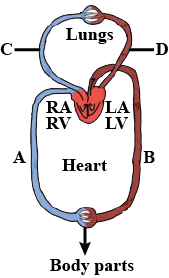
What is the nature of blood passing through blood vessels A, B, C and D respectively?

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The human heart is a muscular organ that is involved in the pumping of the blood. The blood is transported to different body parts through three types of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries.
Complete step by step answer: The correct answer is:
‘A' is the vena cava that carries deoxygenated blood. The vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from all the tissues of the body to the right atrium of the heart. The blood then passes the right ventricle via a valve. The blood is then pumped to the lungs for oxygenation.
'B' is the aorta that carries oxygenated blood. It carries oxygen-rich blood to all the tissues and organs of the body. The aorta receives blood from the left ventricle after it is oxygenated in the lungs.
'C' is the pulmonary artery that carries deoxygenated blood. It is also known as pulmonary circulation. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the lungs.
'D' is the pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood. It is also a part of the pulmonary circulation, where the blood that is oxygenated in the lungs via diffusion and is brought to the left atrium.
Additional information: Blood enters the heart through two large veins; the posterior and the anterior vena cava which carries deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium. Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve. There are three main types of blood vessels involved in the circulation process; arteries, veins and capillaries.
Note: The blood contains a protein called haemoglobin, which is involved in the transportation process. It is a biconcave structure present in the red blood cells that carry oxygen as well as carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step answer: The correct answer is:
‘A' is the vena cava that carries deoxygenated blood. The vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from all the tissues of the body to the right atrium of the heart. The blood then passes the right ventricle via a valve. The blood is then pumped to the lungs for oxygenation.
'B' is the aorta that carries oxygenated blood. It carries oxygen-rich blood to all the tissues and organs of the body. The aorta receives blood from the left ventricle after it is oxygenated in the lungs.
'C' is the pulmonary artery that carries deoxygenated blood. It is also known as pulmonary circulation. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the lungs.
'D' is the pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood. It is also a part of the pulmonary circulation, where the blood that is oxygenated in the lungs via diffusion and is brought to the left atrium.
Additional information: Blood enters the heart through two large veins; the posterior and the anterior vena cava which carries deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium. Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve. There are three main types of blood vessels involved in the circulation process; arteries, veins and capillaries.
Note: The blood contains a protein called haemoglobin, which is involved in the transportation process. It is a biconcave structure present in the red blood cells that carry oxygen as well as carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




