
What is the nature of image formed in a convex mirror?
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: The ray diagrams show the exact position of the image and their nature. Ray diagrams are drawn by drawing rays from the height of the object parallel to the horizontal axis and towards the centre of the mirror. These rays follow the laws of reflection. An image is formed, determined by the intersection point of the two rays.
Complete step by step answer:
When we want to know about the nature and size of the image formed, we need to consider the position of the object. For different positions of the object, there will be subsequently different positions of the image.
Ray diagrams are made using the following rules for a mirror.
a.) A ray parallel to the horizontal, when reflected, passes through the focal point.
b.) A ray passing or pointing towards the centre of curvature, retraces its path after reflection.
c.) The point at which the rays intersect, an image is formed.
So, when the object is at a very distant position from the mirror, let’s say infinity, the rays of light arriving towards the mirror are almost parallel. Thus, they coincide at the centre of curvature.
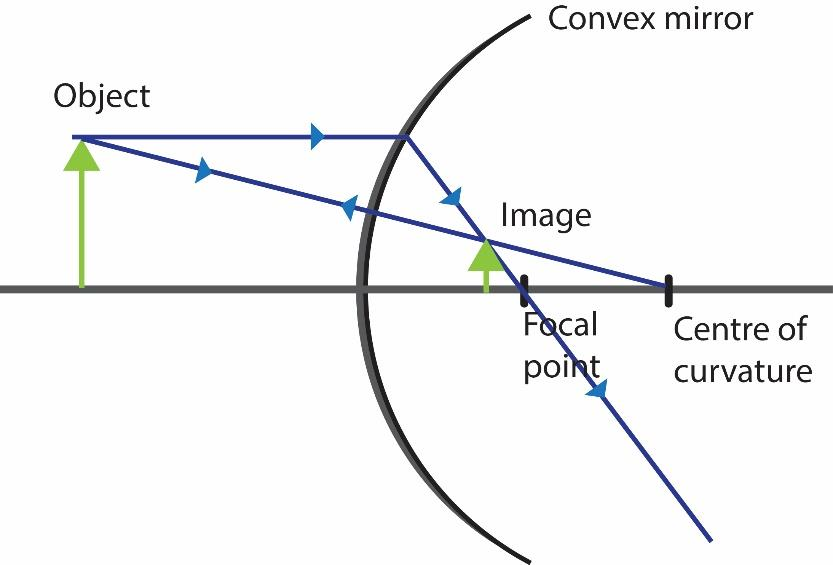
Rays from an object close to the mirror are shown in the ray diagram. For a convex mirror, notice that, wherever you place the object, the ray diagrams will be similar. Therefore, from the figure, it is clear that:
a.) The image will always be formed behind the mirror, that is it will be virtual.
b.) It will have a height less than that of the object, that is the image will be diminished.
c.) The image stands erect.
d.) The image formed is closer to the mirror than the object.
Note: Be careful of the position of the object placed. As for concave mirrors, the position changes the properties of the image. Do not memorize the properties for every mirror, remember how the Ray diagrams are drawn and apply the concepts every time.
Complete step by step answer:
When we want to know about the nature and size of the image formed, we need to consider the position of the object. For different positions of the object, there will be subsequently different positions of the image.
Ray diagrams are made using the following rules for a mirror.
a.) A ray parallel to the horizontal, when reflected, passes through the focal point.
b.) A ray passing or pointing towards the centre of curvature, retraces its path after reflection.
c.) The point at which the rays intersect, an image is formed.
So, when the object is at a very distant position from the mirror, let’s say infinity, the rays of light arriving towards the mirror are almost parallel. Thus, they coincide at the centre of curvature.

Rays from an object close to the mirror are shown in the ray diagram. For a convex mirror, notice that, wherever you place the object, the ray diagrams will be similar. Therefore, from the figure, it is clear that:
a.) The image will always be formed behind the mirror, that is it will be virtual.
b.) It will have a height less than that of the object, that is the image will be diminished.
c.) The image stands erect.
d.) The image formed is closer to the mirror than the object.
Note: Be careful of the position of the object placed. As for concave mirrors, the position changes the properties of the image. Do not memorize the properties for every mirror, remember how the Ray diagrams are drawn and apply the concepts every time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




