
NBS reacts with 1-butene to give:
A. 3-bromobutene-1
B. 1,2-dibromobutane
C. 1-bromobutene
D. 1,2-dibromobutene-1
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: NBS is usually used for allylic bromination, where the hydrogen atom present on the carbon adjacent to a double bond is replaced by the halogen i.e. bromine (allylic halogenation) and it is also used for various electrophilic additions and substitutions.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
NBS which is N-bromosuccinimide reacts with 1-butene.
So, as we know that,
When an allyl is reacted with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), it undergoes allylic bromination where, the hydrogen atom of allylic group which is present on the carbon atom that is adjacent to the double bond is replaced by the bromine of N-bromosuccinimide.
So, here when 1-butene (which is an allyl group) reacts with N-bromosuccinimide, it undergoes allylic bromination which will yield 3-bromo-1-butene and succinimide as the products. The following chemical reaction is explained in the figure,
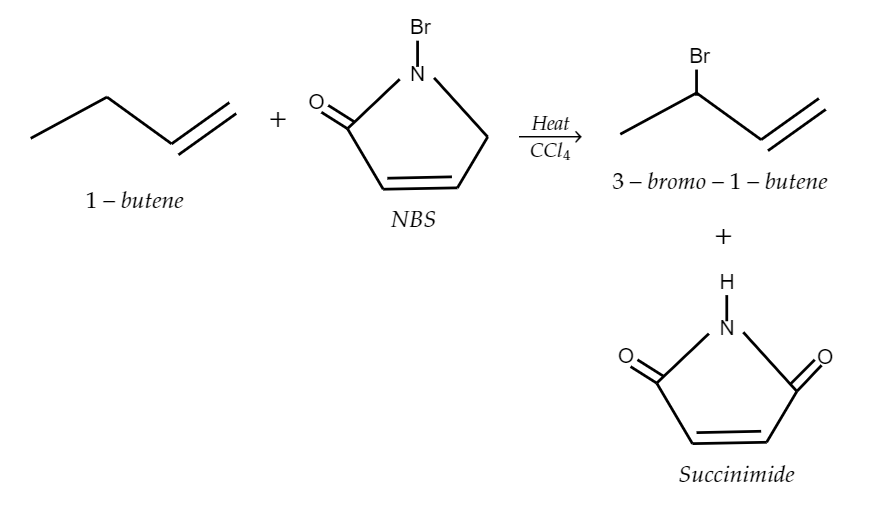
So, as we can see that the following reaction produces 3-bromo-1-butene or 3-bromobutene-1.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Additional Information: NBS or N-Bromosuccinimide is a brominating and oxidizing reagent which is most commonly used as a source for bromine in radical reactions like allylic bromination and various electrophilic additions and substitution reactions in organic chemistry. Allylic bromination is the replacement of a hydrogen on a carbon adjacent to a double bond (or aromatic ring, in which case it’s called aromatic bromination).
Note: When you have an alkene in the presence of a halogen, the halogen group adds to the compound at the allylic position instead of adding to the compound it on the double bond and this is called as allylic halogenation. NBS is used as a substitute for bromine in allylic bromination as bromine tends to react with the double bonds to form dibromides.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
NBS which is N-bromosuccinimide reacts with 1-butene.
So, as we know that,
When an allyl is reacted with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), it undergoes allylic bromination where, the hydrogen atom of allylic group which is present on the carbon atom that is adjacent to the double bond is replaced by the bromine of N-bromosuccinimide.
So, here when 1-butene (which is an allyl group) reacts with N-bromosuccinimide, it undergoes allylic bromination which will yield 3-bromo-1-butene and succinimide as the products. The following chemical reaction is explained in the figure,

So, as we can see that the following reaction produces 3-bromo-1-butene or 3-bromobutene-1.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Additional Information: NBS or N-Bromosuccinimide is a brominating and oxidizing reagent which is most commonly used as a source for bromine in radical reactions like allylic bromination and various electrophilic additions and substitution reactions in organic chemistry. Allylic bromination is the replacement of a hydrogen on a carbon adjacent to a double bond (or aromatic ring, in which case it’s called aromatic bromination).
Note: When you have an alkene in the presence of a halogen, the halogen group adds to the compound at the allylic position instead of adding to the compound it on the double bond and this is called as allylic halogenation. NBS is used as a substitute for bromine in allylic bromination as bromine tends to react with the double bonds to form dibromides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




