
Nerves from the lumbosacral plexus are supplied to
(a) Forelimbs
(b) Hindlimbs
(c) Trunk
(d) None of the above.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: They receive supplies from the lumbosacral plexus and are analogous to pelvic fins in fishes and also they are modified to form scaly claws in birds. They provide support to the animal’s body and allow them to move from one place to another.
Correct step by step answer:
Nerves from the lumbosacral plexus are supplied to the hindlimb. The nerve plexus refers to the network of the intersecting nerves that innervate the same part of the body. The lumbar plexus is formed by the ventral ramification of the C5- C8 and T1 spinal nerves. This plexus supplies skin and musculature of the hindlimbs or the lower limbs.
- The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and nervus coccygeus form the nerve plexus, the primary spinal nerve is usually joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For description the lumbosacral plexus is split into three parts:
- Lumbar plexus: The lumbar plexus which forms a part of the larger nerve plexus may be a web of nerves within the lumbar region of the body. It is formed by the divisions of the primary four lumbar nerves (L1- L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12) , which is that of the last spinal nerve.
- Sacral plexus: In human anatomy, the plexus sacralis may be a plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is a part of the nerve plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4- S4)
- Pudendal plexus: The pudendal plexus is a term used for a compound structure consisting of sacral spinal nerves.
- The anterior and posterior divisions together constitute the lumbar plexus. The anterior division gives rise to the ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral nerves, all of which are derived from L1–L2 and provide sensory innervation to the lower abdomen, upper proximal thigh, and lateral genitalia.
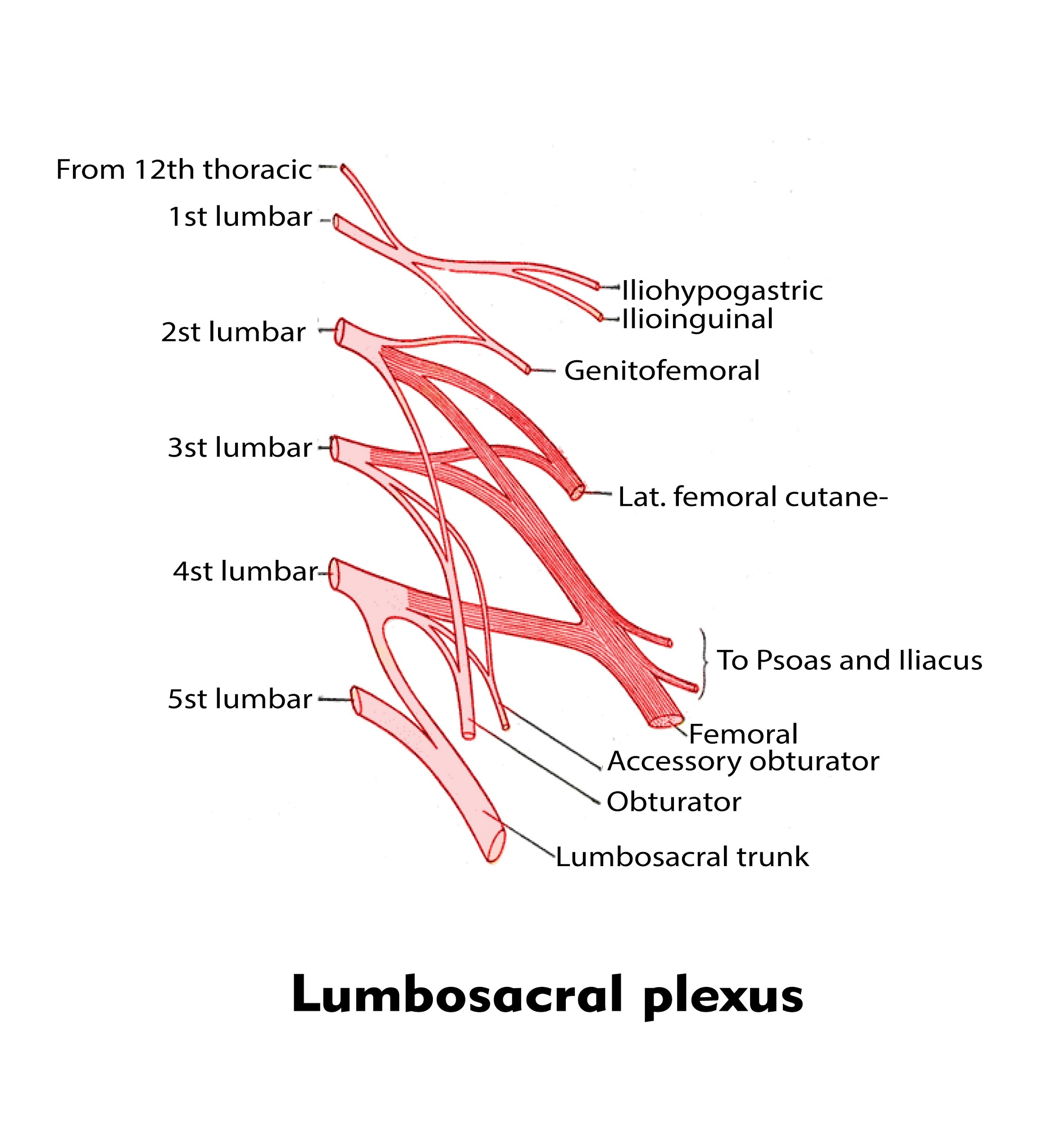
So, the correct answer is, 'Hindlimbs'.
Note:
- Sacral plexopathy may be a disorder affecting the nerves of the plexus sacralis, usually caused by trauma, nervous disorder, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of control, and sensory deficits.
- Injuries to the nerve plexus are predominantly witnessed as bone injuries. Lumbosacral trunk and sacral plexus palsies bear common injury patterns.
Correct step by step answer:
Nerves from the lumbosacral plexus are supplied to the hindlimb. The nerve plexus refers to the network of the intersecting nerves that innervate the same part of the body. The lumbar plexus is formed by the ventral ramification of the C5- C8 and T1 spinal nerves. This plexus supplies skin and musculature of the hindlimbs or the lower limbs.
- The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and nervus coccygeus form the nerve plexus, the primary spinal nerve is usually joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For description the lumbosacral plexus is split into three parts:
- Lumbar plexus: The lumbar plexus which forms a part of the larger nerve plexus may be a web of nerves within the lumbar region of the body. It is formed by the divisions of the primary four lumbar nerves (L1- L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12) , which is that of the last spinal nerve.
- Sacral plexus: In human anatomy, the plexus sacralis may be a plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is a part of the nerve plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4- S4)
- Pudendal plexus: The pudendal plexus is a term used for a compound structure consisting of sacral spinal nerves.
- The anterior and posterior divisions together constitute the lumbar plexus. The anterior division gives rise to the ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral nerves, all of which are derived from L1–L2 and provide sensory innervation to the lower abdomen, upper proximal thigh, and lateral genitalia.

So, the correct answer is, 'Hindlimbs'.
Note:
- Sacral plexopathy may be a disorder affecting the nerves of the plexus sacralis, usually caused by trauma, nervous disorder, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of control, and sensory deficits.
- Injuries to the nerve plexus are predominantly witnessed as bone injuries. Lumbosacral trunk and sacral plexus palsies bear common injury patterns.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




