
‘Nif' gene for nitrogen fixation in cereal crops like wheat, jowar, etc. is introduced by cloning
A. Rhizobium melloti
B. Bacillus thuringiensis
C. Rhizopus stolonifer
D. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The bacteria that involves in the formation of the root nodules in the leguminous plants for nitrogen absorption and show a symbiotic relationship with the leguminous plants.
Complete answer:
The Nif genes are the genes that code for the atmospheric nitrogen fixation and convert into the form of nitrogen which is easily absorbed by the plants. Rhizobium was the first Nif gene to be cloned by Gary Ruvkun and Sharon R. in the 1980s.
Additional Information: -The Nif genes are the nitrogenase enzyme complex which concerts the atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
-Ammonia is the form of nitrogen that is easily available and absorbed by the plants.
-The Nif genes are also responsible for the production of various proteins used in the process of nitrogen fixation.
-These genes are found in symbiotic bacteria as well as in nitrogen-fixing bacteria which is free living.
-For the Nif genes to be expressed it requires a less concentration of both oxygen and fixed nitrogen.
-The transcription of the nif genes is done by the nifA protein which is nitrogen sensitive.
-When the fixed nitrogen present is not enough then the NifA proteins will transcribe and form several nif genes.
-If the oxygen is present is a good amount then the activity of the nifA gene is prevented by the activation of another protein nifL.
-These nif genes are generally found in the chromosomes of bacteria.
So, the correct answer is ‘Rhizobium melloti'.
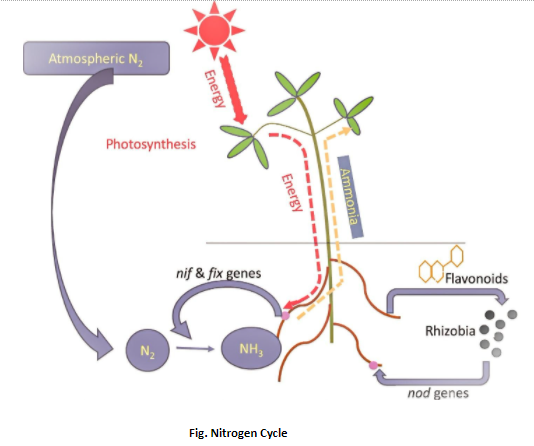
Note: Rhizobium is responsible for the fixation of nitrogen in various plants, they require a host to express their genes during the process of nitrogen fixation. The rhizobium bacteria are rod-shaped, gram-negative, and motile. The first rhizobium bacteria was identified in 1889 called Rhizobium leguminosarum.
Complete answer:
The Nif genes are the genes that code for the atmospheric nitrogen fixation and convert into the form of nitrogen which is easily absorbed by the plants. Rhizobium was the first Nif gene to be cloned by Gary Ruvkun and Sharon R. in the 1980s.
Additional Information: -The Nif genes are the nitrogenase enzyme complex which concerts the atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
-Ammonia is the form of nitrogen that is easily available and absorbed by the plants.
-The Nif genes are also responsible for the production of various proteins used in the process of nitrogen fixation.
-These genes are found in symbiotic bacteria as well as in nitrogen-fixing bacteria which is free living.
-For the Nif genes to be expressed it requires a less concentration of both oxygen and fixed nitrogen.
-The transcription of the nif genes is done by the nifA protein which is nitrogen sensitive.
-When the fixed nitrogen present is not enough then the NifA proteins will transcribe and form several nif genes.
-If the oxygen is present is a good amount then the activity of the nifA gene is prevented by the activation of another protein nifL.
-These nif genes are generally found in the chromosomes of bacteria.
So, the correct answer is ‘Rhizobium melloti'.

Note: Rhizobium is responsible for the fixation of nitrogen in various plants, they require a host to express their genes during the process of nitrogen fixation. The rhizobium bacteria are rod-shaped, gram-negative, and motile. The first rhizobium bacteria was identified in 1889 called Rhizobium leguminosarum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




