
Nitrifying bacteria convert the
(a) Nitrates into nitrites
(b) Nitrites into nitrates
(c) Ammonium salts into nitrates
(d) Ammonium salts into amino acids
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The bacteria that take part in the nitrification process is called nitrifying bacteria. Consequently, it helps to convert the most important salt used in the fertilizer into a chemical compound made of nitrogen and oxygen.
Complete answer:
Nitrification is a process by which ammonium salts are converted into nitrites and nitrites into nitrates.
In agriculture, irrigation with dilute ammonia solutions results in soil nitrates increasing through the action of nitrifying bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria convert the smallest form of nitrogen in the soil, ammonia, into its most oxidized form, nitrate.
It is done in two stages, such as the formation of nitrite and the formation of nitrate.
Usually, the rate-limiting step of nitrification is the transformation of ammonia to nitrite.
Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, and Nitrosospira convert ammonia to nitrites. Nitrospina, Nitrobacter, and Nitrococcus transform nitrites into nitrates.
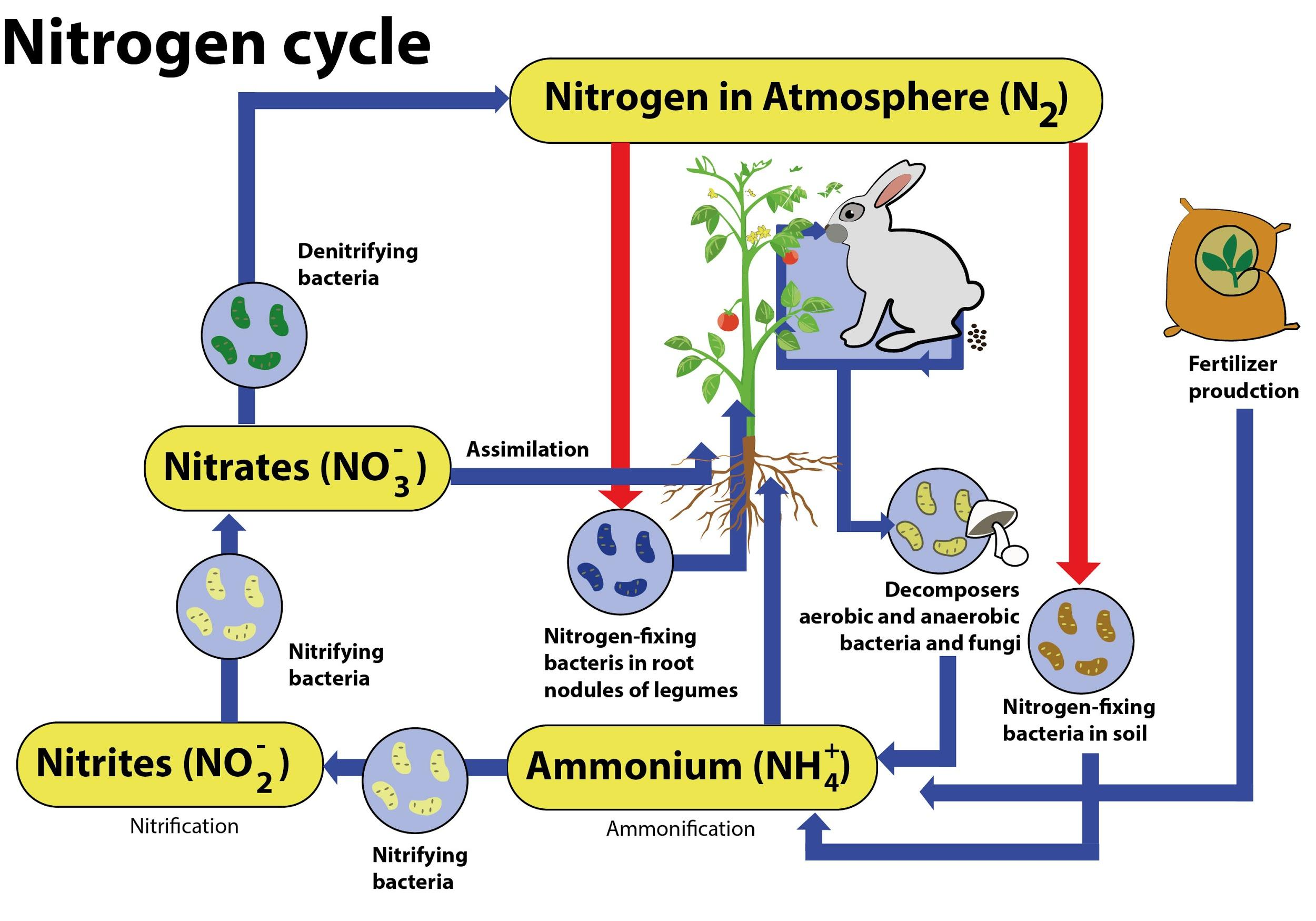
So, the correct answer is, 'Ammonium salts into nitrates’.
Additional Information:
Nitrifying bacteria are chemoautotrophic or chemolithotrophic bacteria depending on the genera (Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Nitrobacter, Nitrococcus) . Chemolithotrophy is a form of metabolism in which energy is obtained by inorganic compound oxidation. Chemoautotrophs use inorganic sources of energy to synthesize carbon dioxide organic compounds. Many species of nitrifying bacteria have complex internal membrane systems that are the location for the main enzymes in nitrification. Ammonia monooxygenase for example oxidizes ammonia to hydroxylamine and oxidizes nitrite to nitrate.
Note: Nitrifying bacteria are a small species in the atmosphere and are present in the lowest numbers where there are large quantities of ammonia (areas of substantial protein decomposition, and plants for sewage treatment). For soil ecosystem function, nitrification is critical in controlling soil nitrogen losses through leaching and nitrate denitrification.
Complete answer:
Nitrification is a process by which ammonium salts are converted into nitrites and nitrites into nitrates.
In agriculture, irrigation with dilute ammonia solutions results in soil nitrates increasing through the action of nitrifying bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria convert the smallest form of nitrogen in the soil, ammonia, into its most oxidized form, nitrate.
It is done in two stages, such as the formation of nitrite and the formation of nitrate.
Usually, the rate-limiting step of nitrification is the transformation of ammonia to nitrite.
Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, and Nitrosospira convert ammonia to nitrites. Nitrospina, Nitrobacter, and Nitrococcus transform nitrites into nitrates.

So, the correct answer is, 'Ammonium salts into nitrates’.
Additional Information:
Nitrifying bacteria are chemoautotrophic or chemolithotrophic bacteria depending on the genera (Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Nitrobacter, Nitrococcus) . Chemolithotrophy is a form of metabolism in which energy is obtained by inorganic compound oxidation. Chemoautotrophs use inorganic sources of energy to synthesize carbon dioxide organic compounds. Many species of nitrifying bacteria have complex internal membrane systems that are the location for the main enzymes in nitrification. Ammonia monooxygenase for example oxidizes ammonia to hydroxylamine and oxidizes nitrite to nitrate.
Note: Nitrifying bacteria are a small species in the atmosphere and are present in the lowest numbers where there are large quantities of ammonia (areas of substantial protein decomposition, and plants for sewage treatment). For soil ecosystem function, nitrification is critical in controlling soil nitrogen losses through leaching and nitrate denitrification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




