
Nitrogen bases of DNA are
(A) ATUC
(B) UTGC
(C) ATGC
(D) AUGC
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: DNA is known as deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is due the presence of deoxyribose ribose in DNA. It is the genetic material of human beings and most organisms. DNA exists as a double helix. A DNA molecule has two unbranched polynucleotide strands. These strands are antiparallel to each other. The famous and popular model of DNA is known as Watson-Crick model.
Complete answer:
The nitrogen bases are projected more or less perpendicular to the sugar phosphate backbone but face inside. The base-pairing is specific. Adenine is always paired with thymine with the help of two bonds that are hydrogen bonds and guanine is always paired with cytosine with triple hydrogen bonds. Thus, all base-pairs consist of one purine and one pyrimidine. Once the sequence of bases in one strand of a DNA double helix is known, the sequence of bases in the other strand is also known because of the specific base pairing. The two strands of a DNA double helix are known as complementary strands as they are not identical This is known as complementary base pairing.
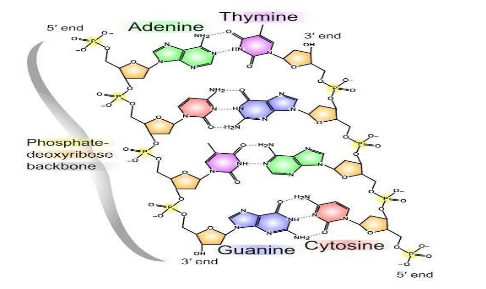
Now let us match the given options:-
ATUC :- adenine bind with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and not with uracil (U). Thus this option is not correct.
UTGC :- adenine binds with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and Thymine not with uracil (U). Thus this option is not correct.
ATGC :- adenine bind with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and not with uracil (U). Thus this option is correct.
AUGC :- Adenine binds with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA. Thus this option is not correct.
Our required answer is C) ATGC.
Note: DNA is the genetic material and forms the molecular basis of heredity (the transmission or genetic characters from parents to offspring) in all organisms. In certain viruses, such as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), RNA is the genetic material. Nucleic acids exhibit a wide variety of secondary structures for example, one of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is the famous Watson Crick model.
Complete answer:
The nitrogen bases are projected more or less perpendicular to the sugar phosphate backbone but face inside. The base-pairing is specific. Adenine is always paired with thymine with the help of two bonds that are hydrogen bonds and guanine is always paired with cytosine with triple hydrogen bonds. Thus, all base-pairs consist of one purine and one pyrimidine. Once the sequence of bases in one strand of a DNA double helix is known, the sequence of bases in the other strand is also known because of the specific base pairing. The two strands of a DNA double helix are known as complementary strands as they are not identical This is known as complementary base pairing.

Now let us match the given options:-
ATUC :- adenine bind with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and not with uracil (U). Thus this option is not correct.
UTGC :- adenine binds with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and Thymine not with uracil (U). Thus this option is not correct.
ATGC :- adenine bind with thymine in DNA and guanine with cytosine and not with uracil (U). Thus this option is correct.
AUGC :- Adenine binds with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA. Thus this option is not correct.
Our required answer is C) ATGC.
Note: DNA is the genetic material and forms the molecular basis of heredity (the transmission or genetic characters from parents to offspring) in all organisms. In certain viruses, such as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), RNA is the genetic material. Nucleic acids exhibit a wide variety of secondary structures for example, one of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is the famous Watson Crick model.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




