
Nitrosyl chloride, $ NOCl $ is a reactive gas that is sometimes formed when $ NO $ reacts with $ C{l_2} $ . $ NOCl $ is a strong electrophile and readily undergoes an additional reaction with an alkene. Complete the diagram to show the mechanism of the electrophilic addition mechanism of the electrophilic addition reaction of $ NOCl $ with ethene.
Include all necessary charges, lone pairs, curly arrows and the structure of organic intermediate.
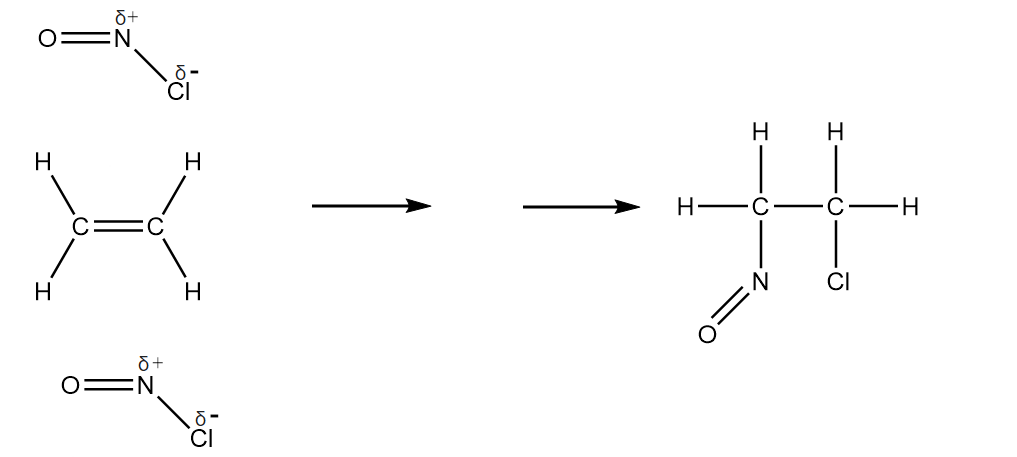

Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: Nitrosyl chloride is a chemical compound with molecular formula $ NOCl $ . It is a yellow gas which is commonly termed as a component of aqua regia i.e., a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is widely used in organic reactions due to its strong electrophilic and oxidizing nature. It is also known as Tilden’s reagent.
Complete answer:
The addition of nitrosyl chloride to an ethene molecule takes place in three steps. The mechanism for the addition reaction of $ NOCl $ to ethene is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of nitrosyl chloride into respective cation and anion. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ NOCl \rightleftharpoons N{O^ + } + C{l^ - } $
Step-2: In ethene, $ s{p^2} $ hybridized carbon is electronegative in nature i.e., it consists of an electron rich carbon atom which attacks the nitrosonium ion and formation of carbocation will take place as an intermediate. The reaction proceeds as follows:
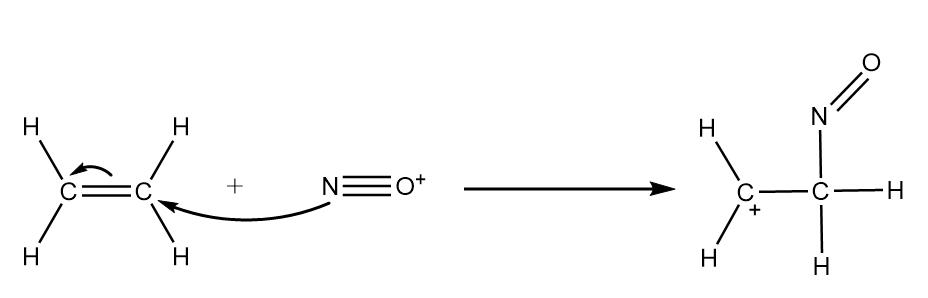
Step-3: The chloride ion will act as a nucleophile and attack the carbocation formed in the previous step to give the final product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
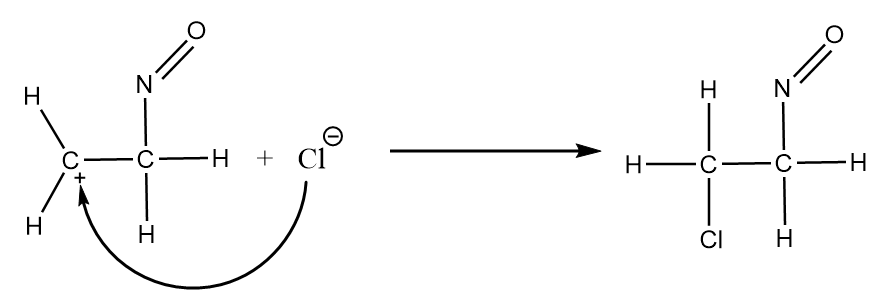
Hence, the final diagram for the given reaction mechanism will be as follows:
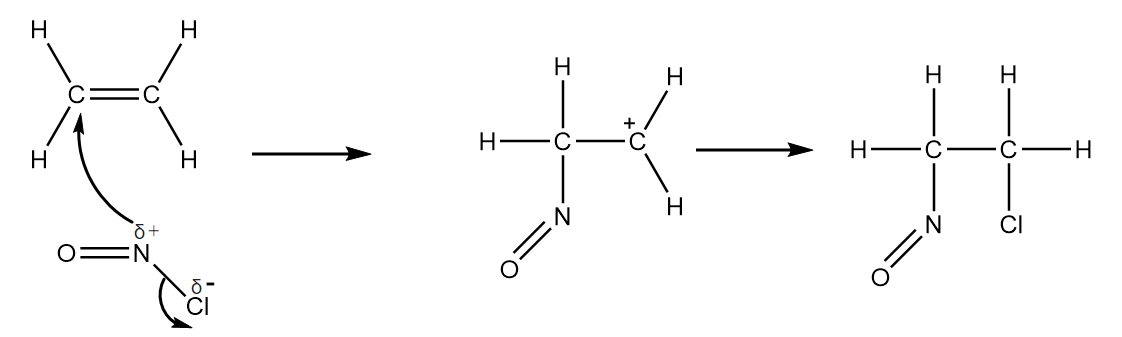
Note:
It is important to note that the addition of nitrosyl chloride to ethene is a stereospecific reaction i.e., the two stereochemical products are possible after the reaction. If chloride ion attacks carbocation from the sample plane where the nitrosyl group is attached, then the product formed is syn whereas if chloride ion attacks from opposite plane, then the product formed is termed as anti.
Complete answer:
The addition of nitrosyl chloride to an ethene molecule takes place in three steps. The mechanism for the addition reaction of $ NOCl $ to ethene is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of nitrosyl chloride into respective cation and anion. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ NOCl \rightleftharpoons N{O^ + } + C{l^ - } $
Step-2: In ethene, $ s{p^2} $ hybridized carbon is electronegative in nature i.e., it consists of an electron rich carbon atom which attacks the nitrosonium ion and formation of carbocation will take place as an intermediate. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Step-3: The chloride ion will act as a nucleophile and attack the carbocation formed in the previous step to give the final product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
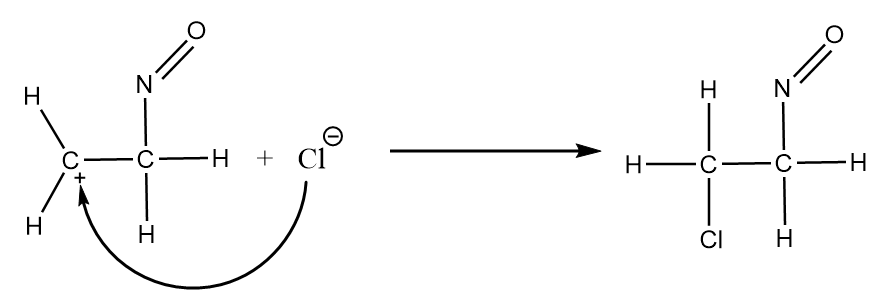
Hence, the final diagram for the given reaction mechanism will be as follows:

Note:
It is important to note that the addition of nitrosyl chloride to ethene is a stereospecific reaction i.e., the two stereochemical products are possible after the reaction. If chloride ion attacks carbocation from the sample plane where the nitrosyl group is attached, then the product formed is syn whereas if chloride ion attacks from opposite plane, then the product formed is termed as anti.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




