
Nodes of Ranvier are
(A)Joints occur between adjacent axons
(B)Axon terminal forms a synapse with dendrites
(C)Dendrites of one nerve cells to adjacent nerve cells
(D)Non-myelinated areas of myelinated nerve fiber
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Node of Ranvier is defined as the periodic gap which is seen in the insulating sheath on the axon of some type of the neurons that serves to facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses.
Complete answer: Nodes of Ranvier are known to be the Non-myelinated areas of the myelinated nerve fiber. The process of saltatory conduction when the nodes of Ranvier will interrupt the insulation at intervals, and due to this discontinuity, the impulses have to jump from one node to another node.
Additional Information: Nodes of Ranvier are approx 1-1.5μm wide and these will help to expose the neuron membrane to the external environment. These gaps are rich in ion channels, which helps to exchange the certain ions, including sodium and chloride, that are required to make an action potential—the reversal of electrical polarization of the neuron membrane that initiates or is a component of a wave of excitation that travels along the axon. The nerve impulse propagated by one node of Ranvier jumps to and is regenerated at a subsequent node along the axon, thereby enabling the nerve impulse to speed along the fiber. The movement of sodium ions which is required to depolarize the membrane will occur at the Node of Ranvier only because the sodium voltage-gated channels are found only at the nodes of Ranvier
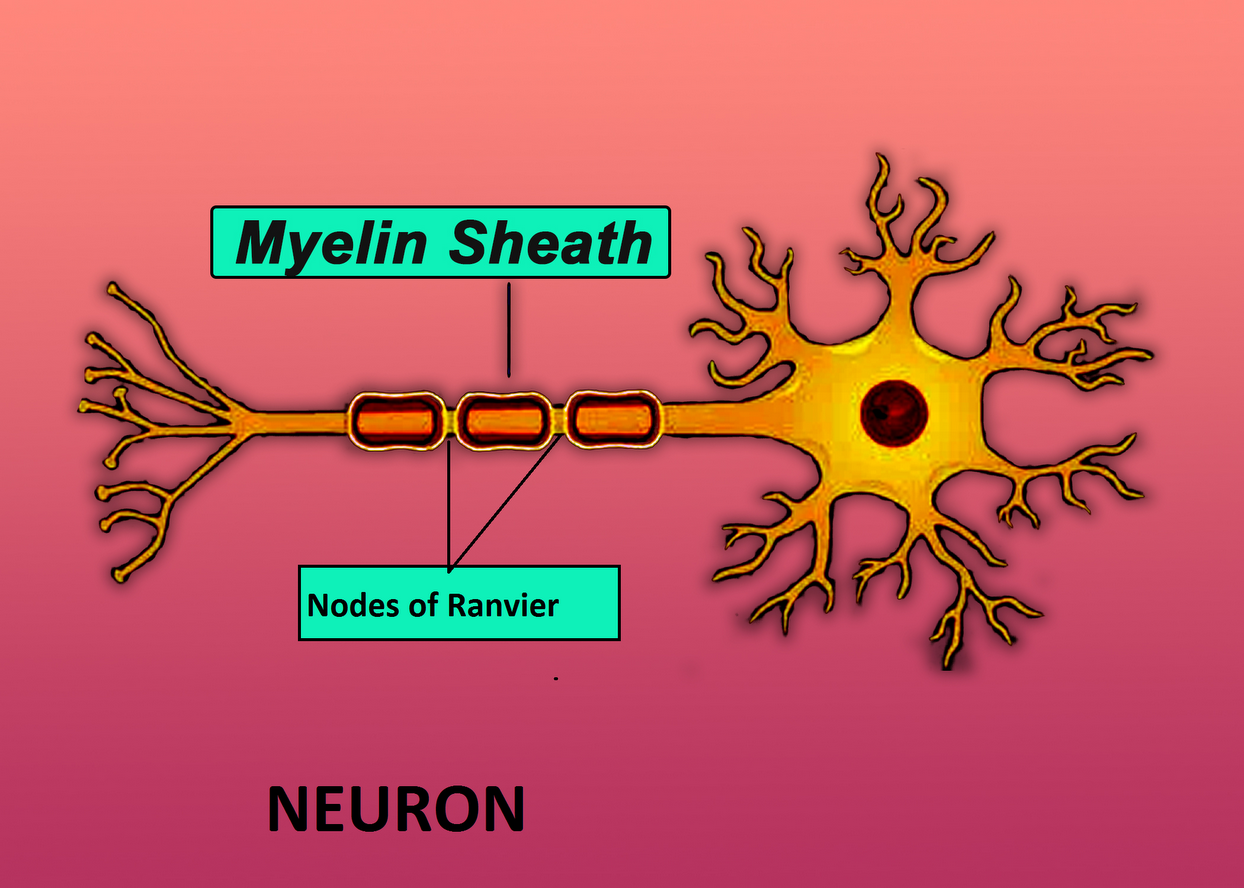
So, the correct answer is ‘Non-myelinated areas of myelinated nerve fiber’.
Note: In the brain and spinal cord myelin is an insulating layer that forms around the nerves. It is usually made up of protein and fatty substances. -It helps in the transmission of electrical impulses very quickly and efficiently with the nerve cells.
Complete answer: Nodes of Ranvier are known to be the Non-myelinated areas of the myelinated nerve fiber. The process of saltatory conduction when the nodes of Ranvier will interrupt the insulation at intervals, and due to this discontinuity, the impulses have to jump from one node to another node.
Additional Information: Nodes of Ranvier are approx 1-1.5μm wide and these will help to expose the neuron membrane to the external environment. These gaps are rich in ion channels, which helps to exchange the certain ions, including sodium and chloride, that are required to make an action potential—the reversal of electrical polarization of the neuron membrane that initiates or is a component of a wave of excitation that travels along the axon. The nerve impulse propagated by one node of Ranvier jumps to and is regenerated at a subsequent node along the axon, thereby enabling the nerve impulse to speed along the fiber. The movement of sodium ions which is required to depolarize the membrane will occur at the Node of Ranvier only because the sodium voltage-gated channels are found only at the nodes of Ranvier

So, the correct answer is ‘Non-myelinated areas of myelinated nerve fiber’.
Note: In the brain and spinal cord myelin is an insulating layer that forms around the nerves. It is usually made up of protein and fatty substances. -It helps in the transmission of electrical impulses very quickly and efficiently with the nerve cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




