
What is the normality of 0.2M \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] solution?
A.0.2 N
B.0.1 N
C.0.4 N
D.0.6 N
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: We need to know the concept of Basicity of an acid to solve this question. It is the number of hydrogen ions which can be produced from one molecule of the acid. For example Acetic acid is acid which means that as it can lose one proton or hydrogen atom, it forms an acetate ion. \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] is a dibasic acid which is evident from its structure.
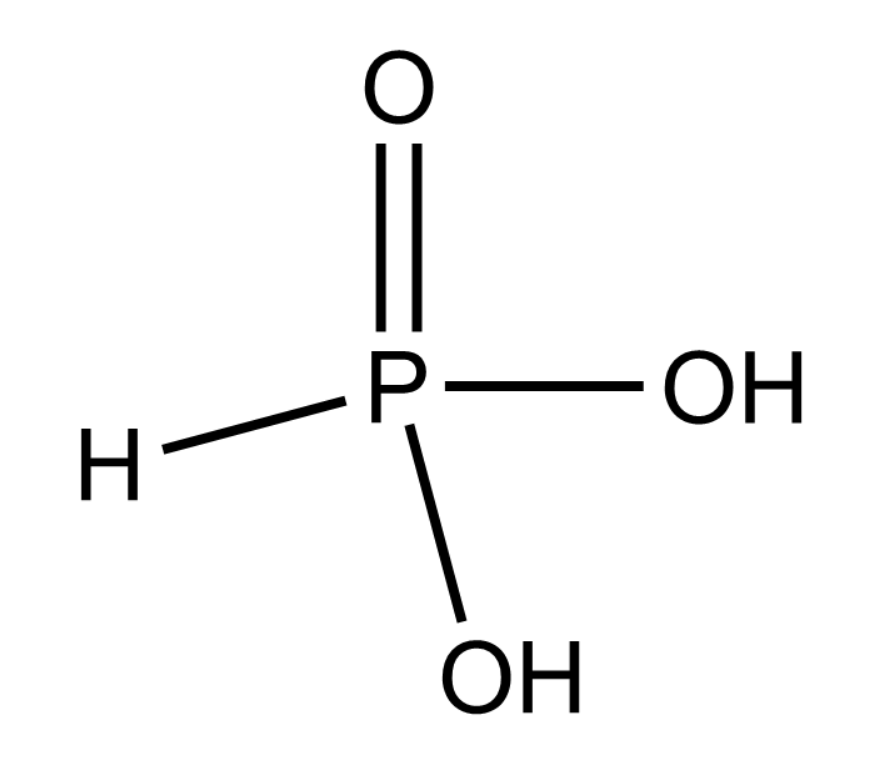
Complete answer:
From the figure given above we can say that \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] is a dibasic acid because both of the \[ - OH\] group can easily lose its hydrogen as \[{H^ + }\] ions making it acidic
We also know that normality can be expressed by the formula
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = Molarity \times n{\text{ }}factor\]
Where n factor is the number of replaceable \[{H^ + }\] ions in that molecule.
Since we are given \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] we can say that the value of n factor will be 2
It is also given to us that the molarity of the given solution is 0.2 M.
Thus we can write that
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = 0.2M \times 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = 0.4{\text{ }}N\]
Thus we can say that the normality of the given solution of 0.2M \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] is 0.4 N
Thus the correct option is C .
Note:
For acids we can say that n factor is the number of replaceable \[{H^ + }\] ions in that molecule.
For bases we can say that n factor is the number \[O{H^ - }\] of ions that the molecule of base would give when dissolved in a suitable solvent.
For Redox reactions n factor will be the change in the oxidation number of the reducing or oxidising agent

Complete answer:
From the figure given above we can say that \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] is a dibasic acid because both of the \[ - OH\] group can easily lose its hydrogen as \[{H^ + }\] ions making it acidic
We also know that normality can be expressed by the formula
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = Molarity \times n{\text{ }}factor\]
Where n factor is the number of replaceable \[{H^ + }\] ions in that molecule.
Since we are given \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] we can say that the value of n factor will be 2
It is also given to us that the molarity of the given solution is 0.2 M.
Thus we can write that
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = 0.2M \times 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow Normality = 0.4{\text{ }}N\]
Thus we can say that the normality of the given solution of 0.2M \[{H_3}P{O_3}\] is 0.4 N
Thus the correct option is C .
Note:
For acids we can say that n factor is the number of replaceable \[{H^ + }\] ions in that molecule.
For bases we can say that n factor is the number \[O{H^ - }\] of ions that the molecule of base would give when dissolved in a suitable solvent.
For Redox reactions n factor will be the change in the oxidation number of the reducing or oxidising agent
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




