
Nucleic acids are polymers of
(a) Nucleotides
(b) Nucleosides
(c) Amino acids
(d) Nitrogen bases
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Nucleic acids are the macromolecules found in the cell. The nucleic acid is a polymer molecule that is made up of several monomeric subunits. These monomeric subunits contain three parts that help in bond formation and form the backbone of double-helix DNA. The nucleic acids in the cell are present in the form of DNA and RNA.
Complete answer:
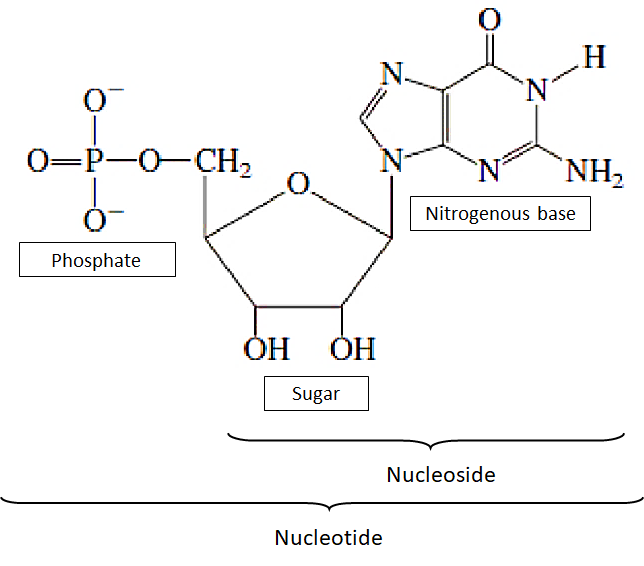
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are present as polymers called polynucleotides. As the name suggests, each polynucleotide is made up of monomers known as nucleotides. A nucleotide is composed of a purine or pyrimidine nitrogenous base joined by pentose sugar in the D configuration which is then linked with a phosphate group to form nucleotides. Nucleic acids are used in storing information and they transmit and help express hereditary information in the next generation.
Additional Information:
-The two types of nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA enable living organisms to reproduce their complex components from one generation to the next.
-DNA is the genetic material that the organism inherits from the parents.
-There is only one phosphate group attached to monomers in each nucleotide. The part of a nucleotide excluding the phosphate groups forms a nucleoside.
-There are two types of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A pyrimidine has one six-membered ring made up of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The two types of pyrimidine are cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
-Purines are larger than the pyrimidine as they have a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
-The sugar present in DNA is a deoxyribose sugar and the sugar in RNA ribose sugar. The deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom on the second atom.
So, the correct answer is ‘Nucleotides.’
Note: Genes are known as the unit of inheritance. Watson and Crick suggested the double-helical structure of DNA. Erwin Chargaff did a quantitative analysis of DNA and gave the base equivalent rule stating that the molar concentration of adenine is equal to thymine and the concentration of guanine is equal to cytosine.
Complete answer:
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that are present as polymers called polynucleotides. As the name suggests, each polynucleotide is made up of monomers known as nucleotides. A nucleotide is composed of a purine or pyrimidine nitrogenous base joined by pentose sugar in the D configuration which is then linked with a phosphate group to form nucleotides. Nucleic acids are used in storing information and they transmit and help express hereditary information in the next generation.
Additional Information:

-The two types of nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA enable living organisms to reproduce their complex components from one generation to the next.
-DNA is the genetic material that the organism inherits from the parents.
-There is only one phosphate group attached to monomers in each nucleotide. The part of a nucleotide excluding the phosphate groups forms a nucleoside.
-There are two types of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A pyrimidine has one six-membered ring made up of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The two types of pyrimidine are cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
-Purines are larger than the pyrimidine as they have a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. The purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
-The sugar present in DNA is a deoxyribose sugar and the sugar in RNA ribose sugar. The deoxyribose lacks an oxygen atom on the second atom.
So, the correct answer is ‘Nucleotides.’
Note: Genes are known as the unit of inheritance. Watson and Crick suggested the double-helical structure of DNA. Erwin Chargaff did a quantitative analysis of DNA and gave the base equivalent rule stating that the molar concentration of adenine is equal to thymine and the concentration of guanine is equal to cytosine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




