
How is the nucleus different from the nucleoid?
(a)The nucleus is a membrane-bound nucleoid is open
(b)Nucleus has nucleoplasm separated by a nuclear membrane but nucleoid do not have any plasma separated by a membrane
(c)Nucleus has nucleolus but nucleoid does not have a nucleolus
(d)All of the above
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Nucleus is found in a eukaryotic cell and nucleolus is found in prokaryotic cells. A nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of eukaryotes in form of DNA. Nucleoids contain the genetic material of prokaryotes as free-floating strands in the cytoplasm in the form of RNA.
Complete answer:
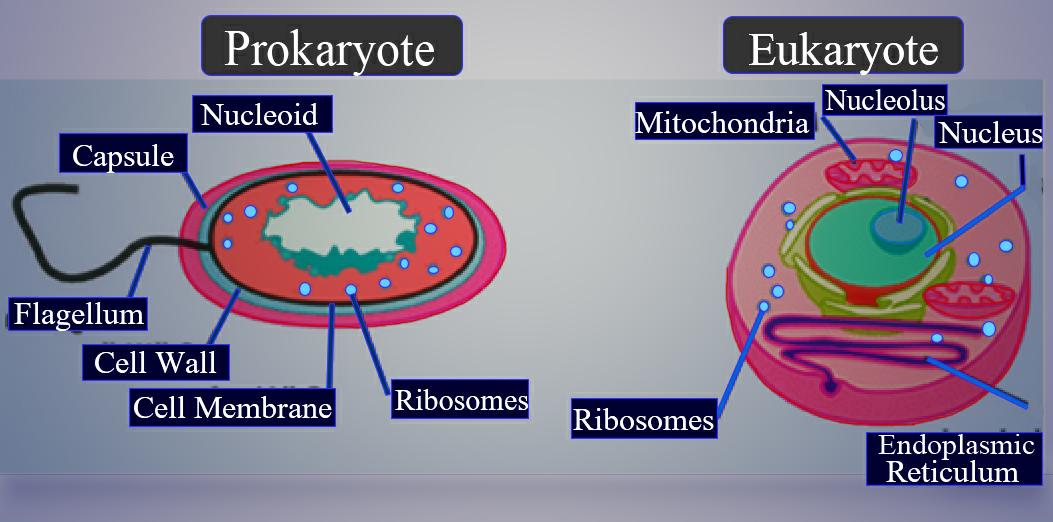
Difference between nucleus and nucleoid:
So, the correct answer is “All of the above”.
Note: The main function of the cell nucleus or nucleoid is to control gene expression and mediate the replication of DNA during the cell cycle. It contains DNA or RNA that carries forward the genetic information to the next generation. It controls primary cellular metabolism by controlling the synthesis of enzymes. It also controls protein production, cell replication, growth, and differentiation.
Complete answer:
Difference between nucleus and nucleoid:
| Nucleus | Nucleoid |
| A nucleus is a membrane-bound structure present in eukaryotes that contains their genetic materials. | Nucleoid is a particular area in prokaryotic cells that contains their genetic materials. |
| It is well organized and large. | It is poorly organized and small. |
| It is enclosed by a double layer membrane known as a nuclear membrane that separates the nucleus from other organelles. | It does not have a protective membrane. |
| It consists of several chromosomes. | It usually houses only one chromosome. |
| It is a spherical shaped organelle. | It is an irregularly shaped organelle. |
| Nucleoplasm and nucleolus are present. | Nucleoplasm and Nucleolus are absent. |

So, the correct answer is “All of the above”.
Note: The main function of the cell nucleus or nucleoid is to control gene expression and mediate the replication of DNA during the cell cycle. It contains DNA or RNA that carries forward the genetic information to the next generation. It controls primary cellular metabolism by controlling the synthesis of enzymes. It also controls protein production, cell replication, growth, and differentiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




