
What is the Nucleus? Explain the structure of the eukaryotic nucleus with a suitable diagram.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: The cell nucleusis a film bound structure that contains the cell's innate data and controls the cell's development and reproduction. It is the war room of a eukaryotic cell and is generally the most noticeable organelle in a cell representing around 10% of the cell's volume. When all is said in done, a eukaryotic cell has just a single core.
Complete answer:
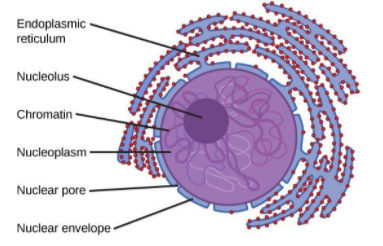
Nucleus Structure: The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
Nucleus types:
- Nuclear membrane
- Nucleoplasm
- Chromosomes
- Nucleolus
Nuclear membrane: The atomic film is a twofold layered structure that encases the substance of the core. The external layer of the film is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Like the cell layer, the atomic envelope comprises phospholipids that structure a lipid bilayer. The envelope assists with keeping up the state of the core and helps with directing the progression of particles into and out of the core through atomic pores.
Nucleoplasm: It is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to the cytoplasm and is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within.
Chromosomes: The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes. Chromosomes comprise of DNA, which contains heredity data and guidelines for cell development, advancement, and multiplication. Chromosomes are available as strings of DNA and histones (protein particles) called chromatin.
Function Nucleolus: The nucleus gives a site to hereditary record that is isolated from the area of interpretation in the cytoplasm, permitting levels of quality guideline that are not accessible to prokaryotes. The primary capacity of the phone core is to control quality articulation and intercede the replication of DNA during the phone cycle
Note: The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes. It is exclusively found in eukaryotic cells and is also one of the largest organelles.
Complete answer:
Nucleus Structure: The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
Nucleus types:
- Nuclear membrane
- Nucleoplasm
- Chromosomes
- Nucleolus
Nuclear membrane: The atomic film is a twofold layered structure that encases the substance of the core. The external layer of the film is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Like the cell layer, the atomic envelope comprises phospholipids that structure a lipid bilayer. The envelope assists with keeping up the state of the core and helps with directing the progression of particles into and out of the core through atomic pores.
Nucleoplasm: It is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to the cytoplasm and is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within.
Chromosomes: The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes. Chromosomes comprise of DNA, which contains heredity data and guidelines for cell development, advancement, and multiplication. Chromosomes are available as strings of DNA and histones (protein particles) called chromatin.
Function Nucleolus: The nucleus gives a site to hereditary record that is isolated from the area of interpretation in the cytoplasm, permitting levels of quality guideline that are not accessible to prokaryotes. The primary capacity of the phone core is to control quality articulation and intercede the replication of DNA during the phone cycle

Note: The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes. It is exclusively found in eukaryotic cells and is also one of the largest organelles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




