
Number of lobes present in ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ orbital is:
(A) 10
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 2
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: To know the information about atomic orbital by referring to the quantum numbers are principal quantum number (n), angular quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m). d- Orbital shape describes with the help of angular quantum number and magnetic quantum number which specifies the angular momentum of d-orbital.
Complete step by step solution:
The relation between the principal quantum number (n), angular quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m) given as,
l= n-1, where n = 1, 2, 3 …
The values of m = -l….-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3…+l
If n= 1, l=0, m= 0, the orbital represents s-orbital and only one sub orbital
If n = 2, l = 1, and m = -1, 0, +1, which represents p-orbital with three p- orbital are ${{p}_{x,}}{{p}_{y}},{{p}_{z}}$
For d- orbital, n= 3, l = 2 and m = +2, +1, 0, 1, 2, which represents five d-orbital ${{d}_{xy}},{{d}_{yz}},{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$
The shape of the ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital has a lobe along the z-axis and a ring along the xy-plane, which looks like the donut with a lobe above and below.
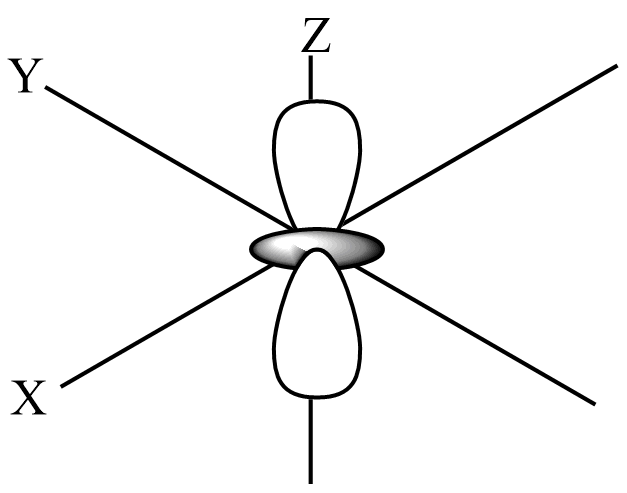
From the above shape of ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital, the number of lobes present in the orbital is 2. The electron density is more along the z-axis than in the ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital and two nodal planes are XY-plane.
Hence, the Number of lobes present in ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ an orbital is 2.
The correct answer is option D.
Note: Generally, d-orbital has four lobes and 2 nodal planes. Except for ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ orbital, all four orbital are four lobes between the two-axis and 2 nodal planes. For example, ${{d}_{xy}}$ orbital has 4 lobes along the XY-plane and 2 nodal planes YZ-plane, ZX-plane.
Complete step by step solution:
The relation between the principal quantum number (n), angular quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m) given as,
l= n-1, where n = 1, 2, 3 …
The values of m = -l….-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3…+l
If n= 1, l=0, m= 0, the orbital represents s-orbital and only one sub orbital
If n = 2, l = 1, and m = -1, 0, +1, which represents p-orbital with three p- orbital are ${{p}_{x,}}{{p}_{y}},{{p}_{z}}$
For d- orbital, n= 3, l = 2 and m = +2, +1, 0, 1, 2, which represents five d-orbital ${{d}_{xy}},{{d}_{yz}},{{d}_{zx}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$
The shape of the ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital has a lobe along the z-axis and a ring along the xy-plane, which looks like the donut with a lobe above and below.

From the above shape of ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital, the number of lobes present in the orbital is 2. The electron density is more along the z-axis than in the ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$-orbital and two nodal planes are XY-plane.
Hence, the Number of lobes present in ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ an orbital is 2.
The correct answer is option D.
Note: Generally, d-orbital has four lobes and 2 nodal planes. Except for ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ orbital, all four orbital are four lobes between the two-axis and 2 nodal planes. For example, ${{d}_{xy}}$ orbital has 4 lobes along the XY-plane and 2 nodal planes YZ-plane, ZX-plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




