
Number of nodal planes in $ 4p $ sub-orbit will be:
(A) $ 0 $
(B) $ 1 $
(C) $ 2 $
(D) $ 3 $
Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint: On the basis of the values of principal quantum number and azimuthal quantum number, we can determine that in which part of the suborbital, the probability of finding an electron is maximum or minimum.
Complete answer:
Node: It is a point, surface or a plane in which the probability of finding an electron is zero. These are categorized into two parts:
Radial nodes: It is also known as the nodal region and it is a spherical surface around the sub orbitals where the probability of finding electrons is zero. Its value is equal to $ n - l - 1 $ , where n is the principal quantum number and $ l $ is the azimuthal quantum number.
Angular nodes: It is also known as a nodal plane. It is a plane around the nucleus where the chances for finding an electron is zero. Its value is equal to azimuthal quantum number $ l $ .
The major concept in quantum mechanics is that the electrons show both wave as well as particle nature and the nodal planes around the nucleus indicate the wave nature of electrons i.e., if there are no electrons present then there would be no amplitude of vibration.
For $ 4p $ suborbital,
The value of principal quantum number $ n = 4 $
So, the value of azimuthal quantum number $ l $ lies between $ 0 $ to $ n - 1 $
$ \Rightarrow l = 0{\text{ to }}4 - 1 $
$ \Rightarrow l = 0{\text{ to }}3 $
We know that for p suborbital, $ l = 1 $
Hence, the number of nodal planes for $ 4p $ suborbital $ = 1 $
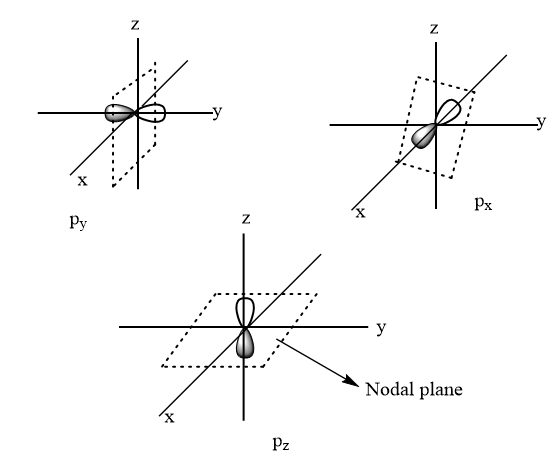
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the atoms or molecules with few numbers of nodal planes are comparatively stable that those who have large numbers of nodal planes because the atoms with greater nodal planes are very unstable and reactive. Also, the number of nodal planes in a molecule directly varies with the free energy associated with the group of bonded atoms.
Complete answer:
Node: It is a point, surface or a plane in which the probability of finding an electron is zero. These are categorized into two parts:
Radial nodes: It is also known as the nodal region and it is a spherical surface around the sub orbitals where the probability of finding electrons is zero. Its value is equal to $ n - l - 1 $ , where n is the principal quantum number and $ l $ is the azimuthal quantum number.
Angular nodes: It is also known as a nodal plane. It is a plane around the nucleus where the chances for finding an electron is zero. Its value is equal to azimuthal quantum number $ l $ .
The major concept in quantum mechanics is that the electrons show both wave as well as particle nature and the nodal planes around the nucleus indicate the wave nature of electrons i.e., if there are no electrons present then there would be no amplitude of vibration.
For $ 4p $ suborbital,
The value of principal quantum number $ n = 4 $
So, the value of azimuthal quantum number $ l $ lies between $ 0 $ to $ n - 1 $
$ \Rightarrow l = 0{\text{ to }}4 - 1 $
$ \Rightarrow l = 0{\text{ to }}3 $
We know that for p suborbital, $ l = 1 $
Hence, the number of nodal planes for $ 4p $ suborbital $ = 1 $

Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the atoms or molecules with few numbers of nodal planes are comparatively stable that those who have large numbers of nodal planes because the atoms with greater nodal planes are very unstable and reactive. Also, the number of nodal planes in a molecule directly varies with the free energy associated with the group of bonded atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




