
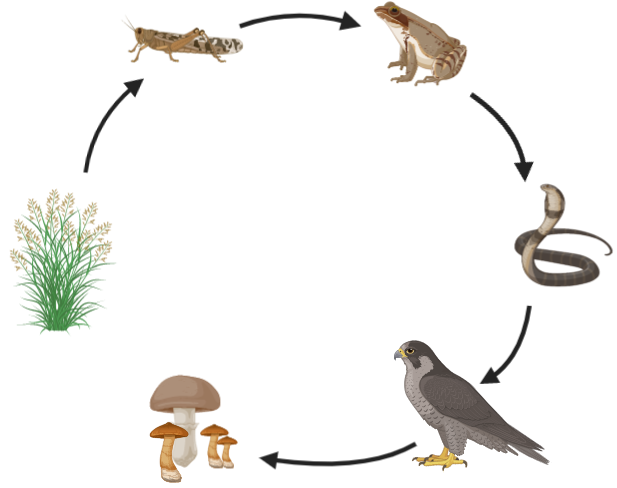
Observe the diagrams given below and answer the questions given:
A. Label the food chain properly as per the trophic levels.
B. If the number of frogs shown in the food chain is suddenly reduced, then what can be different effects on the food chain?
C. Which components of the above food chain, if lost will reflect upon the process of decomposition? What will be the effect of this on the ecosystem?

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In ecology, different groups of organisms like autotrophs, heterotrophs and decomposers form a linear sequence through which the energy is transferred from one organism to the other in the form of food when one organism eats the other organism.
Complete answer:
A.
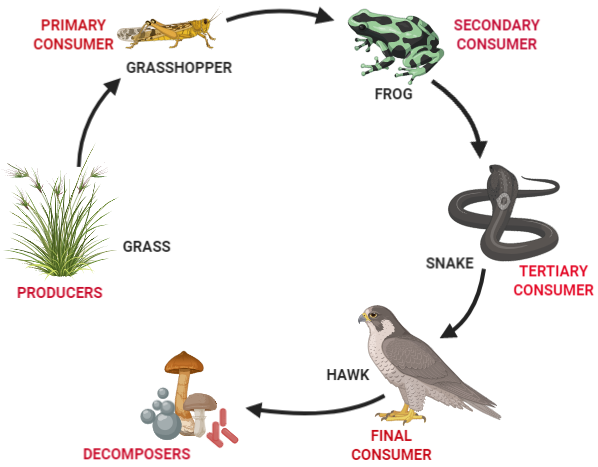
B.In an ecosystem, each organism is dependent on the other organism for its share of food and energy and plays an important role in a food chain. If an organism in one trophic level of the food chain dies, it will directly impact the next trophic level. In the given scenario, If the number of frogs (secondary consumers) is suddenly reduced, it will negatively affect the successive trophic levels. Due to the scarcity of food there will be interspecific competition for food resources among the snakes and soon their population will decline. This will also adversely affect the apex consumers like a hawk. Also, in the absence of a predator, the population of grasshoppers (primary consumers) will rapidly increase. This in turn will affect the growth of plants/grasses (producers). Ultimately, this will lead to an imbalance in the food chain and the ecosystem.
C. When an organism dies, decomposers act on them by releasing enzymes to digest the dead matter. This allows the breakdown of complex organic matter into simple inorganic nutrients which are then released back into the soil. These nutrients are recycled and readily used by the producers. If decomposers are taken out from the environment, then dead remains will accumulate and nutrients will not be released back into the soil. This will disrupt the mineral cycles and affect the growth of plants. Thus, decomposers are very crucial for the proper functioning and sustenance of an ecosystem.
Note:
Energy transfer in an ecosystem follows the laws of thermodynamics which says, energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it can change from one form to another. Plants use the photochemical energy of the sun to prepare food i.e. starch (chemical energy). When a consumer eats a plant, the energy is transferred from the plant to the animal and the subsequent trophic levels in the form of food energy.
Complete answer:
A.

B.In an ecosystem, each organism is dependent on the other organism for its share of food and energy and plays an important role in a food chain. If an organism in one trophic level of the food chain dies, it will directly impact the next trophic level. In the given scenario, If the number of frogs (secondary consumers) is suddenly reduced, it will negatively affect the successive trophic levels. Due to the scarcity of food there will be interspecific competition for food resources among the snakes and soon their population will decline. This will also adversely affect the apex consumers like a hawk. Also, in the absence of a predator, the population of grasshoppers (primary consumers) will rapidly increase. This in turn will affect the growth of plants/grasses (producers). Ultimately, this will lead to an imbalance in the food chain and the ecosystem.
C. When an organism dies, decomposers act on them by releasing enzymes to digest the dead matter. This allows the breakdown of complex organic matter into simple inorganic nutrients which are then released back into the soil. These nutrients are recycled and readily used by the producers. If decomposers are taken out from the environment, then dead remains will accumulate and nutrients will not be released back into the soil. This will disrupt the mineral cycles and affect the growth of plants. Thus, decomposers are very crucial for the proper functioning and sustenance of an ecosystem.
Note:
Energy transfer in an ecosystem follows the laws of thermodynamics which says, energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it can change from one form to another. Plants use the photochemical energy of the sun to prepare food i.e. starch (chemical energy). When a consumer eats a plant, the energy is transferred from the plant to the animal and the subsequent trophic levels in the form of food energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




